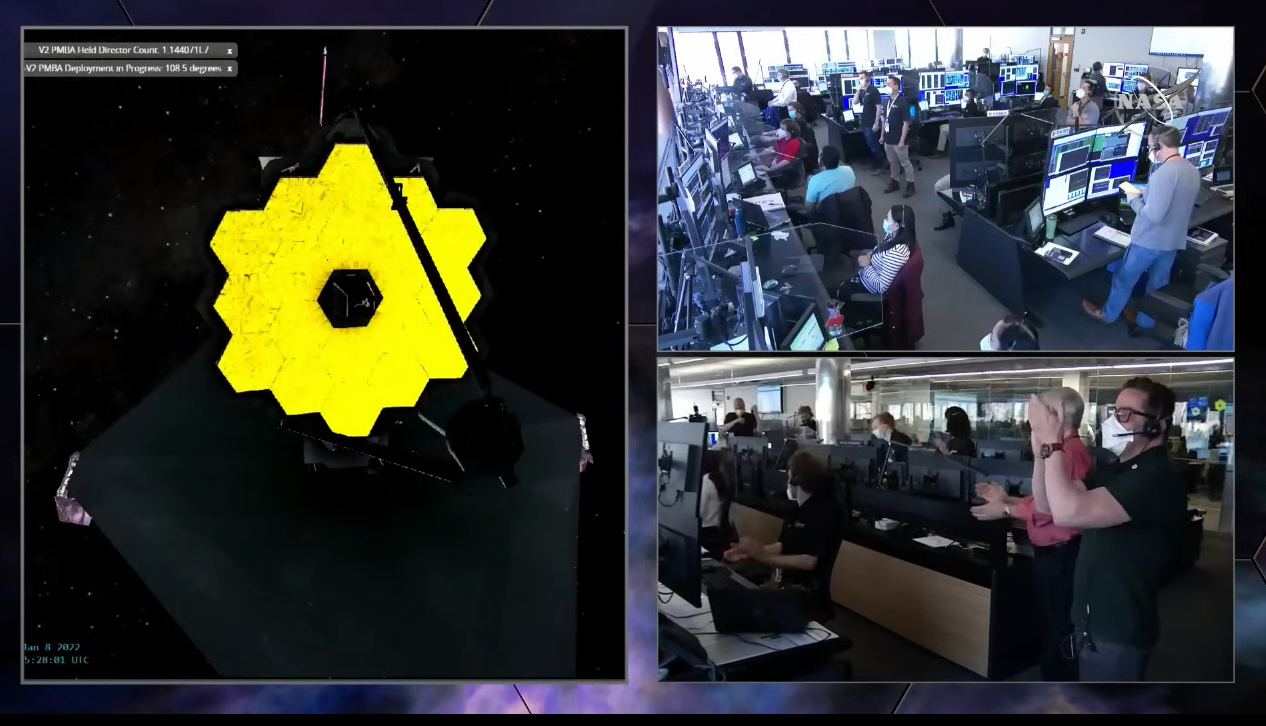
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope mission — Live updates
Read the latest news about NASA's James Webb Space Telescope.

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, the agency's successor to the famous Hubble telescope, launched on Dec. 25, 2021 on a mission to study the earliest stars and peer back farther into the universe's past than ever before.
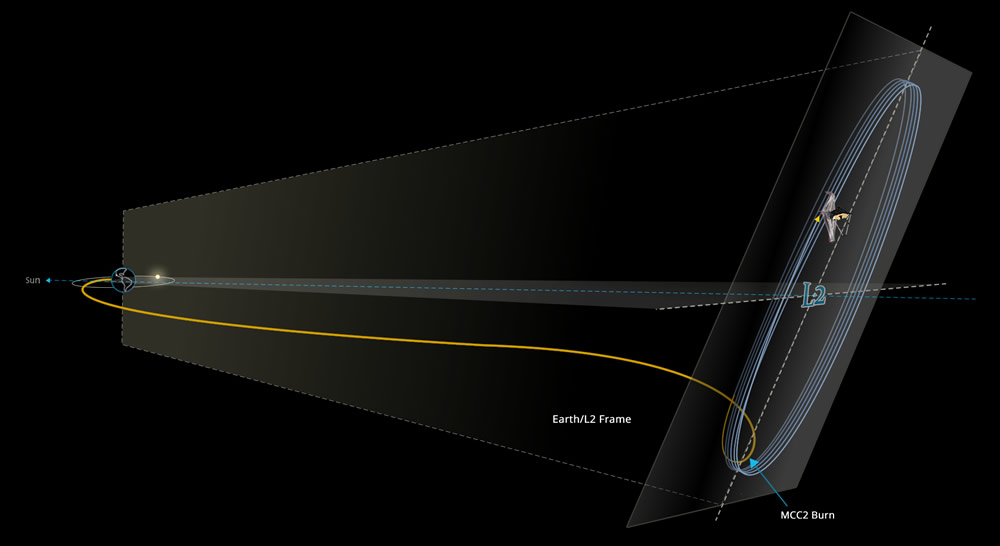
Webb is currently at its observing spot, Lagrange point 2 (L2), nearly 1 million miles (1.6 million km). It is the largest and most powerful space telescope ever launched.
Space.com is sharing live updates about the new space observatory's mission here.
James Webb Space Telescope | Where is Webb? | Webb explained in pictures
Full coverage
James Webb Space Telescope plays cosmic archeologist
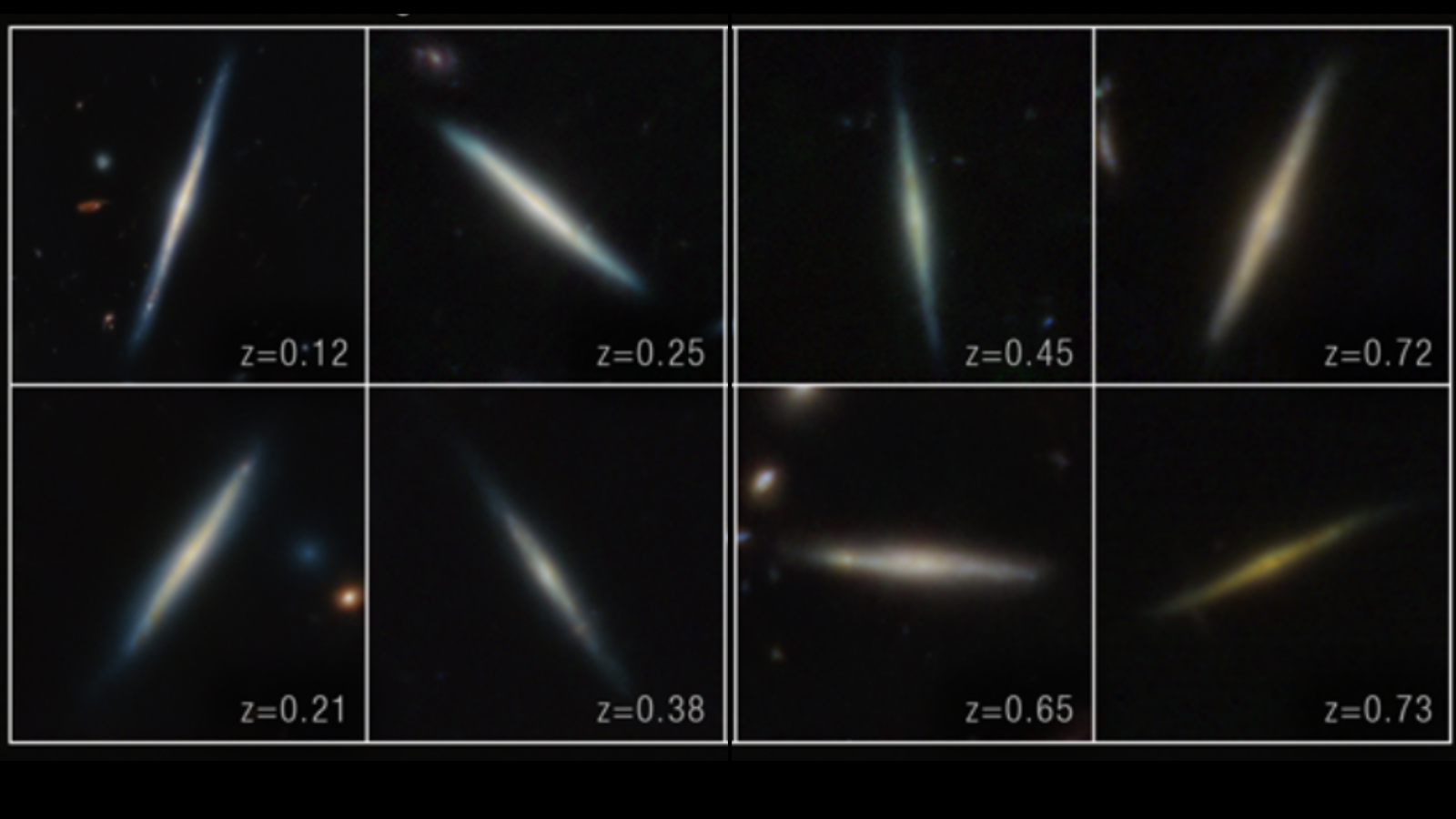

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has allowed astronomers to "excavate" over 100 ancient disk galaxies in the distant universe to retell the story of cosmic evolution.
The team attempted to discover why some galaxies, including the Milky Way, appear to be "double-disked" with a thick platter of stars and an inner and thinner disk of stellar objects.
The astronomers found that the galaxies that existed as early as 2.8 billion years after the Big Bang grew a thinner disk at different times depending on their mass. More massive galaxies burned through their star-forming gas and dust faster and thus grew thinner disks earlier than less massive galaxies.
Read More: James Webb Space Telescope uses cosmic archeology to reveal history of the Milky Way galaxy
James Webb Space Telescope does it again! Earliest galaxy discovery is a recording breaking 'cosmic miracle!'
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has discovered a galaxy that existed just 280 million years after the Big Bang, with the team behind this research lauding the discovery as a "cosmic miracle." This is the earliest and thus most distant galaxy discovered by the $10 billion dollar space telescope yet, it has been designated MoM z14.
"First and foremost, at the moment, this is the most distant object known to humanity. That title changes every so often, but I find it is always cause for pause and reflection," team member and Yale University professor of Astronomy and Physics Pieter van Dokkum told Space.com. "MoM z14 existed when the universe was about 280 million years old - we're getting quite close to the Big Bang. Just to put that in context, sharks have been around on Earth for a longer timespan!"
MoM z14 dethones JADES-GS-z14-0, which existed just 300 million years after the Big Bang, or around 13.5 billion years ago to claim the title of "earliest and most distant galaxy" but the smart money is on the JWST turning up another contender really soon.
Stay tuned!
Read More: 'Cosmic miracle!' James Webb Space Telescope discovers the earliest galaxy ever seen

JWST detects water ice at the edge of a distant star system
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have discovered water ice in a band of icy bodies at the edge of a distant star system.
The discovery was made around the star HD 181327, located around 156 light-years from Earth toward the constellation of Telescopium.
Though no planets have been discovered in this system as of yet, scientists hope that this discovery could help reveal how extrasolar planets, or "exoplanets," are created in star systems like that of HD 181327.
Read More: James Webb Space Telescope discovers an alien planetary system's icy edge

James Webb Space Telescope snaps an image of a cosmic monster!

Ever noticed how those alleged photos of Earth-bound cryptids like the Loch Ness Monster and Big Foot are always blurry and indistinguishable?
Well, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) doesn't have that problem when catching images of cosmic monsters.
Case in point: this stunning image of monster supermassive star cluster Westerlund 1. Over 6.6 light-years wide, Westerlund 1 has a stellar mass equivalent to around 63,000 suns.
This local supercluster, located just 12,000 light-years away, is also host to the most compact population of monster stars in the Milky Way, with hundreds of very massive stars packed in a relatively small region.
That's like finding out Nessie is packed with 100s of Bigfoots! No wonder astronomers are so keen to study it!
Read More: James Webb Space Telescope explores monster star supercluster Westerlund 1 (image)
James Webb Space Telescope may have seen record breaking early galaxies
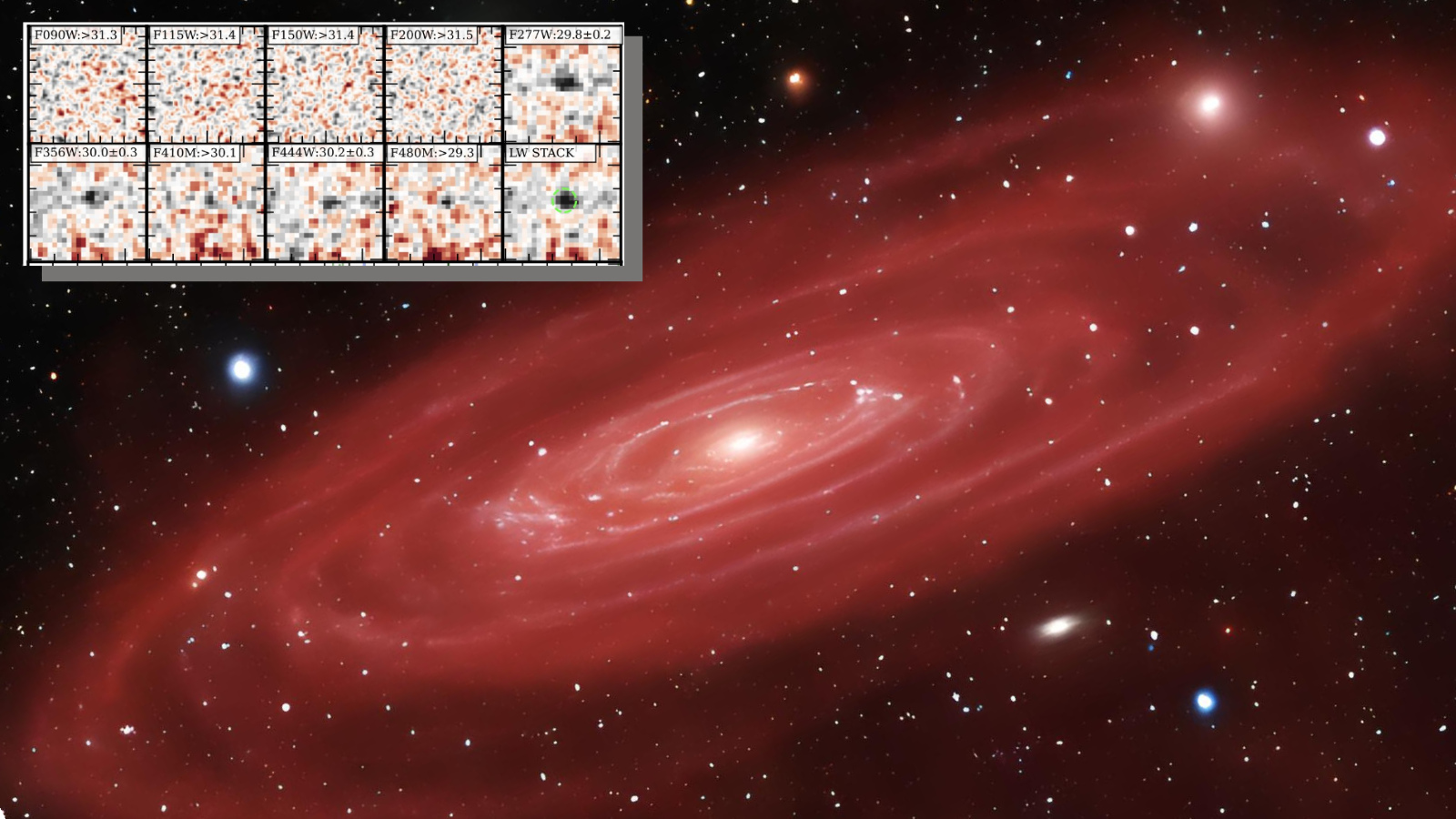

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has potentially smashed one of its own records again, potentially spotting the earliest and most distant galaxies ever seen.
The five candidate galaxies are so distant that the powerful space telescope sees them as they were just 200 million years after the Big Bang. That means the light from these galaxies has been traveling to the JWST for 13.6 billion years, almost the entire life span of the universe. If the five galaxies are confirmed, they beat the next earliest galaxy ever discovered JADES-GS-z14-0 , also seen by the JWST, by 80 million years!
In the time that has elapsed since the infrared light that the JWST saw left these galaxies, the universe has expanded so much that they are now staggering 34 billion light-years away.
"It remains quite challenging to estimate the exact age of these galaxies and to determine when they formed, but we are certainly approaching the first generation of galaxies because we are left with only around 150 million years to form these galaxies," discovery team member Hakim Atek, a researcher at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, told Space.com. "With so little time available, there are not many ways you can form galaxies."
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope 'pushed to its limits' to see most distant galaxies ever
James Webb Space Telescope images a 'cosmic sombrero'
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured a stunning new image of the galaxy Messier 104, also known as NGC 4594, nicknamed the "Sombrero Galaxy."
Located about 31 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo, this massive spiral galaxy has a mass equivalent to around 260 billion suns, which is almost five times the mass of all the stars in the Milky Way.
Using its Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), the JWST allowed astronomers to determine why the formation of stars appears to have slowed in the Sombrero Galaxy despite its intimidating mass.
Investigating the origins of 3 of the universe's earliest galaxies
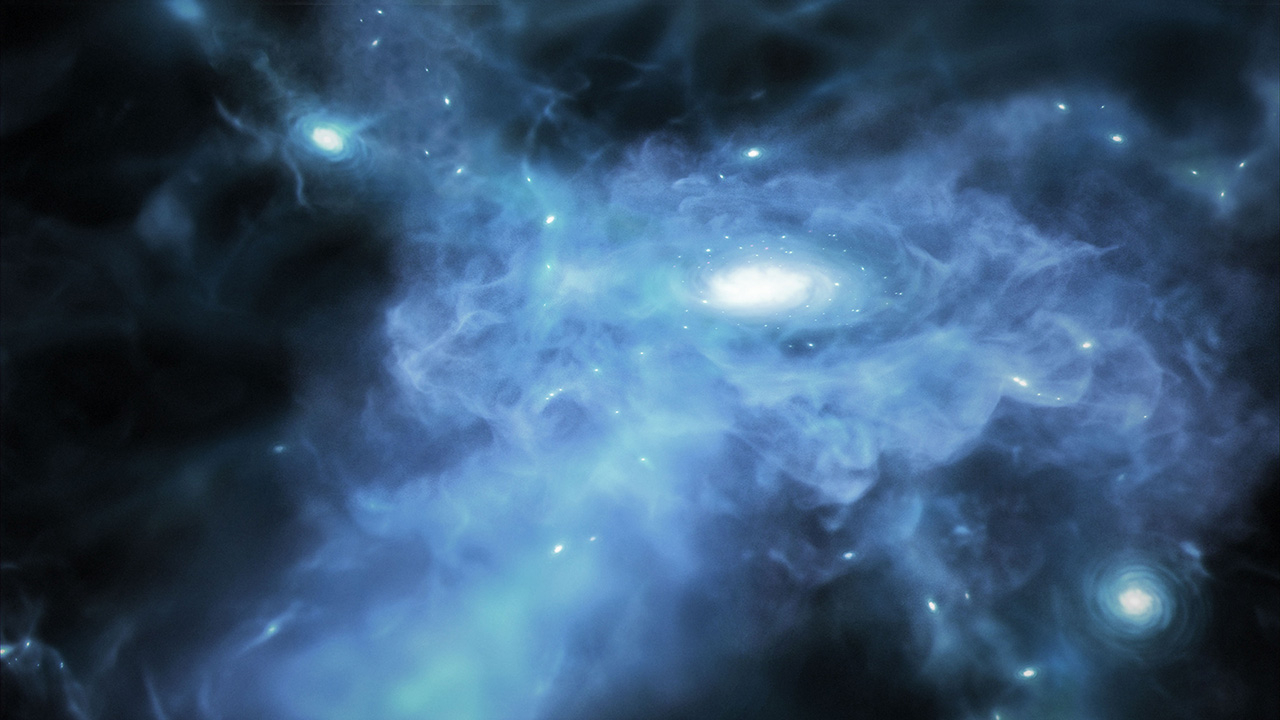

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has helped astronomers see what could be three of the universe's earliest galaxies. The galaxies are seen as they were when the 13.8 billion-year-old cosmos was between 400 million and 600 million years old.
The three galaxies are in the process of forming as the JWST imaged them, feeding on surrounding hydrogen and helium to facilitate the creation of new stars and, thus, their growth. Though shapeless and disorganized, as we see them less than a billion years after the Big Bang, these galaxies will eventually evolve into more familiar morphologies, such as the spiral shape of the Milky Way.
"You could say that these are the first 'direct' images of galaxy formation that we've ever seen," study lead author Kasper Elm Heintz, an astrophysicist at the Cosmic Dawn Center, said in a statement. "Whereas James Webb has previously shown us early galaxies at later stages of evolution, here we witness their very birth, and thus, the construction of the first star systems in the universe."
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope spots 3 of our universe's earliest galaxies
No we haven't spotted life on an alien planet (yet)
Last year, it was widely reported that the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) had spotted what could be the telltale signs of life in the atmosphere of a distant extrasolar planet, or exoplanet.
It had been reported that the powerful space telescope had seen dimethyl sulfide, or DMS, in the atmosphere of the exoplanet K2-18 b, a super-Earth located around 120 light-years from Earth. This was significant because on Earth DMS is created primarily by ocean phytoplankton.
New research suggests, however, that this detection was a false positive with a reassessment of the JWST data, causing the DMS signal to fade away. The research calls into question whether the JWST would even be capable of seeing DMS unless it is in incredibly large volumes in the atmosphere of this super-Earth.
"The signal strongly overlaps with methane, and we think that picking out DMS from methane is beyond this instrument's capability," team member and UCR project scientist Shang-Min Tsai said in a statement.
Read more: Did the James Webb Space Telescope really find life beyond Earth? Scientists aren't so sure
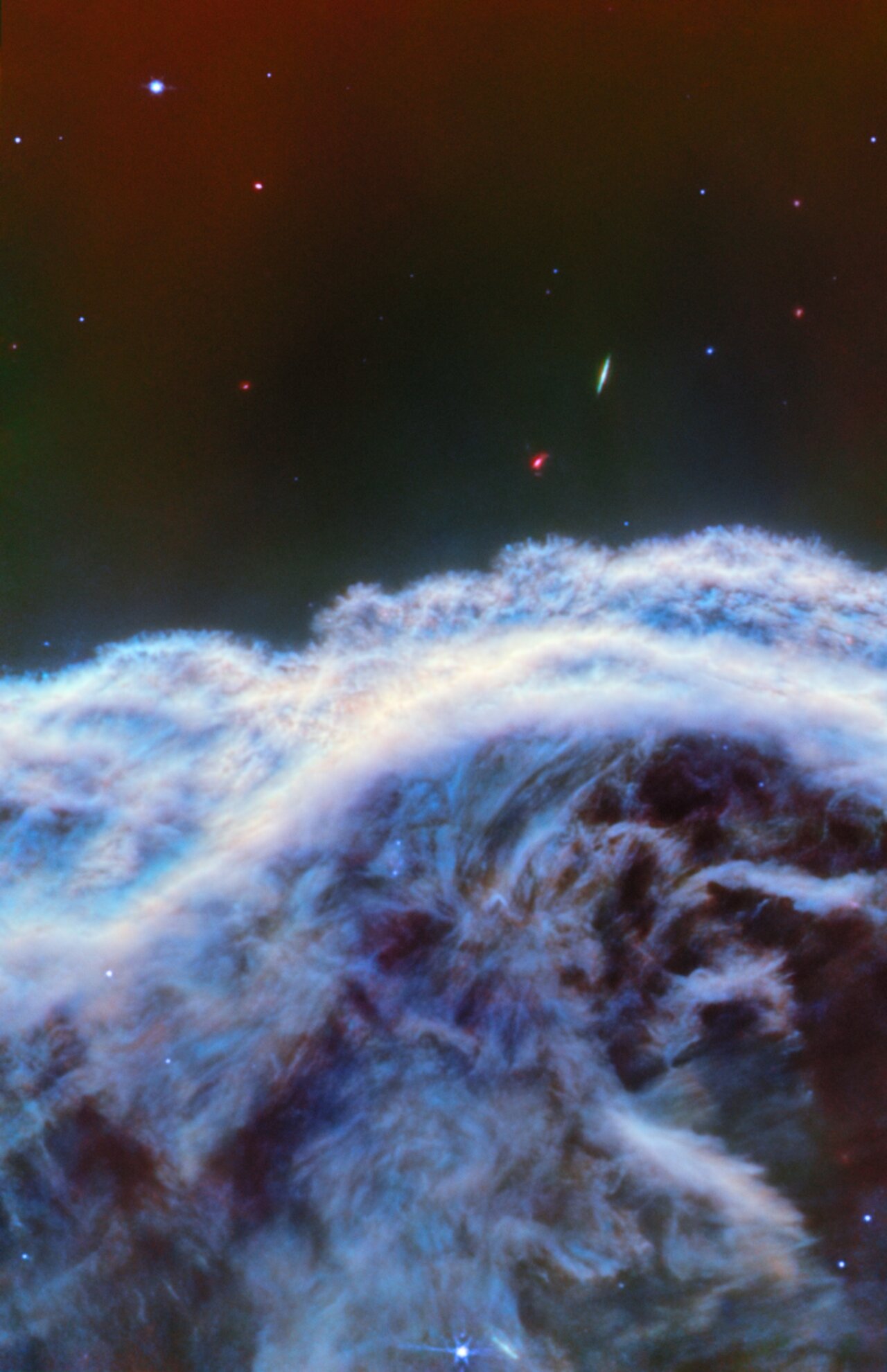
A new stunning view of the Horsehead Nebula
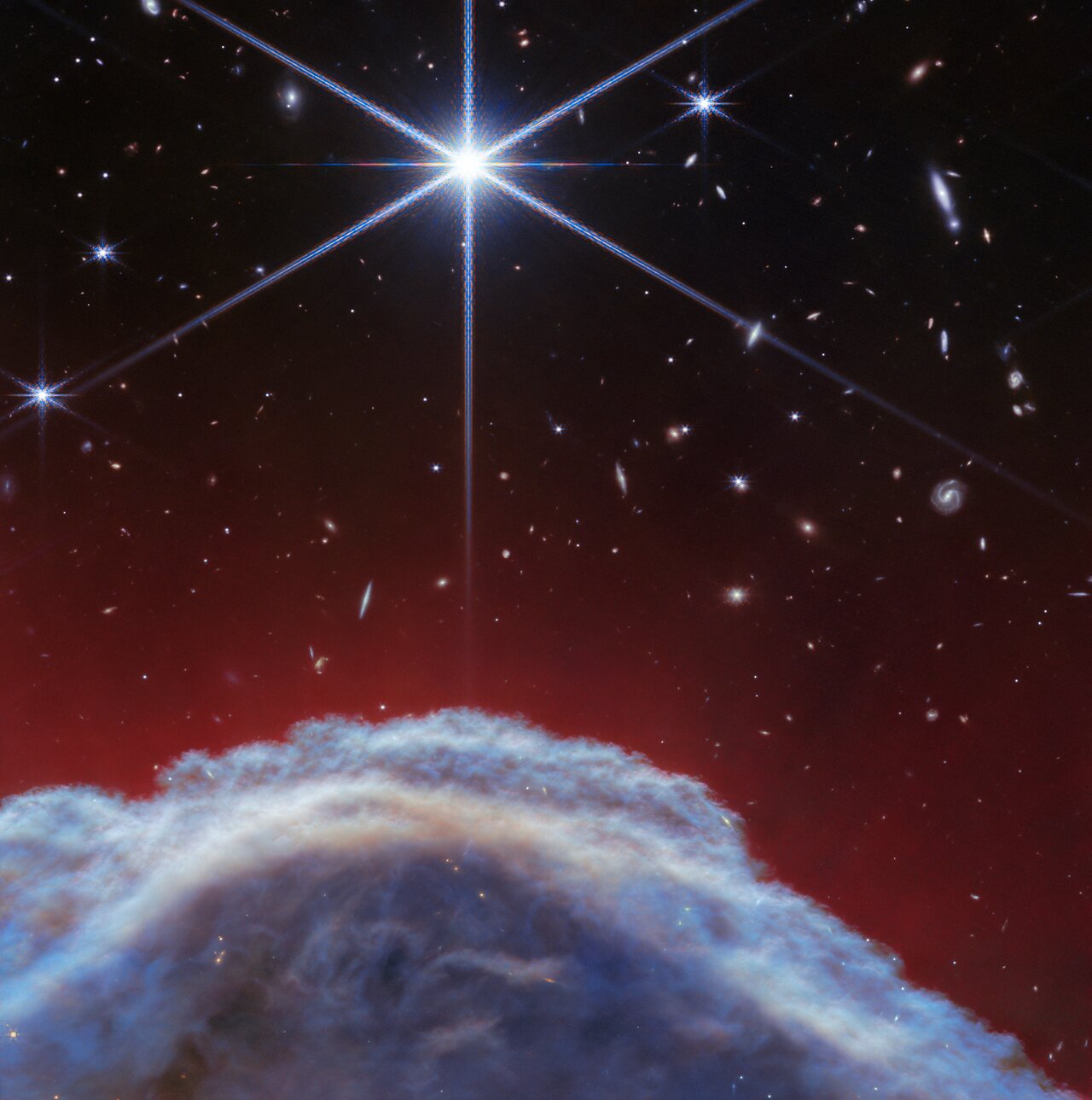

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has proved to be the "mane" telescope when it comes to looking at stunning celestial objects.
The JWST was able to see never-before-seen details of the Horsehead Nebula, also known as Barnard 33, revealing some regions of this iconic astronomical target in a completely new light.
The JWST images show turbulent waves of gas rising from the western side of Orion B, a star-forming molecular cloud located 1,300 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Orion, where the nebula is located.

Investigating the starburst Cigar Galaxy
Using its powerful and sensitive infrared eye, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has peered through the dense gas and dust at the heart of the Cigar Galaxy to investigate a region of intense star formation.
This starburst galaxy, also known as Messier 82 (M82), produces stars around 10 times as fast as our galaxy, the Milky Way. Much of this star birth is concentrated in a central region, which NIRCam imaged in long and short-wave infrared light. This revealed a hitherto unknown connection between sooty chemical molecules known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and structures of hot ionized gas.
"M82 has garnered a variety of observations over the years because it can be considered as the prototypical starburst galaxy," Alberto Bolatto, team leader and University of Maryland researcher, said in a statement. "Both Spitzer and Hubble space telescopes have observed this target. With the JWST's size and resolution, we can look at this star-forming galaxy and see all of this beautiful new detail."
Read More: James Webb Space Telescope gets to the heart of a smoking starburst galaxy (images)
Solving the mystery of gas giant formation
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has investigated gas flowing from a protoplanetary disk surrounding an infant star, an outflow known as "disk winds." The observations could help scientists better understand how gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn are born.
The team behind the study focused the JWST on a young, low-mass star called T Cha, located around 350 light-years from Earth. This star is known to have a large gap in the protoplanetary disk that swirls around it. Gaps like this indicate a budding young planet is moving around the star, gathering material.
By studying how gas escapes from this disk, the team could learn what conditions favor the formation of gas giants and what conditions favor the formation of rocky planets like Earth.
"Rocky planets very close to the star will have very little or no atmosphere [like Mercury], as it will be stripped away by the sun's high energy photons — similar to photoevaporation," Naman Bajaj, lead author of the new disk-wind analysis and a scientist with the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Science Laboratory, told Space.com. "For gas giants, if they happen to form close to the star, it is possible that they find a balance between their gas and the sun's energy."
Read more: The James Webb Space Telescope is digging deep into the mysteries of gas planets
That's cool! Icy ingredients for life swirl around infant stars

Astronomers have used the James Webb Space Telescope to spot several of the building blocks of stars, planets, and even life in ice form swirling around two infant stars, or "protostars."
The complex organic molecules (COMs) spotted range from relatively simple molecules to complex compounds. Some of the familiar compounds spotted around the protostars IRAS 2A and IRAS23385 include ethanol, which we call alcohol on Earth, acetic acid found in vinegar, and formic acid, the compound that makes bee stings and ant bites painful.
The discovery of the compounds around IRAS 2A is particularly interesting because these protostars, a lot like the sun, would have 4.6 billion years ago in its infancy before the formation of the planets. That means the discovery of these icy compounds may help confirm that the vital ingredients for life were delivered to Earth by comet bombardments.
"This finding contributes to one of the long-standing questions in astrochemistry," team leader and Leiden University researcher Will Rocha said in a statement. "What is the origin of COMs in space? Are they made in the gas phase or in ice? The detection of COMs in ices suggests that solid-phase chemical reactions on the surfaces of cold dust grains can build complex kinds of molecules."
Related: James Webb Space Telescope spots the icy building blocks of life swirling around infant stars
Checking Hubble's work complicates expanding universe picture

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has double-checked the Hubble Space Telescope's calculations of the expanding universe, finding its older sibling telescope was spot on the money. This possibly intensifies an existing headache for cosmologists called the "Hubble tension."
The Hubble Tension arises from the fact that measurements of the rate of the expansion of the universe made with a cosmic fossil called the cosmic microwave background (CMB) don't tally with a measurement technique referred to as the "cosmic distance ladder." One possibility for Hubble tension was that measurements made by the Hubble telescope to form the bottom rung of this ladder were inaccurate.
This distance ladder is made up of "rungs" of different techniques to measure increasingly larger cosmic distances. The JWST discovered that the bottom rung, measurements to stars that pulse in brightness called "Cepheid variables," isn't a little loose after all. Observations made with the increased resolution of the JWST revealed that a suspected error in Hubble's measurement of Cepheid variables isn't present.
"We've now spanned the whole range of what Hubble observed and we can rule out a measurement error as the cause of the Hubble tension with very high confidence," research leader and John Hopkins University scientist Adam Riess said in a statement. "With measurement errors negated, what remains is the real and exciting possibility we have misunderstood the universe."
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope complicates expanding universe paradox by checking Hubble's work
How do some balck holes get so big?

Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) researchers identified a population of supermassive black hole-powered quasars that could help explain how such objects grew to sizes equivalent to millions or billions of times that of the sun.
The relatively small quasars, which were identified as tiny red dots of light, represent a transitional stage on the road to becoming truly gigantic supermassive black holes. This means that this quasar population could fill a mass gap, the existence of which has perplexed scientists.
"One issue with quasars is that some of them seem to be overly massive, too massive given the age of the universe at which the quasars are observed," Jorryt Matthee, lead author of the study and an assistant professor at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria, said in a statement. "We call them the 'problematic quasars.'"
Read more: How do some black holes get so big? The James Webb Space Telescope may have an answer
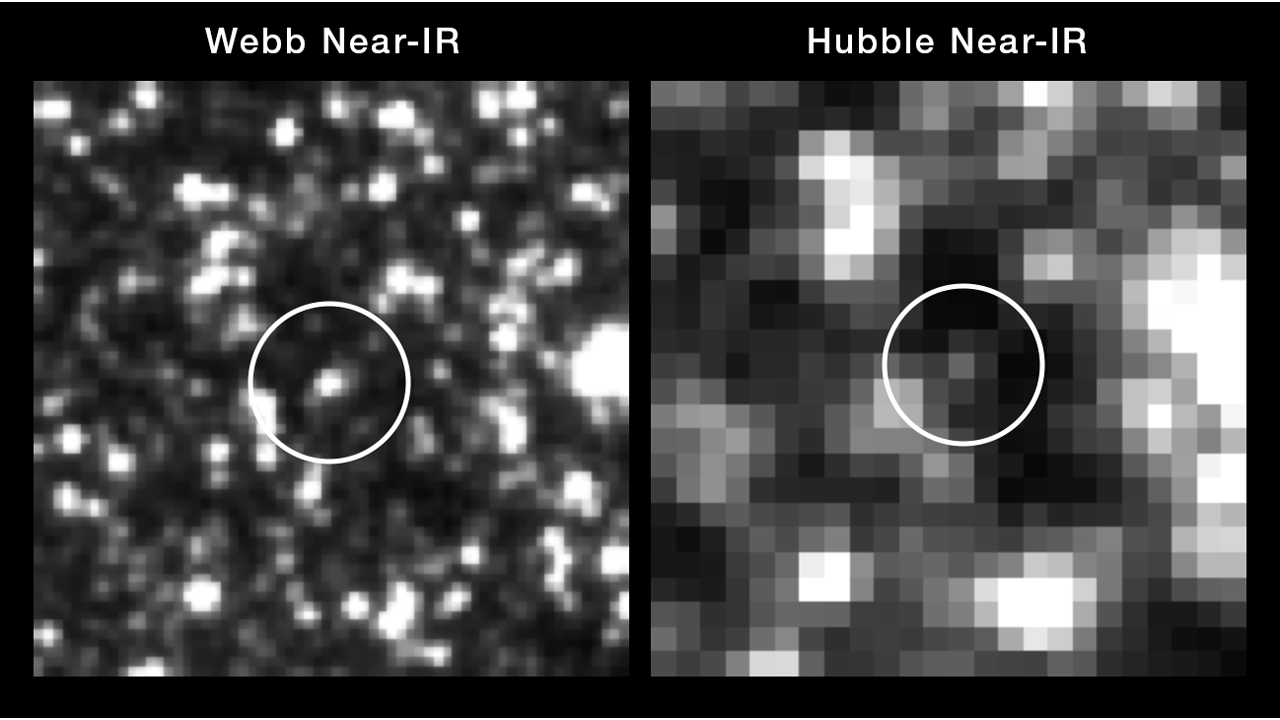
Small galaxies packed a punch in the early universe

Using the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have observed small galaxies that existed when the universe was less than 1 billion years old, finding they were responsible for shaping the entire cosmos.
The galaxies with masses less than 1 billion times that of the sun provided most of the light that transformed neutral hydrogen to ionized hydrogen during a point in the universe's evolution called the epoch of reionization.
"We're really talking about the global transformation of the entire universe," Hakim Atek, research lead author and an astronomer at the Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris told Space.com. "The main surprise is that these small, faint galaxies had so much power, their cumulative radiation could transform the entire universe."
Extremely red supermassive black hole discovered
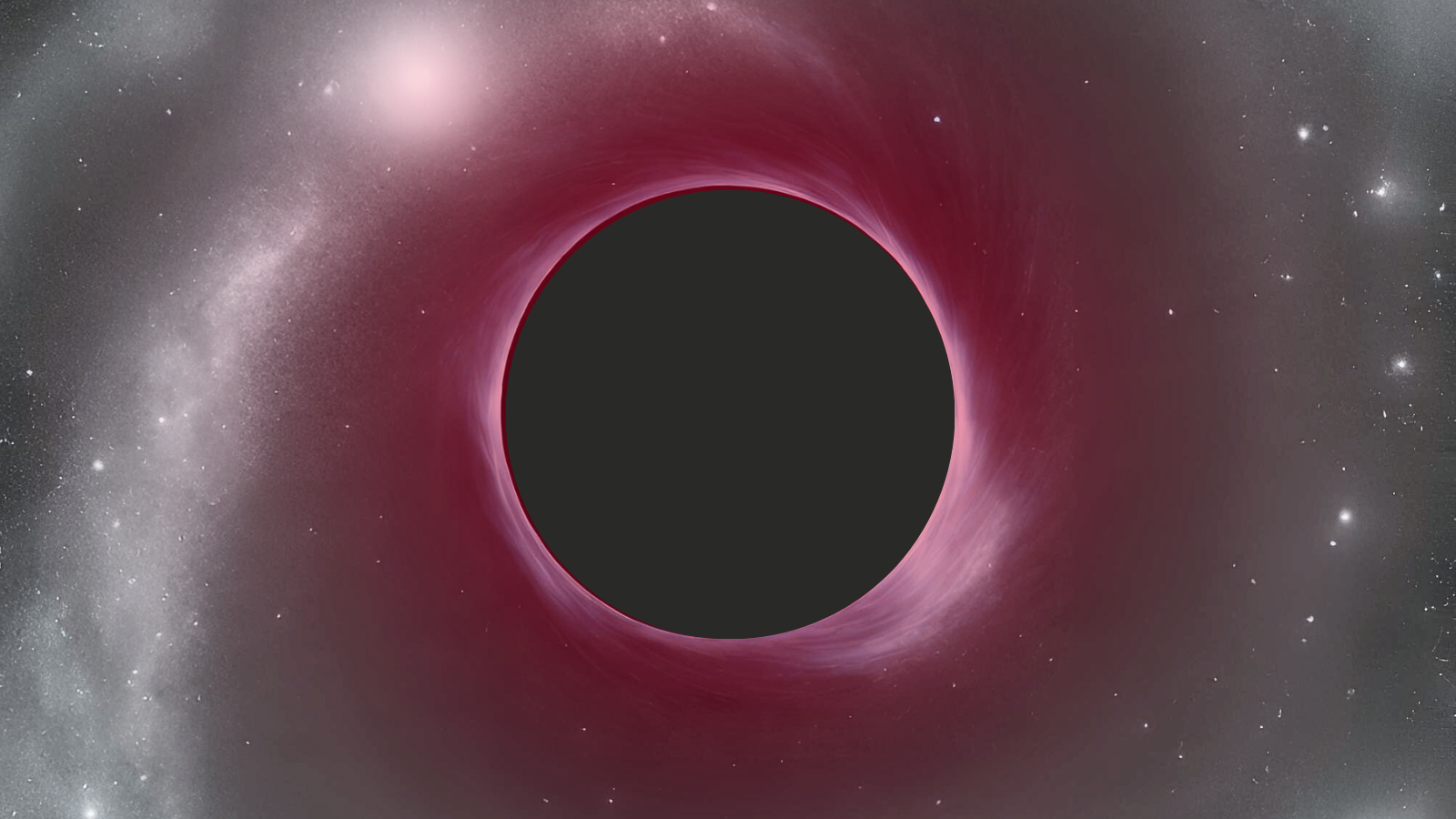
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) astronomers have discovered an extremely red supermassive black hole that existed when the universe was under 1 billion years old.
Not only is the supermassive black hole as massive as 40 million suns, it is growing by rapidly swallowing or accreting matter. Its red color comes from the shroud of gas and dust that surrounds it.
"Several other supermassive black holes in the early universe have now been found to show a similar behavior, which leads to some intriguing views of the black hole and host galaxy growth, and the interplay between them, which is not well understood," Princeton University researcher Jenny Greene said.
Quartz crystals detected on alien planet
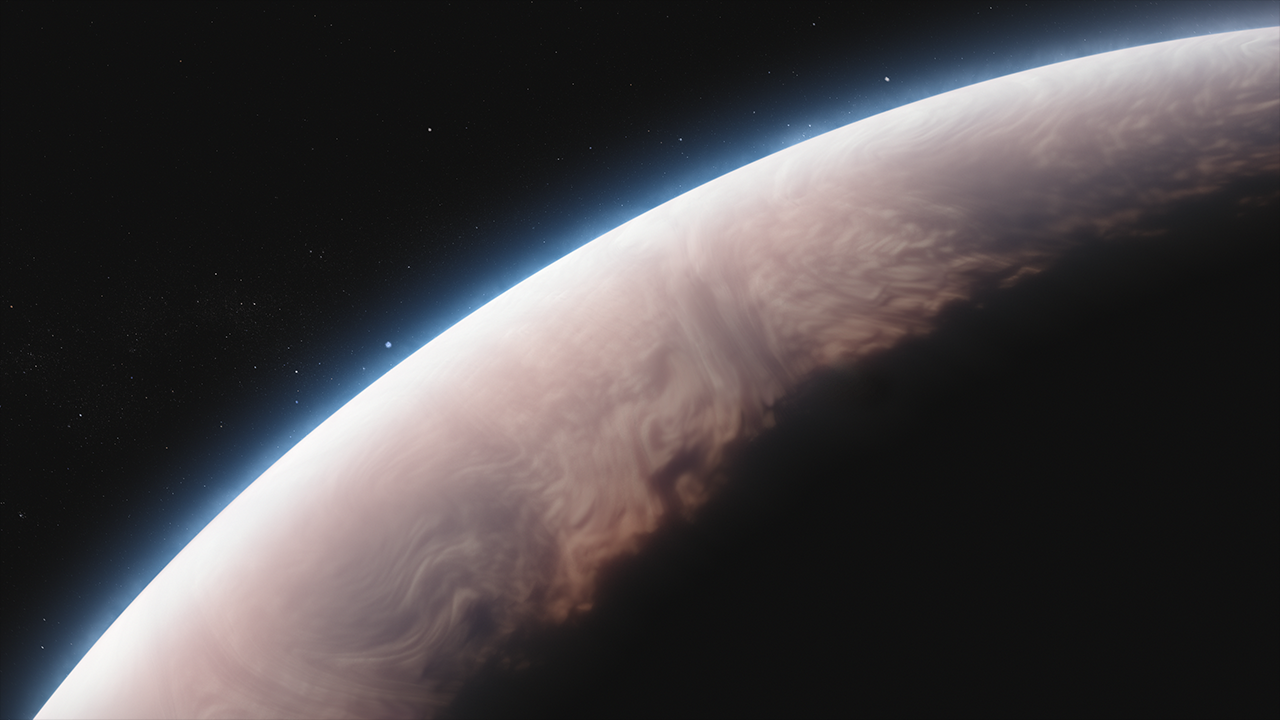
Thousand-mile-per-hour winds are blowing a hail of tiny quartz crystals through the silicate-enhanced, scorching hot atmosphere of a distant gas giant planet called WASP-17b, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has found.
"We knew from Hubble [Space Telescope] observations that there must be aerosols — tiny particles making up clouds or haze — in WASP-17b’s atmosphere, but we didn’t expect them to be made of quartz," Daniel Grant of the University of Bristol in the UK and leader of a new study on the discovery, said in a statement.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope detects quartz crystals in an exoplanet's atmosphere
Stunning image of young stars in the galaxy next door
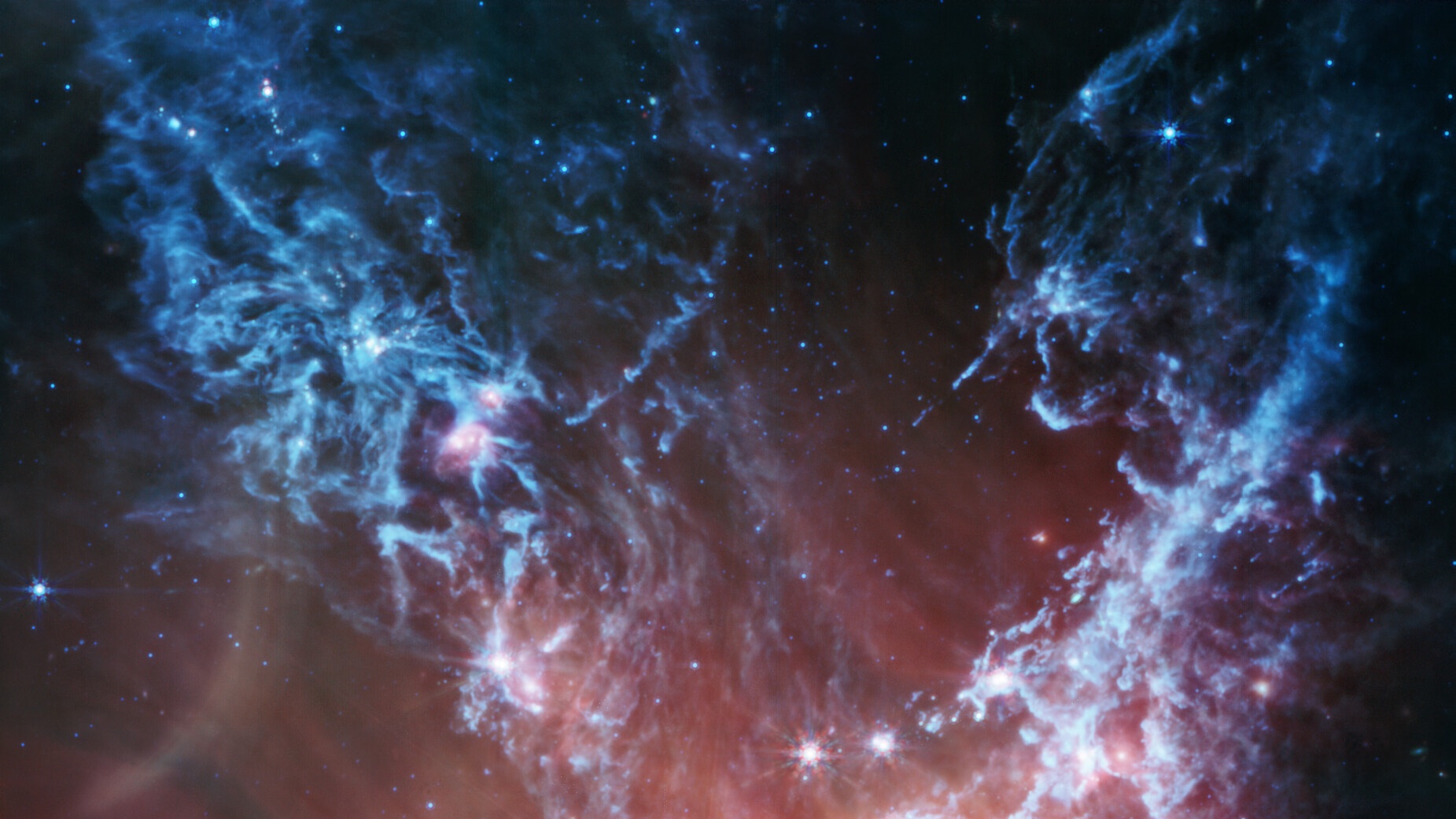

A star-studded cosmic neighbor 210,000 light-years away is now available to view on our computer screens in unprecedented detail, thanks to NASA’s mighty James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the power of modern internet connection.
The newly released James Webb Space Telescope photo captures NGC 346, a star-forming region in a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way called the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC).
Read more and see the entire image: James Webb Space Telescope spotlights gorgeous young stars in a galaxy next door (photo)
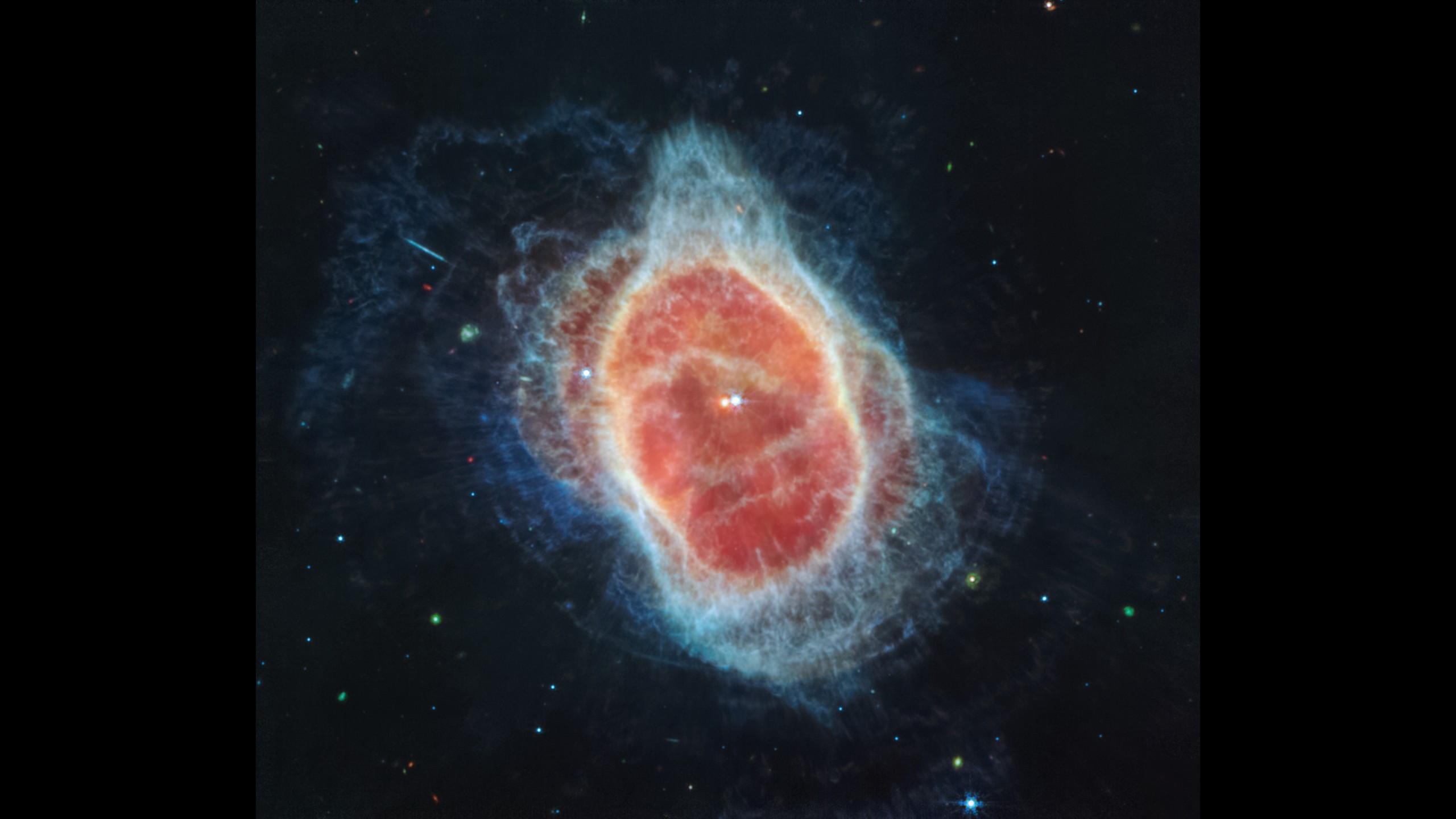
JWST strikes gold (again) with stunning images of the Ring Nebula
Approximately 2,200 light-years from where you're sitting lie the Cheerio-shaped remains of a dying star — remnants that form a structure famously known as the Ring Nebula. And on Monday (Aug. 21), scientists announced the James Webb Space Telescope has struck gold once again, earning a rather beautiful new view of this iconic cosmic halo.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope offers a mesmerizing look at the Ring Nebula (photos)
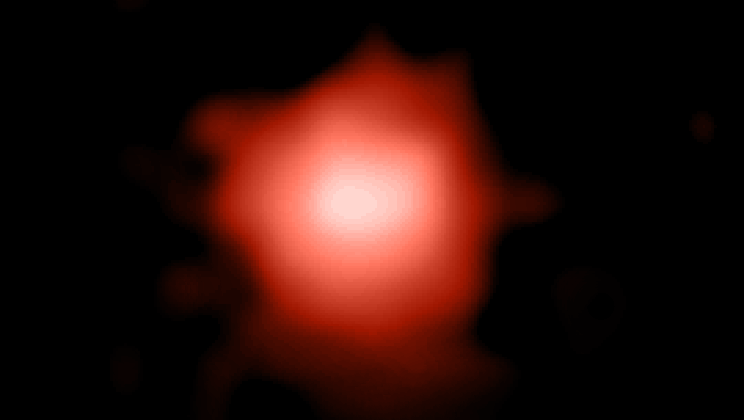
JWST lifts veil on the most distant star known in the universe
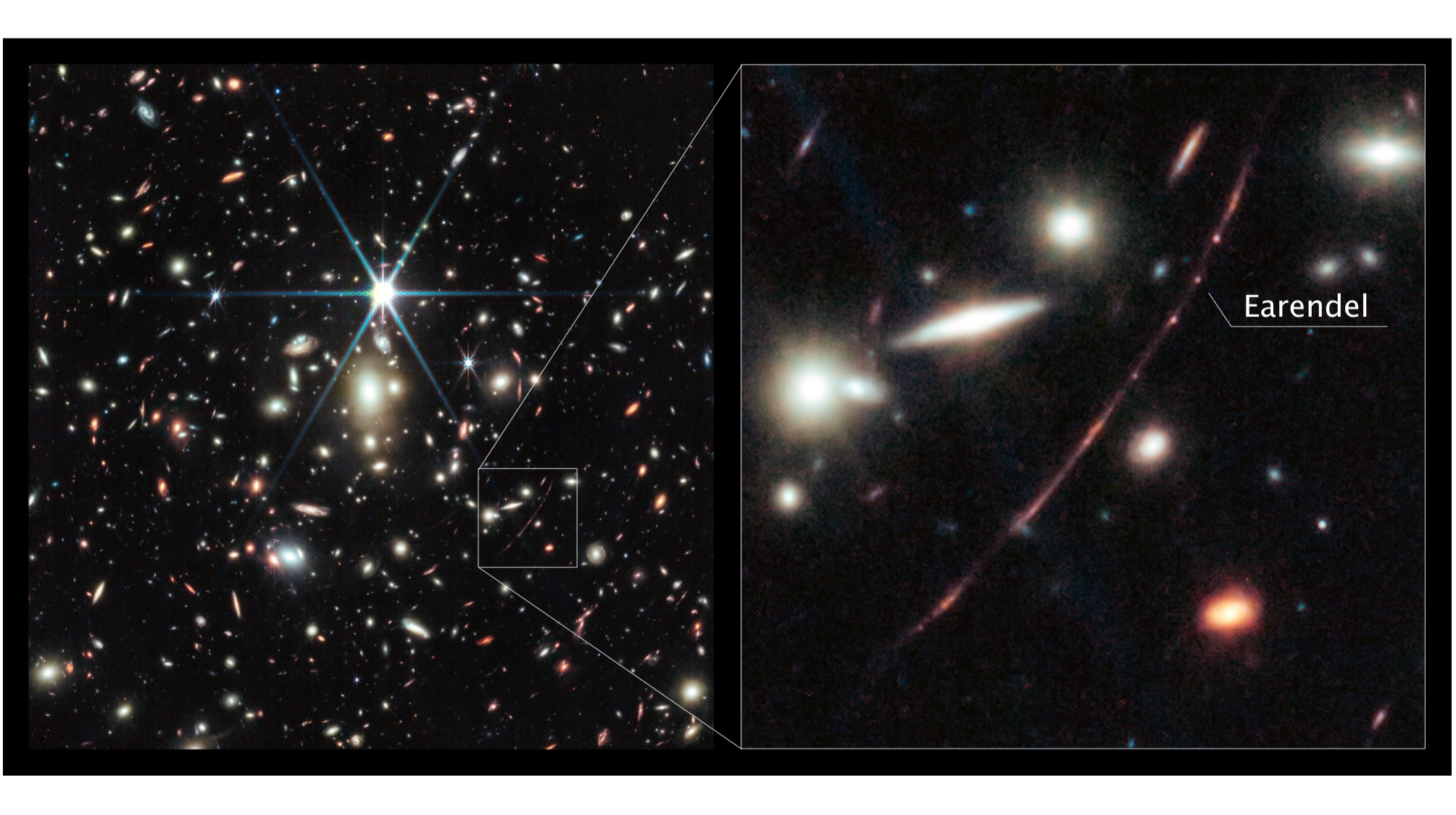
Astronomers have begun measuring the most distant star ever detected, thanks to the powerful eyes of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
That star, known as Earendel, was discovered last year by the Hubble Space Telescope. It has taken 12.9 billion years for Earendel's light to reach Earth, meaning the star was shining less than a billion years after the Big Bang spurred our universe into existence. However, Earendel doesn't lie a mere 12.9 billion light-years away from us.
New JWST image stuns with glowing portrait of actively forming stars
This marks the most detailed image yet of the striking stellar pair Herbig-Haro 46/47 located about 1,470 light-years away.
Produced with the scope's powerful infrared eyes, the image showcases a striking salmon-colored smear at its center. This represents the area where the stars, collectively named Herbig-Haro 46/47, are found.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope stuns with glowing portrait of actively forming stars (photo)
Water detected near center of planet-forming disk in cosmic 1st
Astronomers have for the first time discovered that rocky alien worlds could possess large amounts of water from the moment they form, a new study finds.
Life is found virtually wherever there is water on Earth. As such, the search for potentially habitable exoplanets has mainly focused on hunting for the presence of water.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope spies water near center of planet-forming disk in cosmic 1st
Diamond-like carbon dust detected in the universe's earliest stars
The James Webb Space Telescope has detected the earliest-known carbon dust in a galaxy ever.
Using the powerful space telescope, a team of astronomers spotted signs of the element that forms the backbone of all life in ten different galaxies that existed as early as 1 billion years after the Big Bang.
1st year of observations has some astronomers in tears — but in a good way
July 12 marks one year since the James Webb Space Telescope's first four images were released to the public.
To mark the occasion, NASA expert Taylor Hutchison spoke to Space.com about the impact the $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has had on science in its first 12 months. The astrophysicist also explained what could be forthcoming from the JWST during its second year of operations.
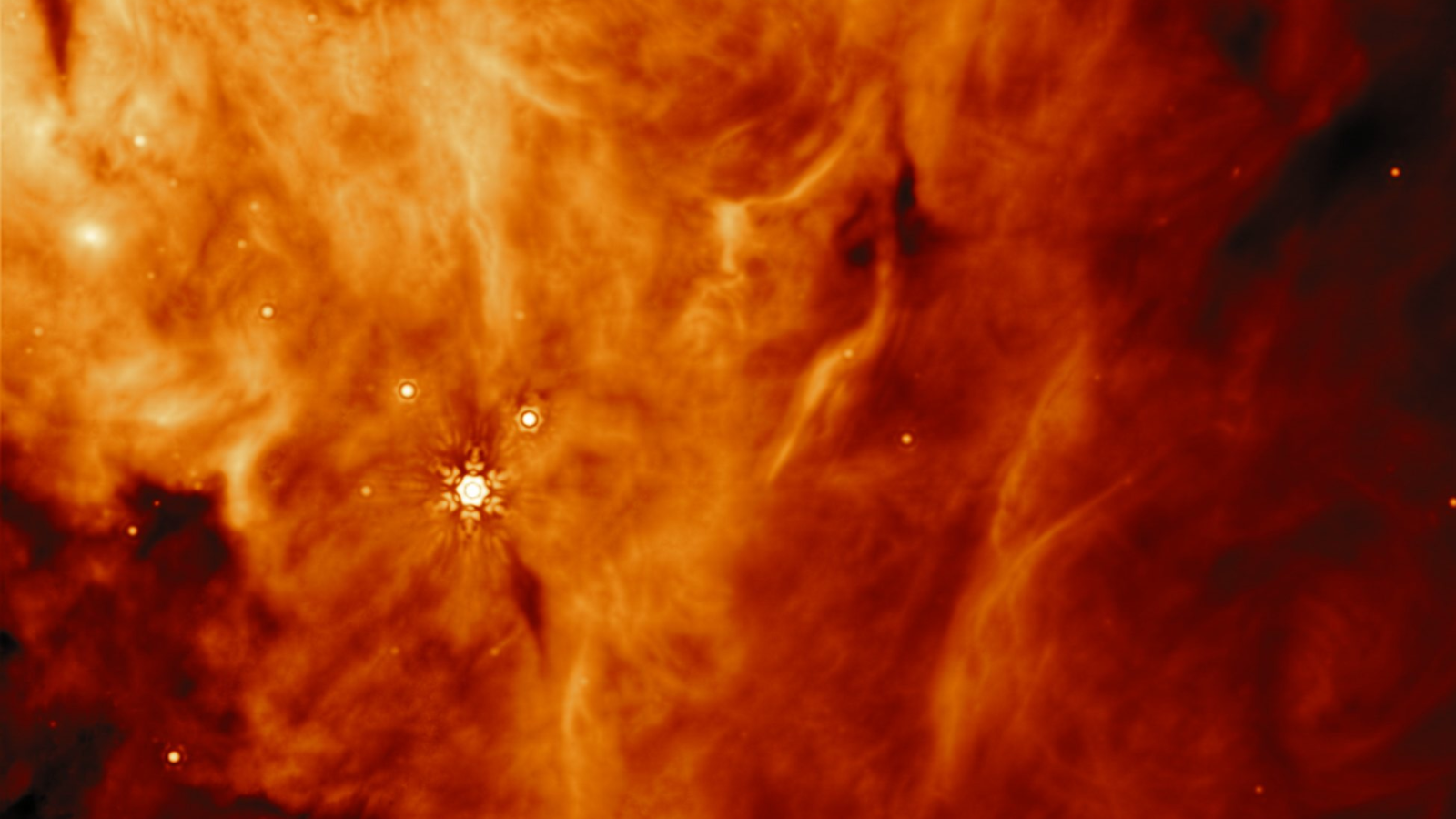
New image of stellar nursery released to celebrate 1st year of JWST observations
To mark the one-year anniversary of James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observations on Wednesday, July 12, 2023, NASA has released a stunning image that shows star birth in a way that it has never been seen before.
The new JWST image features the closest star-forming region to Earth, the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. Though a small and relatively peaceful stellar nursery, the powerful telescope's visualization represents a chaotic close-up of the region located 390 light-years from Earth.
Read more and see the photo here: New James Webb Space Telescope image released to celebrate 1st year of observations is absolutely stunning (photo)
New 3D visualization journeys back in time
A new 3D visualization from the James Webb Space Telescope takes viewers on a journey back in time to just after the Big Bang.
In the video, over 5,000 galaxies can be seen in gorgeous full color and three dimensions. The cosmic journey begins with relatively nearby galaxies located within a few billion light-years of Earth and concludes at Maisie's Galaxy, which at 13.4 billion light-years from Earth is one of the most distant galaxies ever observed by humanity and is seen as it was just around 390 million years after the Big Bang.
Read more and watch the video here: James Webb Space Telescope time travels billions of years in amazing 3D visualization (video)
Detected: Most distant active supermassive black hole ever seen
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has detected the most distant active supermassive black hole.
The galaxy that hosts the ancient black hole, CEERS 1019, formed fairly early in the universe's history, just 570 million years after the Big Bang. The active supermassive black hole at the center of CEERS 1019 is unusual not only for its age and distance but also in that it weighs in at just 9 million solar masses, meaning it's 9 million times heftier than the sun.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope detects most distant active supermassive black hole ever seen
1st starlight from ancient quasars spotted in groundbreaking discovery
With the aid of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have seen starlight from two early galaxies that host feeding supermassive black holes, or quasars, for the first time.
The active galaxies and the feeding supermassive black hole-powered quasars are seen as they were when the universe was less than one billion years old.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope sees 1st starlight from ancient quasars in groundbreaking discovery
JWST captures stunning raw images of Saturn
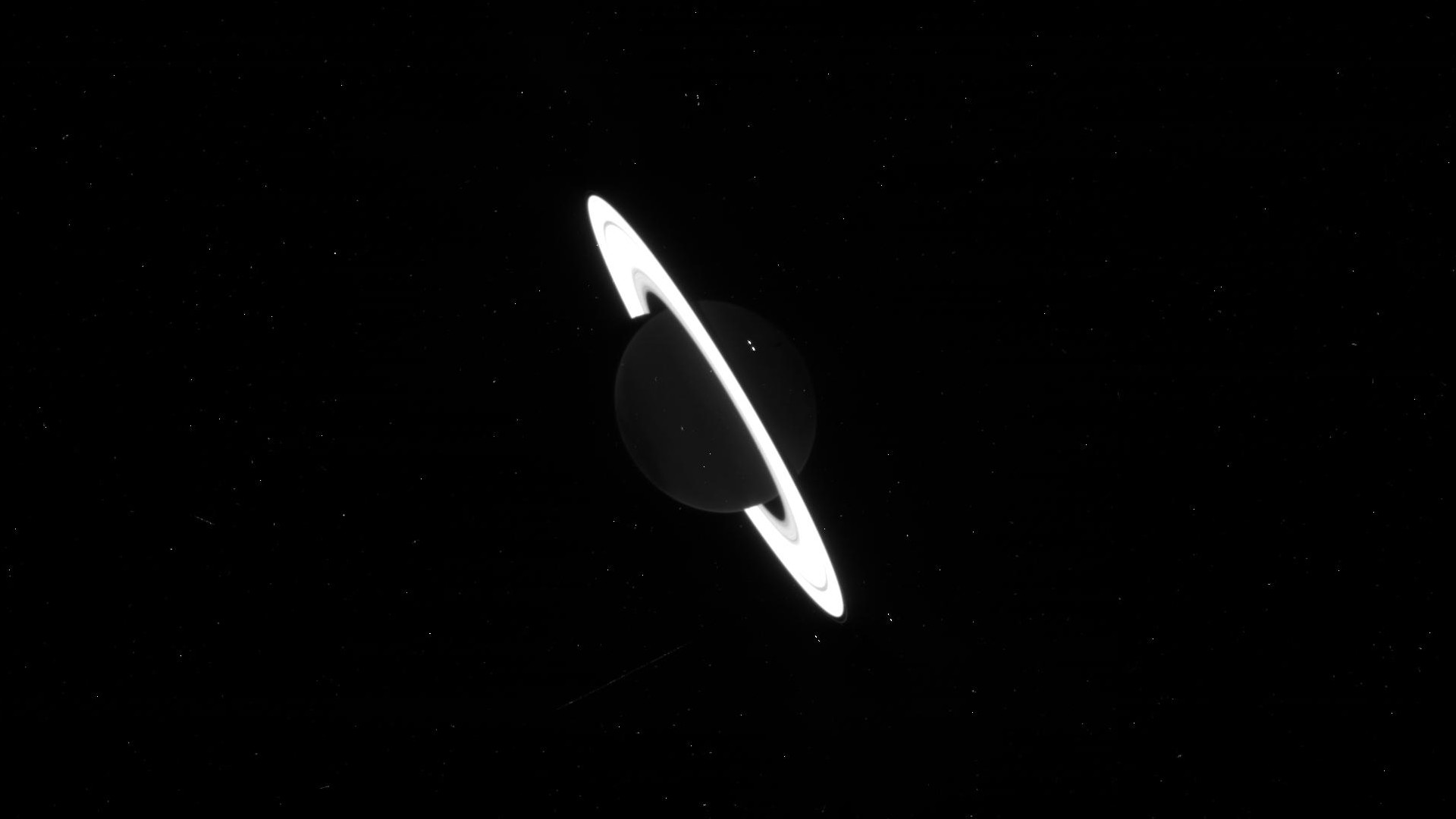

The James Webb Space Telescope has captured its first incredible images of the gas giant Saturn, but they aren't quite ready for the public yet.
The raw images of Saturn were revealed on the unofficial website JWST feed, which contains every piece of data collected by the powerful space telescope since it began operations in mid-2023.
Read more: Saturn looks incredible in these raw James Webb Space Telescope images (photos)
JWST spies on rocky TRAPPIST-1 exoplanet, finds bad news for life
New data from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) shows that the atmosphere of a rocky exoplanet in the TRAPPIST-1 system is either non-existent or incredibly thin, making it unfavorable for hosting life as we know it.
Astronomers using JWST were able to calculate the amount of heat energy coming from TRAPPIST-1 c, revealing that the dayside temperature of the rocky world is about 225 degrees Fahrenheit (107 degrees Celsius) — the coolest rocky exoplanet ever characterized. At this temperature, the exoplanet's atmosphere is likely extremely thin, if it exists at all, according to a statement from NASA.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope spies on rocky TRAPPIST-1 exoplanet, finds bad news for life
James Webb Space Telescope reveals how galaxies made the early universe transparent
Shortly after the Big Bang, the universe was a dark and mysterious place. The gas between stars and galaxies was opaque, so no light could shine through.
Using observations from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, an international team of astronomers led by Simon Lilly of ETH Zürich in Switzerland has found how the universe changed in opacity. The team looked back in time at galaxies from the end of the Era of Reionization, a dramatic period in the universe's history in which gas was heated, cooled and then reionized (given an electrical charge once again).
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope reveals how galaxies made the early universe transparent
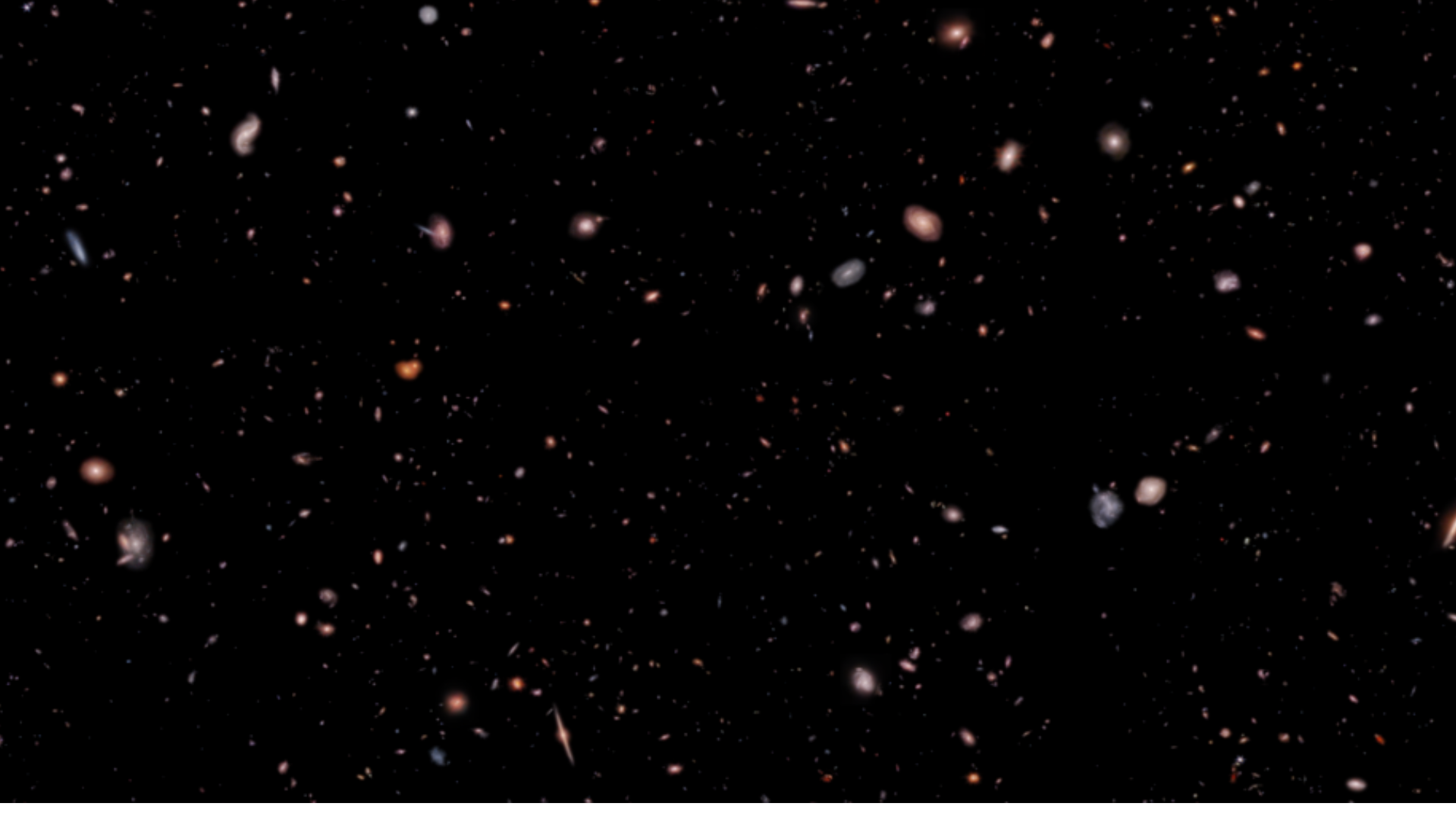
JWST discovers 717 ancient galaxies
The James Webb Telescope has unveiled hundreds of ancient galaxies that could be among the first members of the universe — a leap from only a handful that were previously known to exist at the time.
93% of the newfound galaxies that Webb spotted had never been seen before.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope discovers 717 ancient galaxies that flooded the universe with 1st light
Faintest galaxy yet in the infant universe found
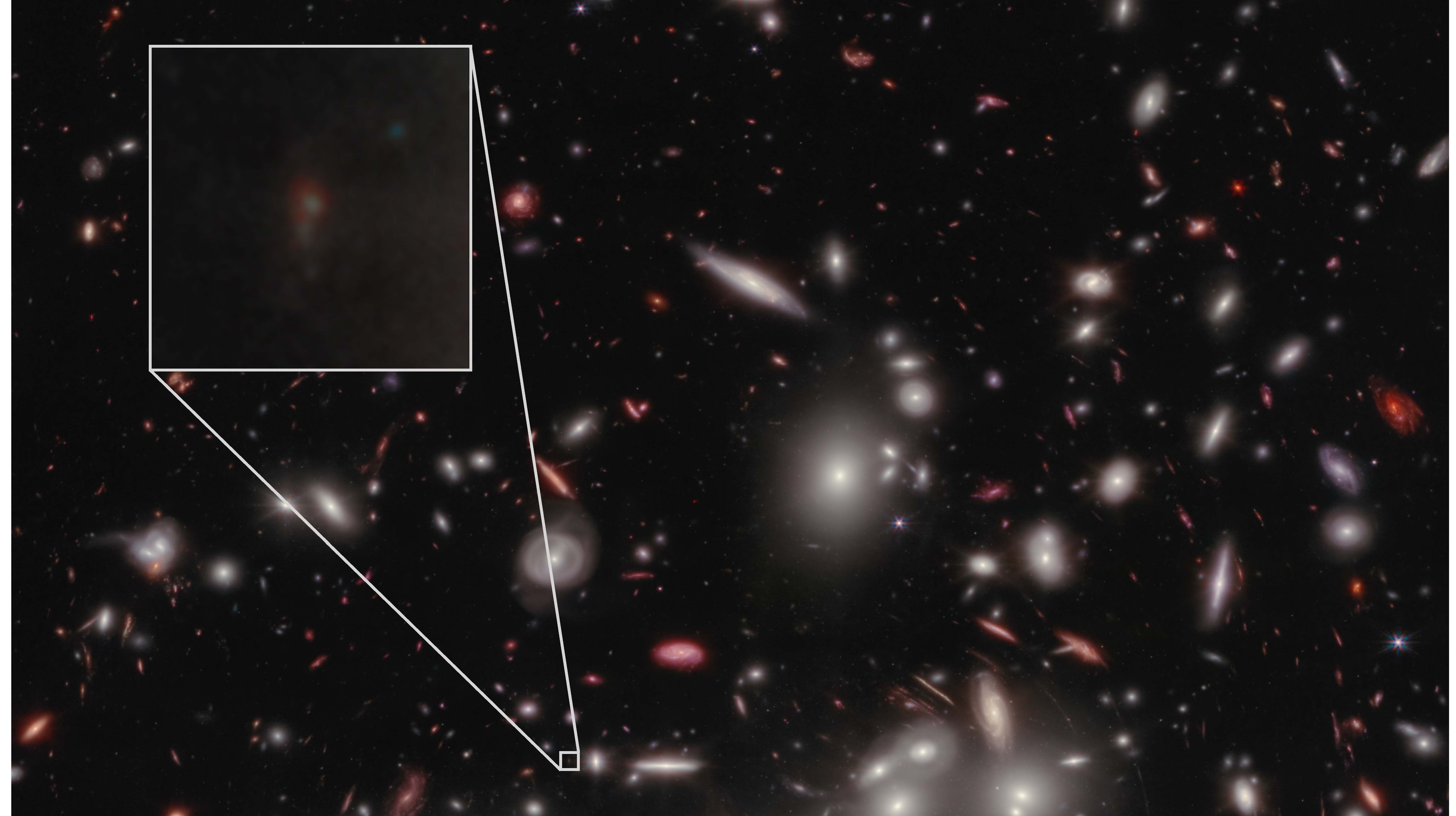

The James Webb Space Telescope has detected the faintest galaxy yet in the infant universe.
The galaxy, known as JD1, is part of the first generation of galaxies to pop up in our universe's 13.8-billion-year history. It's about 13.3 billion light-years away from us, meaning we're observing it as it looked when the universe was only a few hundred million years old — a meager 4% of its current age.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope spots faintest galaxy yet in the infant universe (photo)
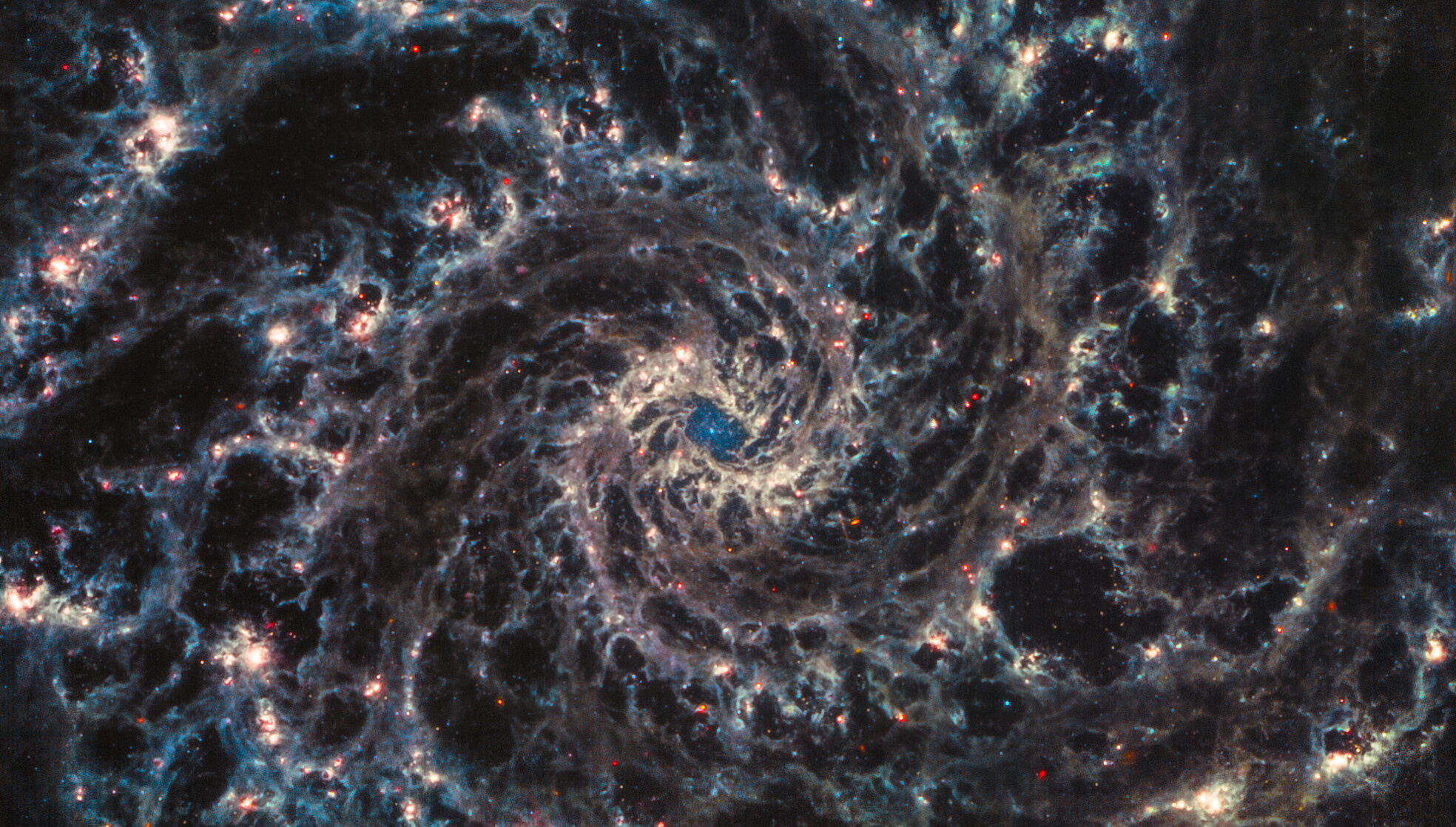
Cosmic 'treasure trove' found behind bars
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured a stunning image of a distant barred spiral galaxy as astronomers aim to study star birth in the deeper regions of space.
JWST observed the galaxy NGC 5068, located 17 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo, as part of its mission to build what the European Space Agency (ESA) calls a "treasure trove" of star formation observations in relatively nearby galaxies.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope peers behind bars to reveal a cosmic 'treasure trove' (video)
Oldest known examples of complex organic molecules found
The James Webb Space Telescope has spied the oldest known examples of complex organic molecules in the universe, a new study reports.
These chemicals — much like ones found in smoke and soot on Earth — reside within an early galaxy that formed when the universe was about 10% of its current age. The chemicals were spotted in a galaxy known as SPT0418-47 more than 12 billion light-years from Earth.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope spies earliest complex organic molecules in the universe
Traces of water vapor found in super-hot exoplanet's atmosphere
The James Webb Space Telescope has found traces of water vapor in the atmosphere of a super-hot gas giant exoplanet some 400 light-years away from Earth.
The exoplanet in question, WASP-18 b, is a gas giant 10 times more massive than the solar system's largest planet, Jupiter.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope finds water in super-hot exoplanet's atmosphere
JWST discovers water around mysterious comet
The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted water around a rare comet located in the main asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars.
The observation represents another scientific breakthrough for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), representing the first time that gas, in this case, water vapor, has been detected around a comet in the main asteroid belt. This is important as it shows that water in the early solar system could have been preserved as ice in the main asteroid belt.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope discovers water around a mysterious comet
Key instrument is facing sensor issues
A mode of the JWST's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) is receiving less sensor "throughput", meaning it's receiving less than the expected amount of light at the longest wavelengths. NASA officials are currently investigating the cause.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope faces sensor glitch in deep space
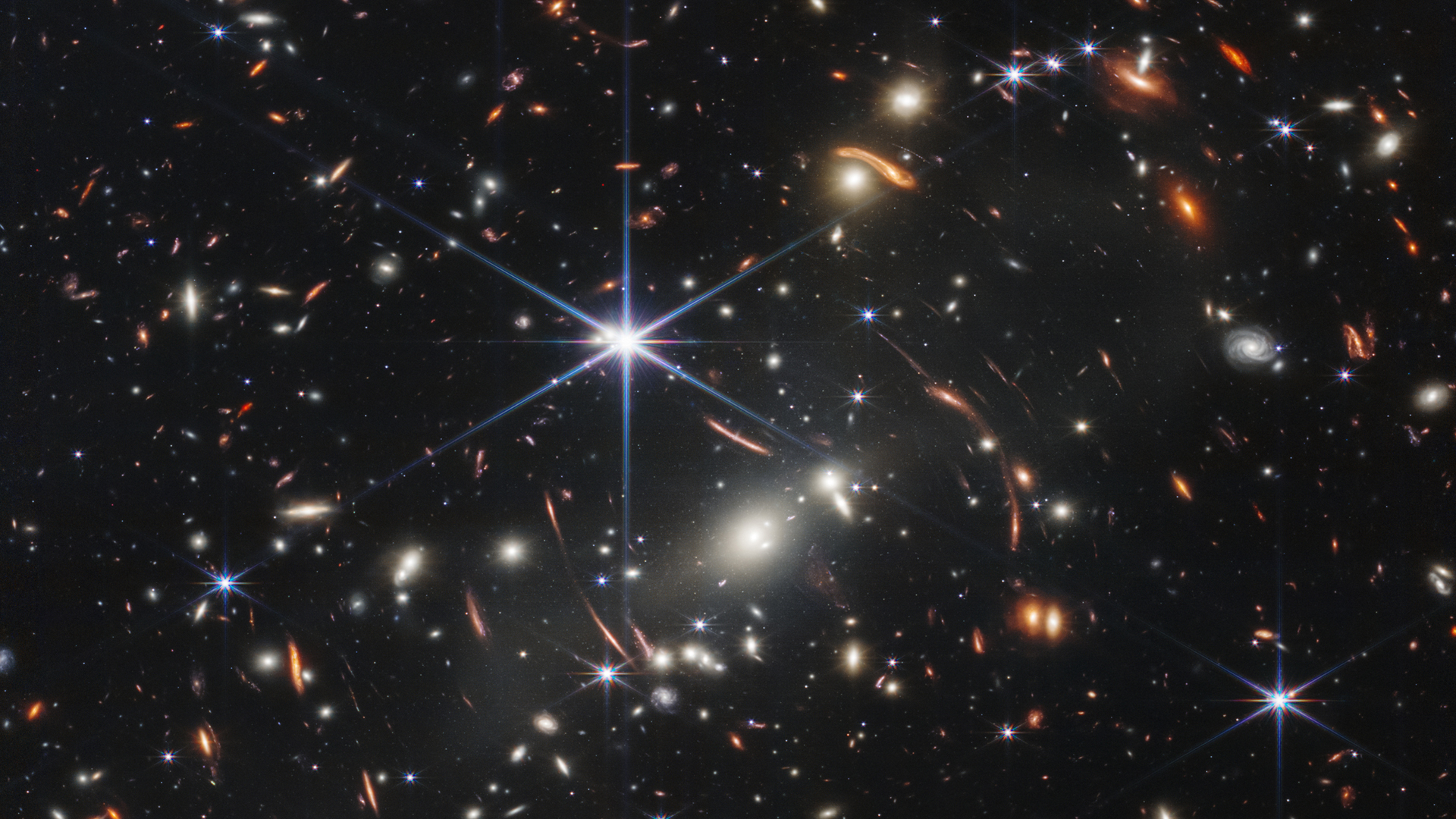
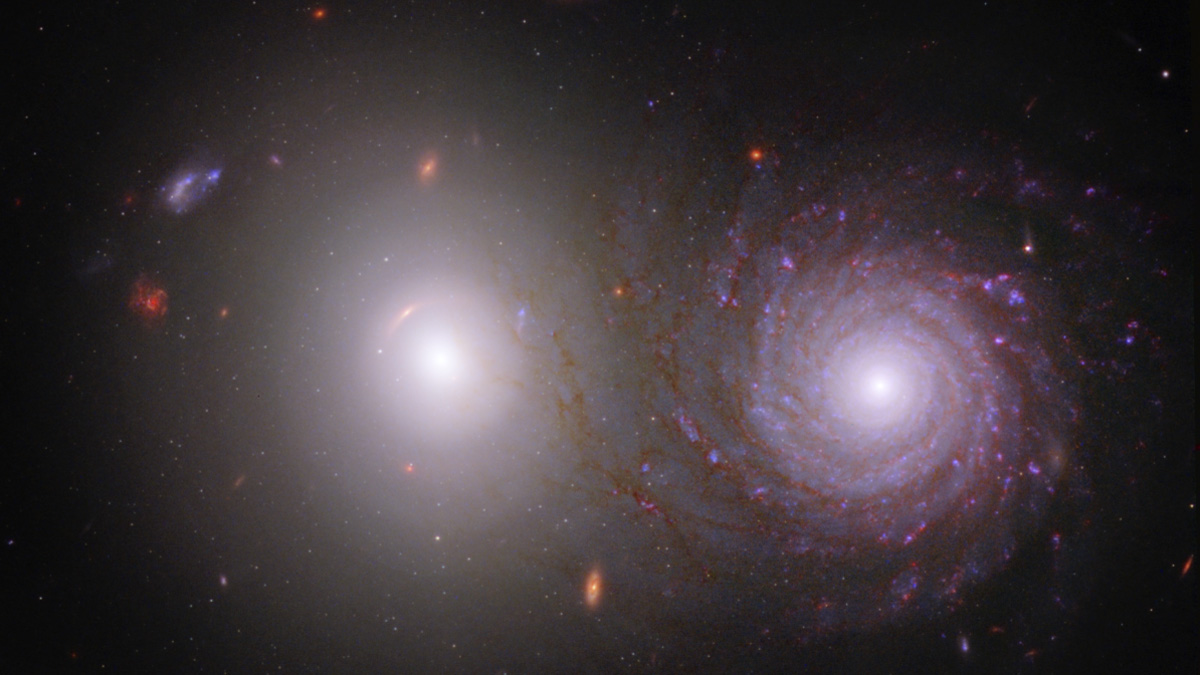
James Webb Space Telescope sees same supernova three times over
A stunning new image from the James Webb Space Telescope shows a galaxy with a supernova, three times over. That phenomenon is due to light bending from the massive gravitational influence of a foreground galactic cluster, as predicted by Albert Einstein. The lensing object is the galactic cluster RX J2129, located around 3.2 billion light-years away in the constellation Aquarius.
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope 'sees triple' with help from Einstein (photos)
Webb's second instrument glitch
The James Webb Space Telescope has experienced its second instrument glitch. The observatory's Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS) instrument experienced a glitch on Jan. 15 and has been unavailable for science operations since, according to a NASA statement. Read more>
In the mean time, scientists have unveiled a host of new findings from the observatory, in particular in conjunction with this month's 241st meeting of the American Astronomical Society held in Seattle and online. Here's an array of highlights from JWST:
Early James Webb Space Telescope findings take center stage at key astronomy conference
James Webb Space Telescope notches 1st rocky planet confirmation
James Webb Space Telescope uncovers starbirth clues at 'cosmic noon' for 33,000 young stars
James Webb Space Telescope discovers coldest interstellar ice ever seen
James Webb Space Telescope discovers water ice at ringed asteroid Chariklo 'by remarkable luck'
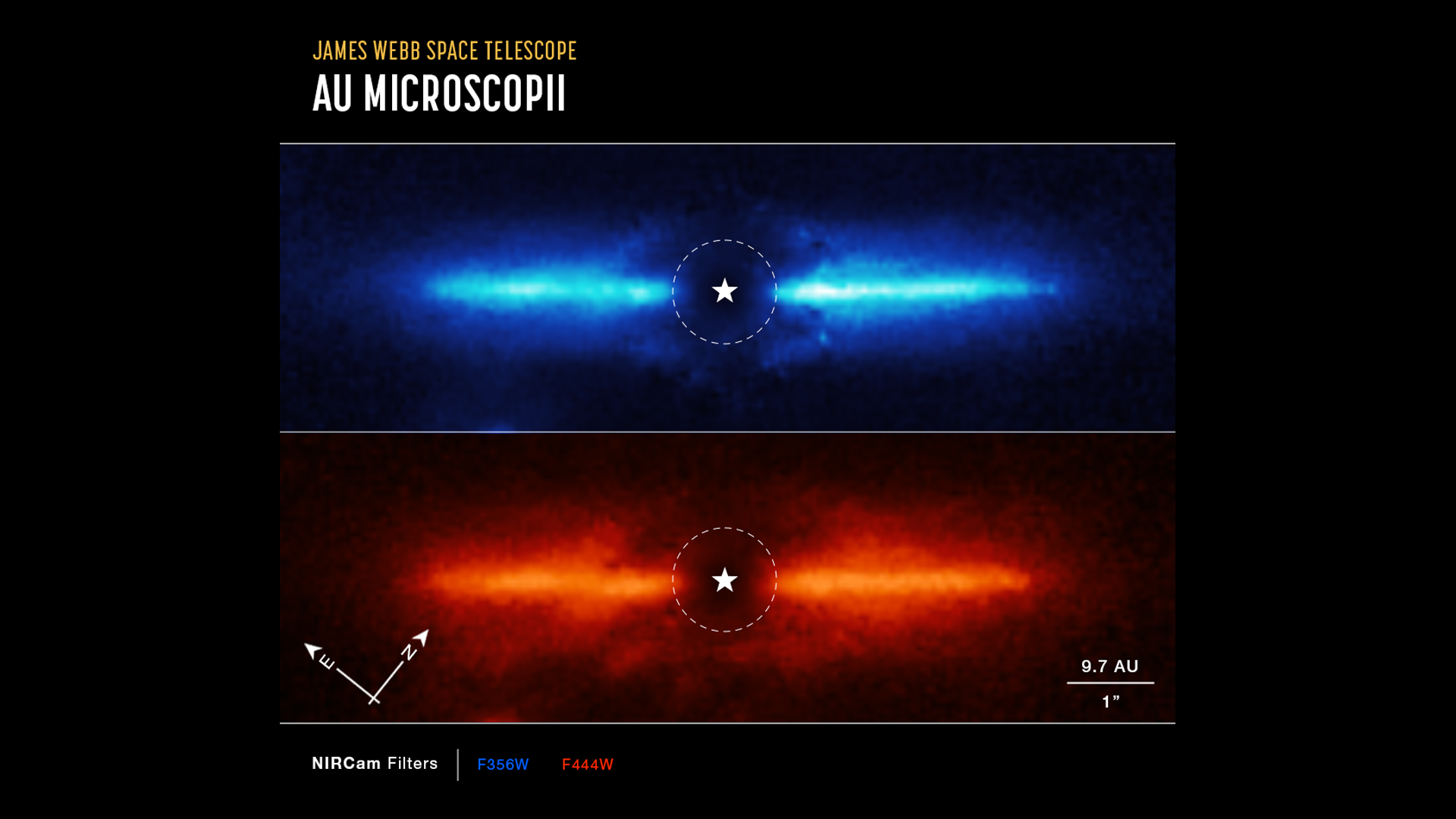
Webb studies a planet-forming disk
The James Webb Space Telescope's near-infrared camera (NIRCam) probed a planet-forming disk around a red dwarf star known as AU Microscopii or AU Mic. The study has implications for studies of future planet-friendly zones, according to astronomers.
James Webb Space Telescope recovers from glitch
The James Webb Space Telescope missed a few days' worth of science this month, NASA has announced.
The observatory's glitch began on Dec. 7 when a software hiccup in the spacecraft's attitude control system, which keeps the spacecraft properly oriented, sent the full observatory into safe mode. Between Dec. 7 and Dec. 20, when normal observations resumed, the telescope missed a few days' worth of science work that will be rescheduled, according to the statement.
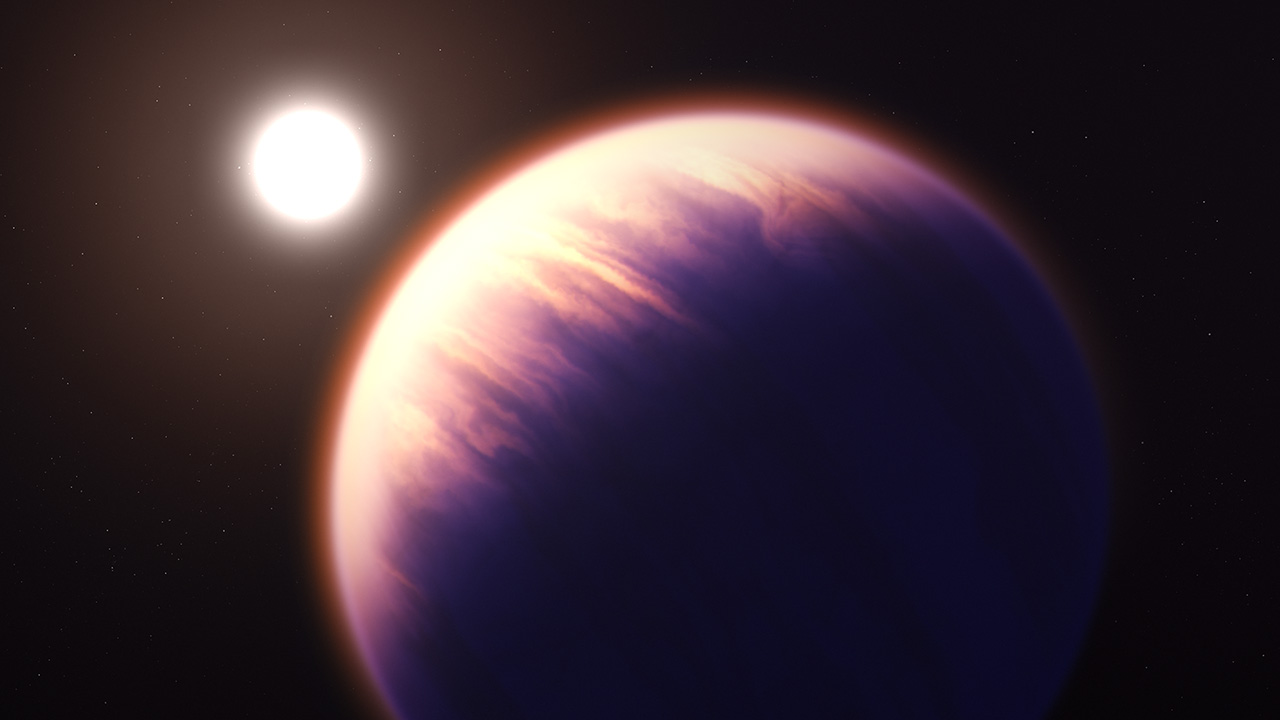
James Webb Space Telescope showcases new detail in alien planet's atmosphere
The James Webb Space Telescope (Webb or JWST) has even more detail about the exoplanet WASP-39b after finding carbon dioxide in its atmosphere in August. New details showcased in studies in November, based on looking at the planet's atmosphere, are telling astronomers more about its formation history.
"These early observations are a harbinger of more amazing science to come with JWST," Laura Kreidberg, director of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) in Germany who was involved in the observations, said in a statement. "We put the telescope through its paces to test the performance, and it was nearly flawless — even better than we hoped."
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope reveals alien planet's atmosphere like never before
James Webb Space Telescope provides rich view of early galaxies
The James Webb Space Telescope is already providing detailed and unique observations concerning galaxies in its first five months of operations, according to astronomers. "We're really on track to realizing the dream of understanding galaxies at the earliest times," Garth Illingworth, an astronomer at the University of California, Santa Cruz, said during a NASA news conference held Thursday (Nov. 17) dedicated to early science results from the new observatory.
Managers have elected to tweak the operations of the telescope to avoid micrometeoroids, as 14 dust-sized specks smacked its 21-foot (6.5-meter) golden mirror in recent months. The view Webb provides is still pristine, but personnel will make the changes to avoid "micrometeoroid avoidance zones," NASA officials said on Monday (Nov. 15).
Webb's supercold camera back to normal operations
The James Webb Space Telescope is back to standard science operations after losing one of its 17 observation modes in August.
Mission personnel paused use of one observing mode on Aug. 24 after the telescope's supercold Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) began showing signs of friction in a grating wheel that allows astronomers to choose which wavelength of light to observe.
After two months of investigation, the Webb team designed new guidelines for using the mechanism that should eliminate the friction. Test observations with the new approach on Nov. 2 cleared the way for the instrument to resume work, according to a statement from the Space Telescope Science Institute, which operates the observatory.
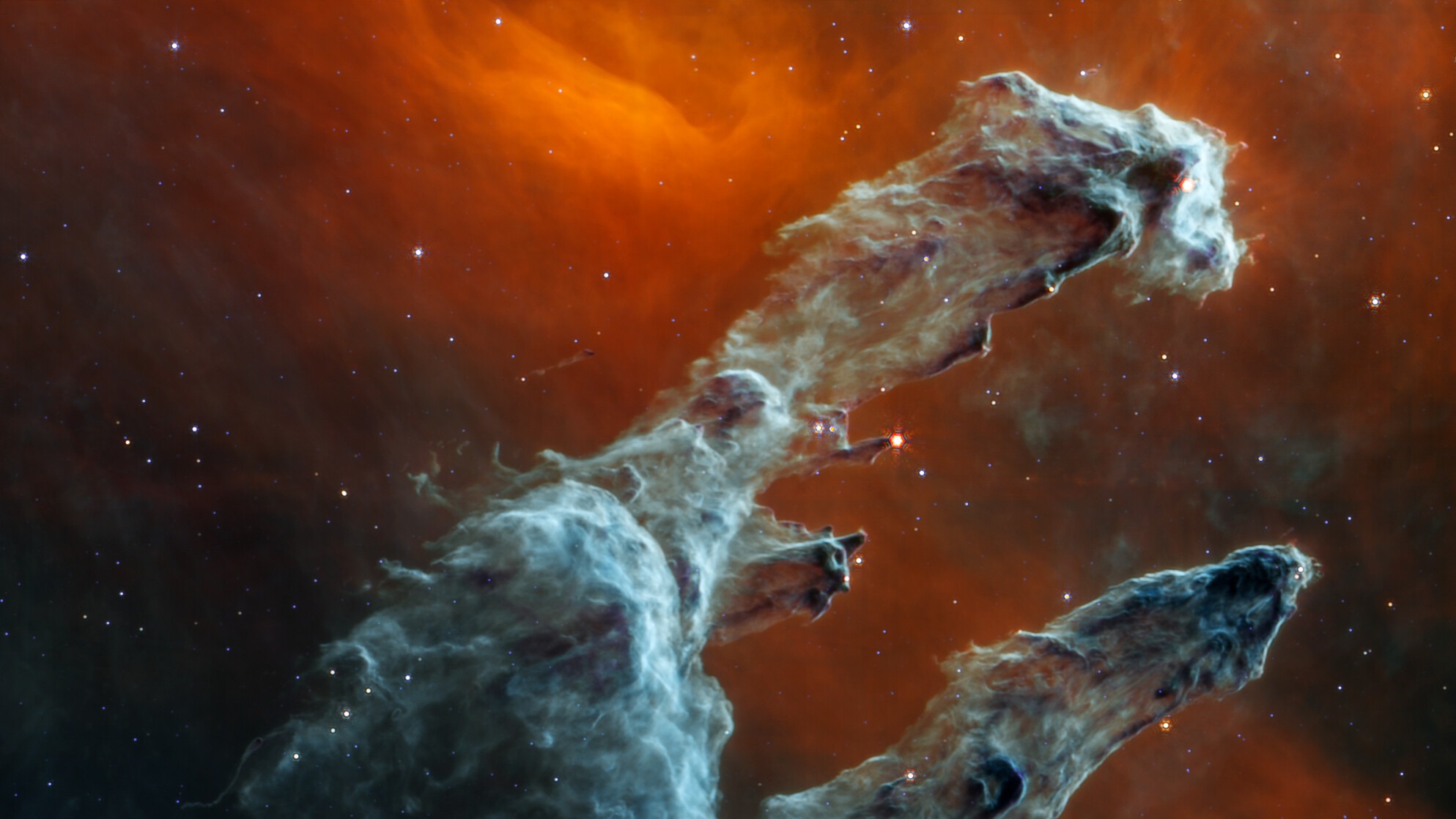
A web of Webb observations spin out before Halloween
The James Webb Space Telescope released yet another spooky picture of the Pillars of Creation amid a creepy set of fresh imagery. Lurking deep in the mid-infrared, dust clouds loom in blue in front of a reddish background, and the stars are blotted out. The new mid-infrared image came while scientists are still buzzing from another Pillars view in different wavelengths taken only the week before.
Other creepy tricks in the telescope's roster this week include catching a galaxy bending light and revealing a mystery, as scientists aren't sure if they are seeing two galaxies or two star cluster in behind. Hidden star formation also came forth in a galaxy collision imaged in unprecedented detail.
James Webb Space Telescope still surpassing expectations
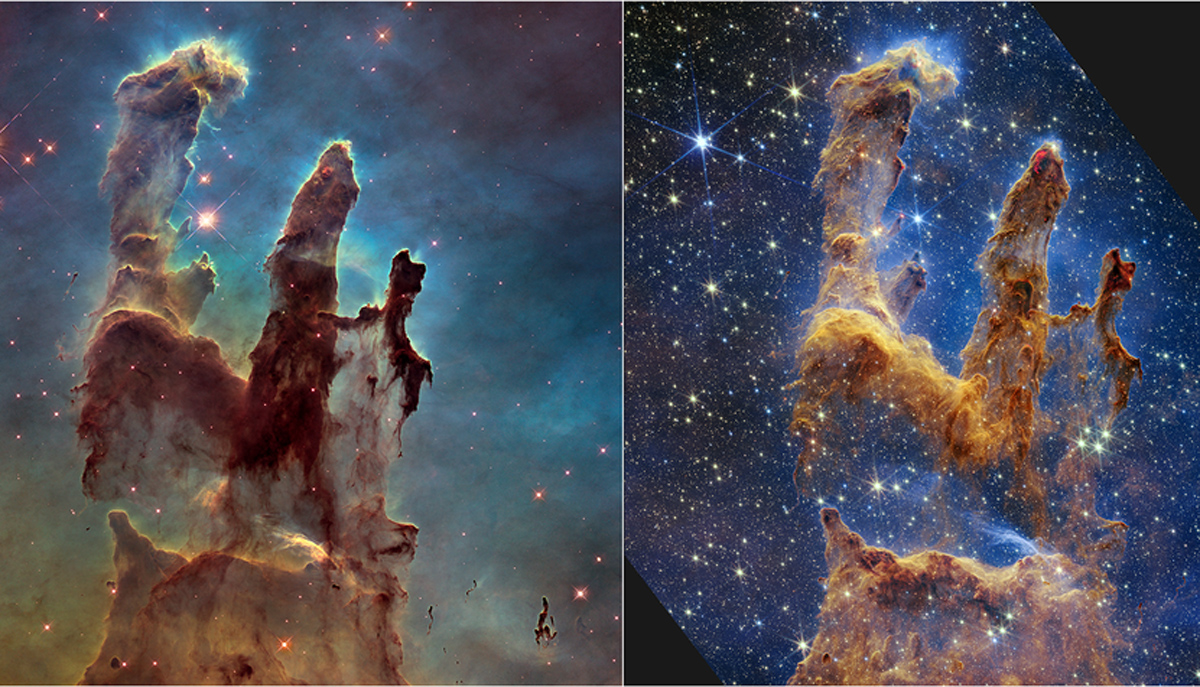

The James Webb Space Telescope has been in space for nearly 10 months and, despite a micrometeroid issue and a glitch, the telescope's performance is surpassing expectations, mission officials said in a new update today (Oct. 20).
That's good news for astronomers given the impressive observations coming from Webb, including a new view released Wednesday (Oct. 19) of the iconic Pillars of Creation first made famous by the observatory's predecessor: the Hubble Space Telescope.
Bizarre rings spotted by James Webb Space Telescope
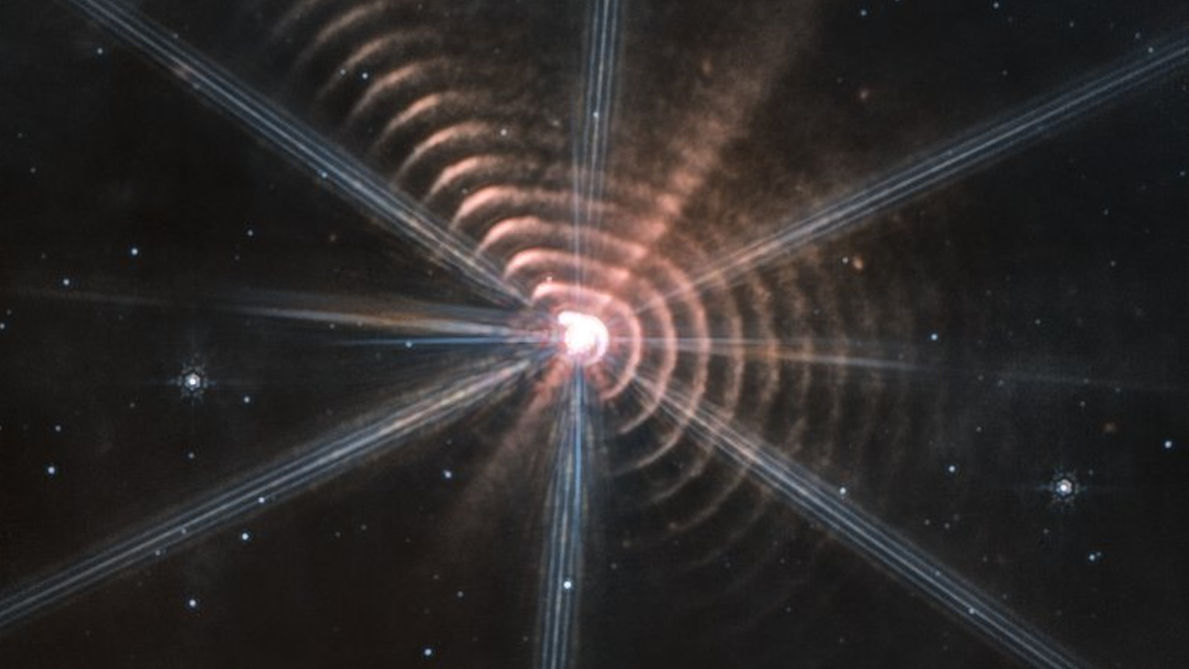

The James Webb Space Telescope spotted a set of concentric angular rings around a giant, distant star in September. A pair of new studies shows the first visible evidence of starlight pushing dust around, and exhibits the strange environment of the star WR140, which is in fact a system of two stars that orbit each other.
Scientists also modeled the molten surfaces of 16 lava world types in the laboratory, as they seek to create a database of rocky exoplanets to help Webb better understand and identify alien worlds.
James Webb Space Telescope and Hubble team up for dust examination
In a striking image, Astronomers captured two galaxies (under the common name VV 191) that appear close to each other, combining the infrared measurements taken by the James Webb Space Telescope with the visible and ultraviolet light imaging done by the Hubble Space Telescope.
In another team-up investigation, NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory are demonstrating how its X-ray observations are providing new perspective for Webb images. In fact, Webb may be at its most effective when it works with other telescopes.
Wait begins for James Webb Space Telescope DART footage
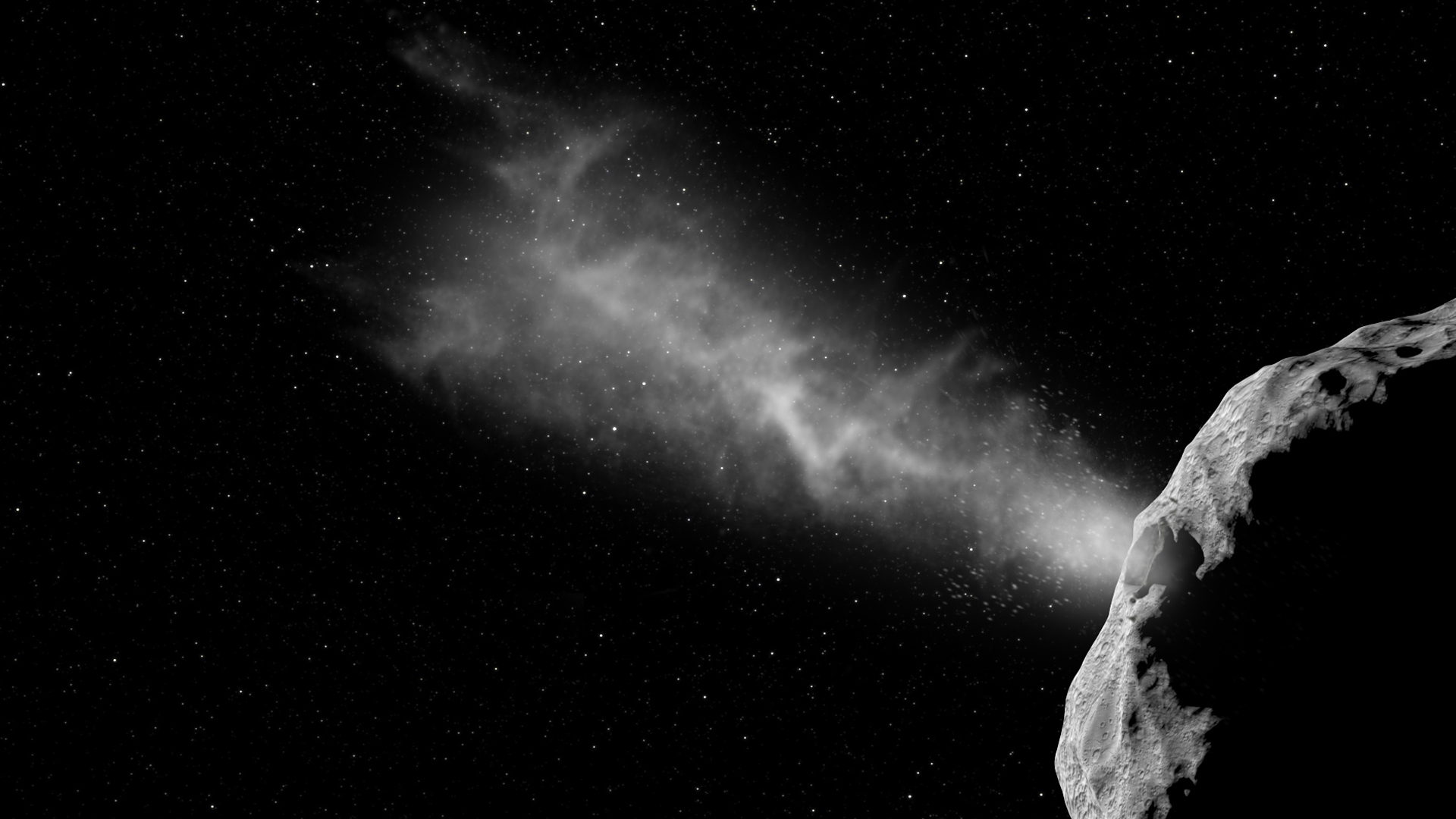

NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission slammed into an asteroid moonlet Monday (Sept. 26) to test a planetary defense technique that could redirect a future large asteroid on a collision course with Earth. The James Webb Space Telescope was among the observatories watching, and footage will flow back from it in the coming weeks.
Scientists have also been talking about Webb's ability to peer much further back in time, very close to the formation of the universe some 13.7 billion years ago. The telescope's infrared light is perfect for examining ancient stars and galaxies.
James Webb Space Telescope's ultracold camera has a glitch
The James Webb Space Telescope's Mid-Infrared Instrument's (MIRI) grating wheel is experiencing a problem affecting some observations. The wheel, which allows selection between light wavelengths, is used in only one of MIRI's four observation modes. You can read more about the glitch and NASA's efforts for a deep-space fix here.
Webb's past observations have delivered a huge range of science in recent days. An incredible image of Neptune's rings and moons has been hailed as one of the best of a generation. Fresh atmospheric images of Mars are delivering new insights, and scientists are gaining information about exoplanets after Webb's alien planet investigation.
Astronomers may be getting Webb Space Telescope exoplanet measurements wrong

Astronomers may be misinterpreting James Webb Space Telescope's measurements of exoplanet atmospheres "by an order of magnitude", a new study suggests.
The telescope's ambitious mission in deep space includes taking measurements of the chemical compositions of the intriguing stars, galaxies and nebulas it sees, like these fresh images of baby stars in the Orion Nebula released earlier this week.
To assist with exoplanet work, telescope scientists use complex models for interpretation. But a new study by researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), found that these models lack the accuracy to showcase Webb's nuances.
Full story: Astronomers may be getting Webb Space Telescope exoplanet measurements wrong
Webb finds an exoplanet and observes a nebula
The James Webb Space Telescope's discoveries continue to span the universe.
The deep-space observatory observed an exoplanet with evidence of silicate-rich clouds; the brown dwarf is nearly 20 times the size of Jupiter. The brown dwarf is called VHS 1256 b and orbits two small red dwarf stars, 72 light-years from Earth.
Webb's sensitive instruments also revealed unprecedented detail in a gas cloud called Doradus 30, initially nicknamed Tarantula for its spider-like appearance. The Tarantula Nebula is located 161,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud and is the brightest star-forming region in our neighborhood aside from our own Milky Way.
Meanwhile, astronomers are fighting disinformation and pseudoscience suggesting that Webb disproved the Big Bang. Spoiler alert: not correct.
James Webb Space Telescope snags first direct image of planet, mysterious rings
Only weeks into its operational phase, the James Webb Space Telescope continues to make history.
The deep-space telescope caught its first direct image of another alien world. The planet is roughly 385 light-years from Earth and looks like a splotch beside the store HIP 65426. Webb saw the exoplanet using its Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) and the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), which each look at different wavelengths of infrared light.
Scientists are also trying to figure out strange concentric rings around a faraway star, called WR140. The image was released on Twitter by citizen scientist Judy Schmidt. The ripples around the star are not perfectly circular and are puzzling to scientists.
New gems from the James Webb Space Telescope
James Webb Space Telescope data continues to stun.
In an early science result, astronomers used the observatory to detect carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. It's the first time scientists have confirmed that particular chemical's presence.
And multimedia whizzes have begun digging into imagery from the observatory. First, a new video compares views of the "Phantom Galaxy" from JWST and the Hubble Space Telescope. Then, experts have sonified the iconic Carina Nebula photo from the observatory's first science-quality images, turning it into music.
Jupiter's auroras and early galaxies glow in Webb imagery
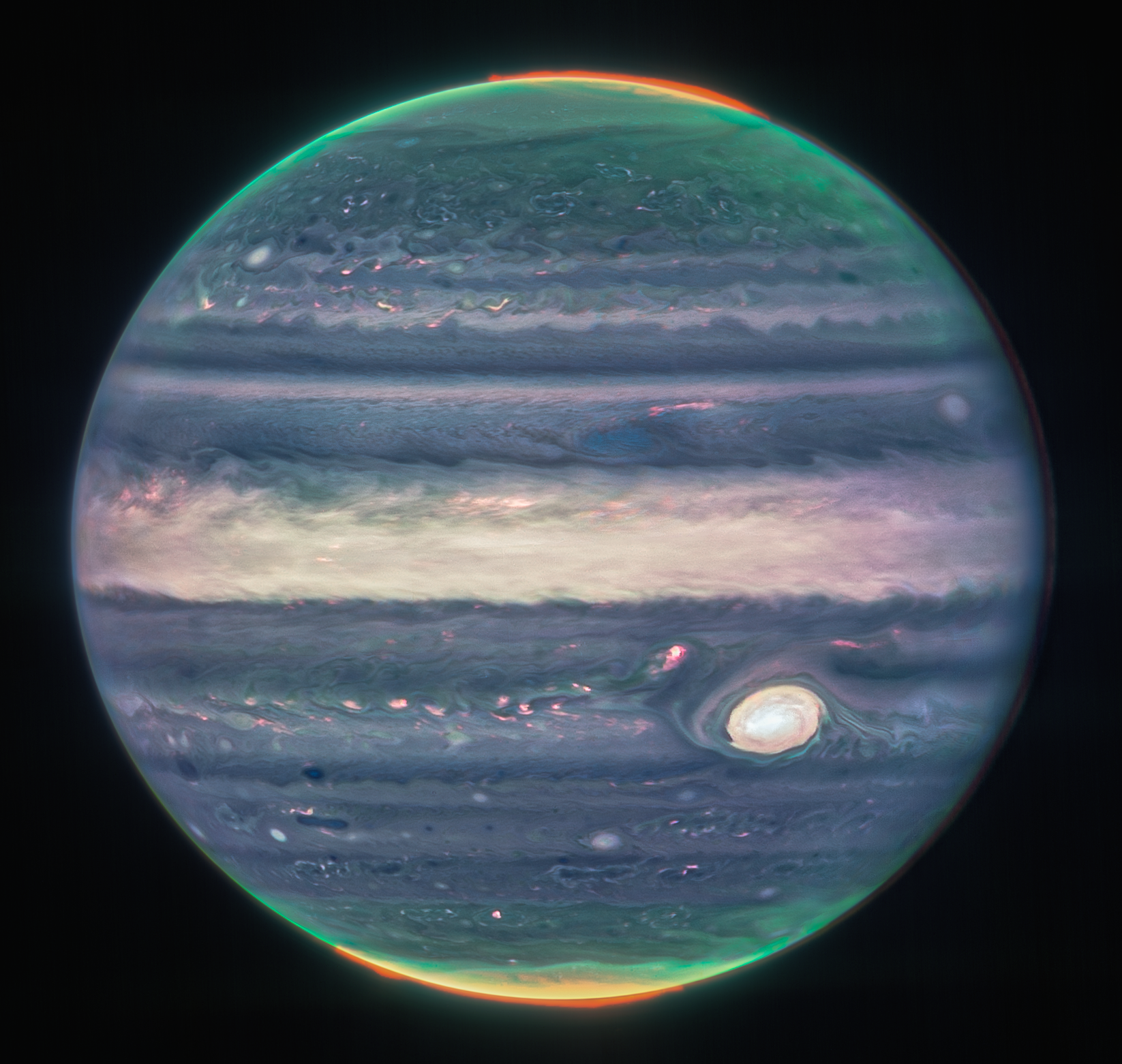

Incredible images of Jupiter and its auroras shine in fresh new images from the James Webb Space Telescope created by citizen scientist Judy Schmidt, based on Webb data. By the way, if you want to create Webb images of your own, we have an up-to-date editing guide with Schmidt that discusses the tools, techniques and how to make the right choices. You can do all of this for free using a generic computer.
Meanwhile, scientists released a gobsmacking new mosaic image from Webb showcasing distant galaxies whose light shifted into infrared (from visible) light. Coming from an era nicknamed Epoch 1, this image comes from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science Survey (CEERS) and will likely push forward more study.
JWST investigates iron rains on hot Jupiter
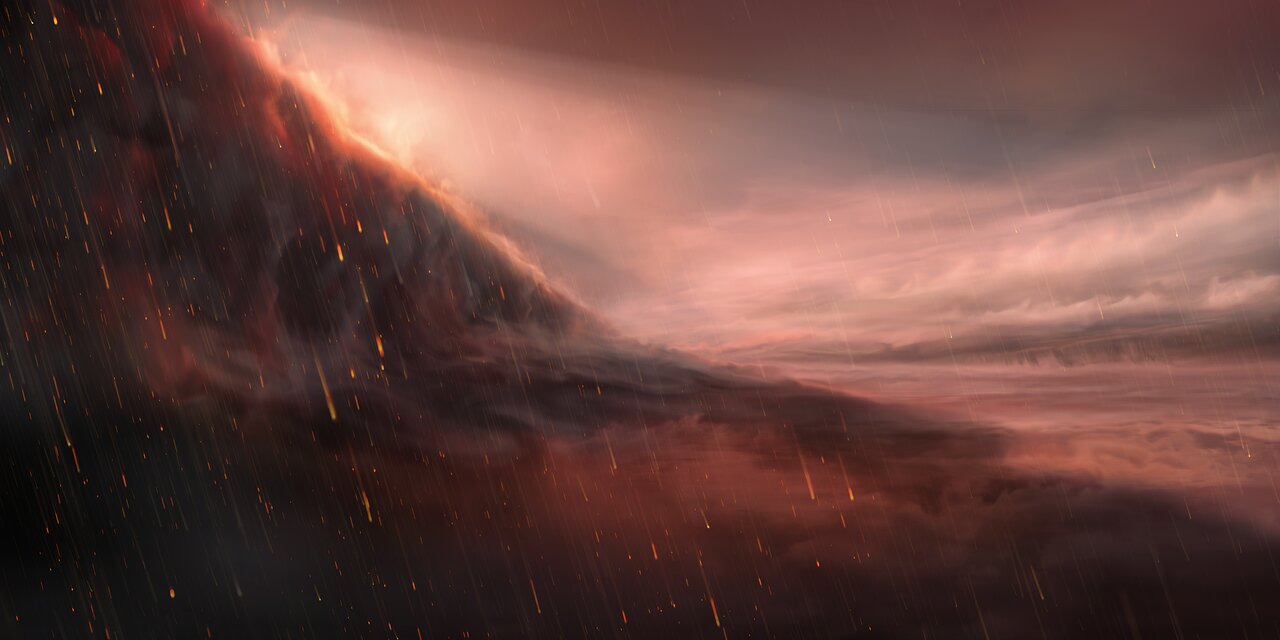

Exoplanets will be among the pioneering investigations of the James Webb Space Telescope. Scientists hope that the telescope will shed light on hot Jupiter exoplanet atmospheres with molten rain, hurling vaporized rock or crystals from up high.
"On Earth, a lot of these minerals are jewels," Tiffany Kataria, who is an exoplanetary scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said in a statement. "A geologist would study them as rocks on Earth, but they can form clouds on exoplanets. That's pretty wild."
Read more: James Webb Space Telescope will seek clouds of vaporized gems on exoplanets

Elizabeth Howell, Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before that, since 2012. Elizabeth's on-site reporting includes two human spaceflight launches from Kazakhstan, three space shuttle missions in Florida, and embedded reporting from a simulated Mars mission in Utah.
James Webb Space Telescope stunning video and engineering solutions
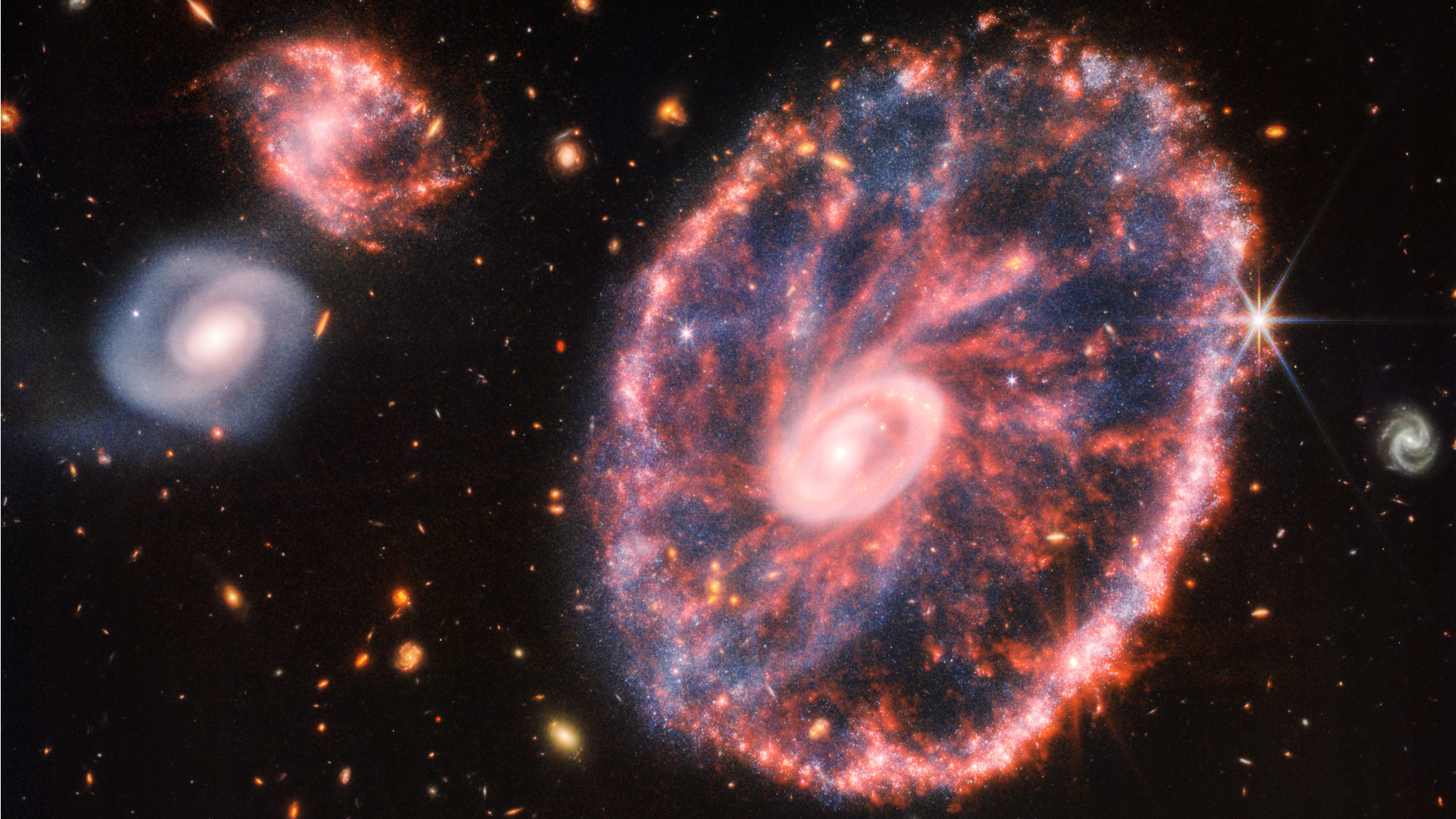
Whip through the universe on a new video tour by NASA's deep-space telescope. The James Webb Space Telescope collaboration released a "Star Wars" video tour zooming in to land upon a spectacular galaxy, called the Cartwheel Galaxy. It's an intriguing look at starbirth, including near a supermassive black hole.
Meanwhile, engineers talked about the new technologies they used to build Webb to test out things never done in space before. Northrop Grumman (the prime contractor) and others did groundbreaking engineering to get the telescope working in deep space.
James Webb Space Telescope 'photo' just a chorizo
A physicist pulled a prank on Twitter last week showcasing a photo from the James Webb Space Telescope, which ended up being a chorizo.
The scientist Étienne Klein, director of France's Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission, shared the purported James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) photo on July 31. But after Klein's photo went viral, he clarified the image was not from Webb. Instead, it was a slice of the Spanish sausage chorizo.
Read more: Scientist admits 'space telescope' photo is actually chorizo in tasty Twitter prank
James Webb Space Telescope breaking records again

The James Webb Space Telescope has just barely started operations, but is breaking records and performing intriguing observations in its first few weeks.
One week after the James Webb Space Telescope released the first science images, astronomers detected galaxies at redshift 13, equating to about 300 million years after the Big Bang. Not long after, intriguing new results suggests astronomers are blasting past that metric with possible detections up to redshift 20. If confirmed, those galaxies are quite early, as they were in existence just 200 million years after the Big Bang.
Webb then turned its attention to the most distant star, called Earendel, after a character in J.R.R. Tolkien's "Lord of the Rings" prequel "The Silmarillion." The star's light took about 12.9 billion years to reach Earth and is now visible in a bit more detail than previous imaging from a Hubble Space Telescope deep field image.
Webb also observed a wheel-shaped galaxy, called the Cartwheel, showing unprecedented detail in the galaxy's structure. Using infrared light, Webb detected individual stars within the galaxy's star-forming regions, and more young star clusters surrounding the galaxy's central supermassive black hole. These zones are full of dust and best visible in infrared light, which can peer through that.
The science scramble is in full swing!
Just weeks into its tenure, the James Webb Space Telescope is keeping scientists and space fans busy.
The astronomy community's preprint server, arXiv.org, has seen a host of new papers analyzing JWST data. One particularly hot topic is the search for ever-more-distant galaxies: The observatory is now beating its own records, spotting galaxies that we may be seeing just 200 to 300 million years after the Big Bang.
Other scientists are looking ahead to what the observatory will be able to uncover about supermassive black holes.
Meanwhile, amateur image processors are digging into early observations, turning data into works of art, like a spiraling galaxy that looks like a wormhole. And for those more inclined to snail mail than high-tech image analysis, the U.S. Postal Service has a stellar new stamp on offer.
Breaking records already!
Scientists are already making record-breaking discoveries in data from the James Webb Space Telescope. For example, astronomers have spotted two galaxies that may be the most distant ever seen. If the analysis is confirmed, we are seeing the galaxies as they existed 300 to 400 million years after the Big Bang. Read more>
Micrometeoroid aftermath
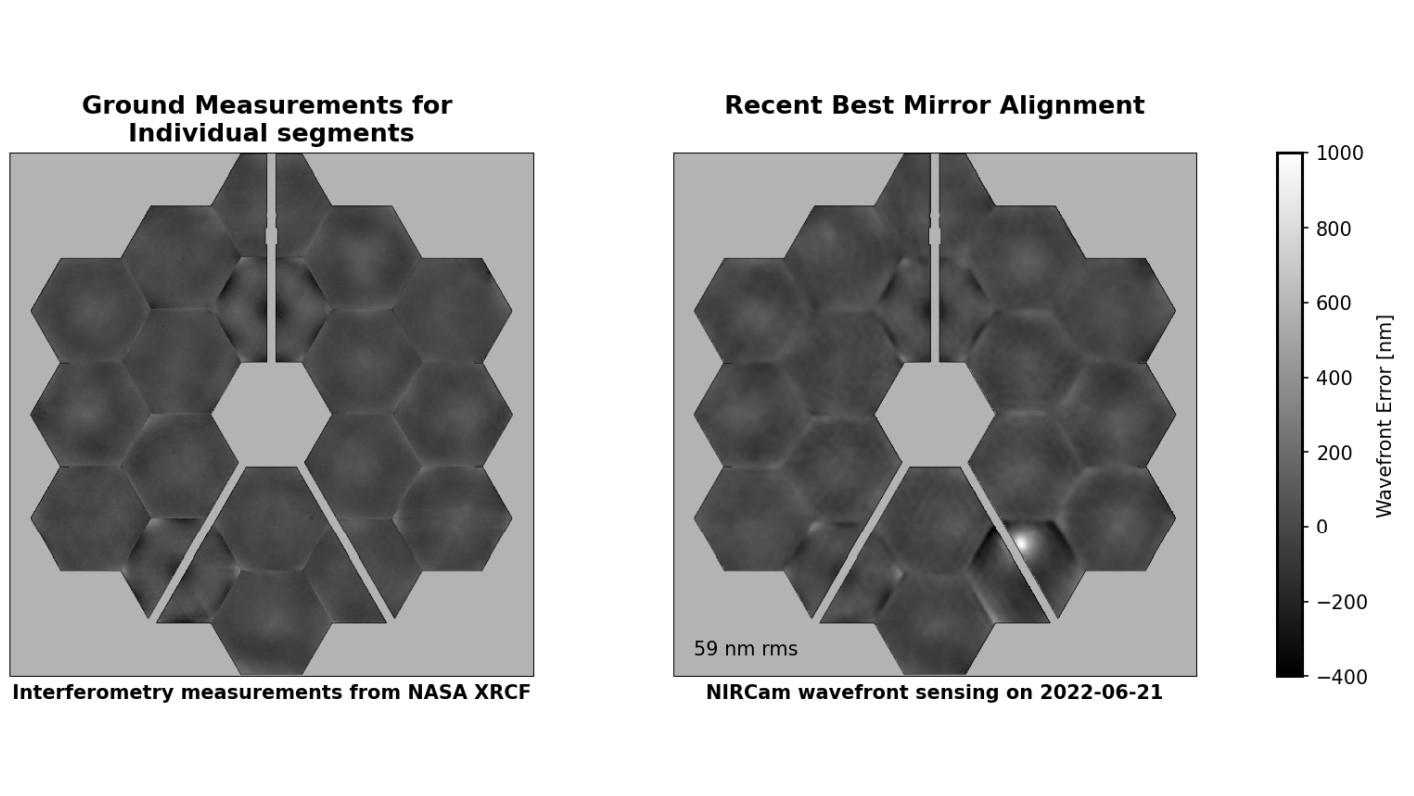
A report from the James Webb Space Telescope team published on July 12 includes details about the unexpectedly large micrometeoroid impact the observatory experienced in late May. Of particular interest is an image showing the alignment error remaining after engineering teams adjusted the mirror to compensate. Read more>
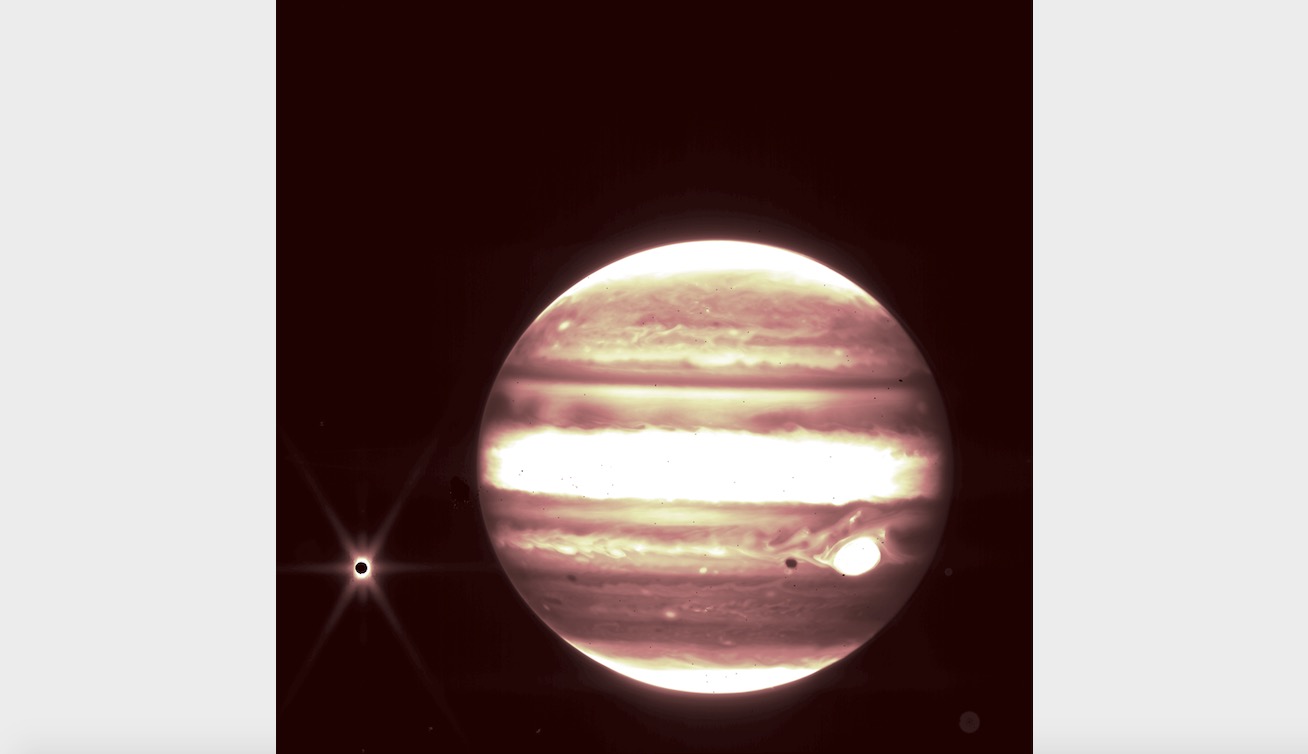
Hello, Jupiter!
On Thursday (July 14), NASA released its first images of solar system targets captured by the James Webb Space Telescope. The images show Jupiter, as well as some of its moons and rings.
"I couldn't believe that we saw everything so clearly, and how bright they were," Stefanie Milam, Webb's deputy project scientist for planetary science based at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, said in a statement. "It's really exciting to think of the capability and opportunity that we have for observing these kinds of objects in our solar system."
A first-hand account of Tuesday's big reveal
While the rest of us settled for watching from home, a lucky audience crowded into an auditorium in Greenbelt, Maryland, to experience the release of the James Webb Space Telescope's first science-quality images first-hand. Space.com Contributor Rebecca Sohn was one of those attendees, and she shared what it was like to be at the center of the universe. Read her account>
What's next for Webb?
With the first stunning images unveiled, what comes next for the James Webb Space Telescope? Scientists have promised that more observations will pour out from the mission this week, including the first images of Jupiter, due on Thursday (July 14).
Meanwhile, the telescope is digging into both its early science suite and its first year projects. But scientists are already looking ahead the observatory's second year, which begins next summer, since the telescope is out-performing the expectations researchers planned this year's work around. Read more>
And in case you're catching up, here's all our coverage so far of yesterday's image release:
Behold! The James Webb Space Telescope's stunning 1st science images are here.>
Gallery: James Webb Space Telescope's 1st photos>
1st James Webb Space Telescope images thrill astronauts, celebs and more>
Science and emotion meet as astronomers respond to 1st images from James Webb Space Telescope>
Webb images on the big screens
Lucky passers-by were treated to quite the spectacle when the first scientific images of the James Webb Space Telescope shone amid the bright lights of Times Square, New York, and Piccadilly Circus, London, on Tuesday (July 12).
The stunning images of Stephan's Quintet, the striking Southern Ring Nebula (seen here), the Cosmic Cliffs in the Carina Nebula and the deep field image that was unveiled on Monday (July 11) by President Joe Biden at the White House adorned the streets, gifting city-dwellers a unique view of the cosmos.
Google marks the occasion
Google gets in on the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) action with an adorable Google Doodle celebrating the space observatory's first images.
The doodle shows Webb snapping photos of the Stephan's Quintet, the striking Southern Ring Nebula, the Cosmic Cliffs in the Carina Nebula and the deep field image that was unveiled yesterday by President Joe Biden, Vice President Kamala Harris and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson at the White House.
Full coverage of Webb's first images
We're enjoying a brief pause in the excitement as NASA prepares for a news conference beginning at 12:30 p.m. EDT (1630 GMT), during which scientists and officials will answer more questions about the newly released images. While we wait, check out our full coverage of today's reveals! Read more>
Last but not least!
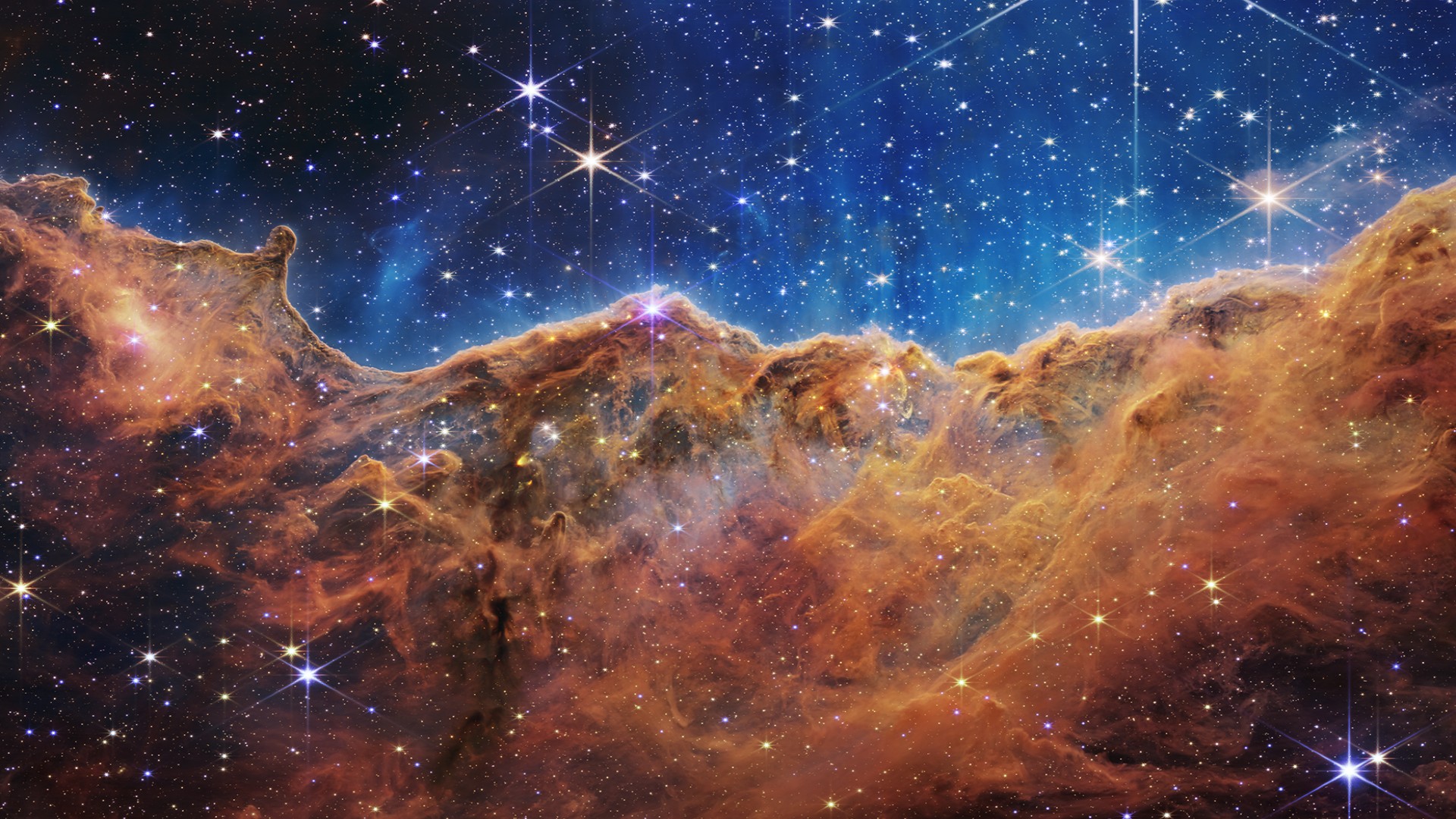
Finally, NASA unveiled a brand new image of the Carina Nebula, a distant, massive cloud of gas and dust where stars are both forming and dying.
"This stunning vista of the cosmic cliff of the Carina Nebula reveals new details about this cosmic nursery," Amber Straughn, an astrophysicist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, said. "There's so much going on here, it's so beautiful."
Stephan's Quintet
Next up from the live reveal: stunning views of what scientists call Stephan's Quintet, a collection of five galaxies, as seen in both near- and mid-infrared.
"It's just the beginning," Mark McCraughrean, an astronomer at the European Space Agency, said. "We're ready now, this telescope is working fantastically well."
Check out the Southern Ring!
"When we saw the first color images, we knew that we had a winner," Karl Gordon, an astronomer at Space Telescope Science Institute, said of the science team's earliest looks at the James Webb Space Telescope's data. Here, JWST's talents are applied to the Southern Ring nebula.
See inside an exoplanet's atmosphere
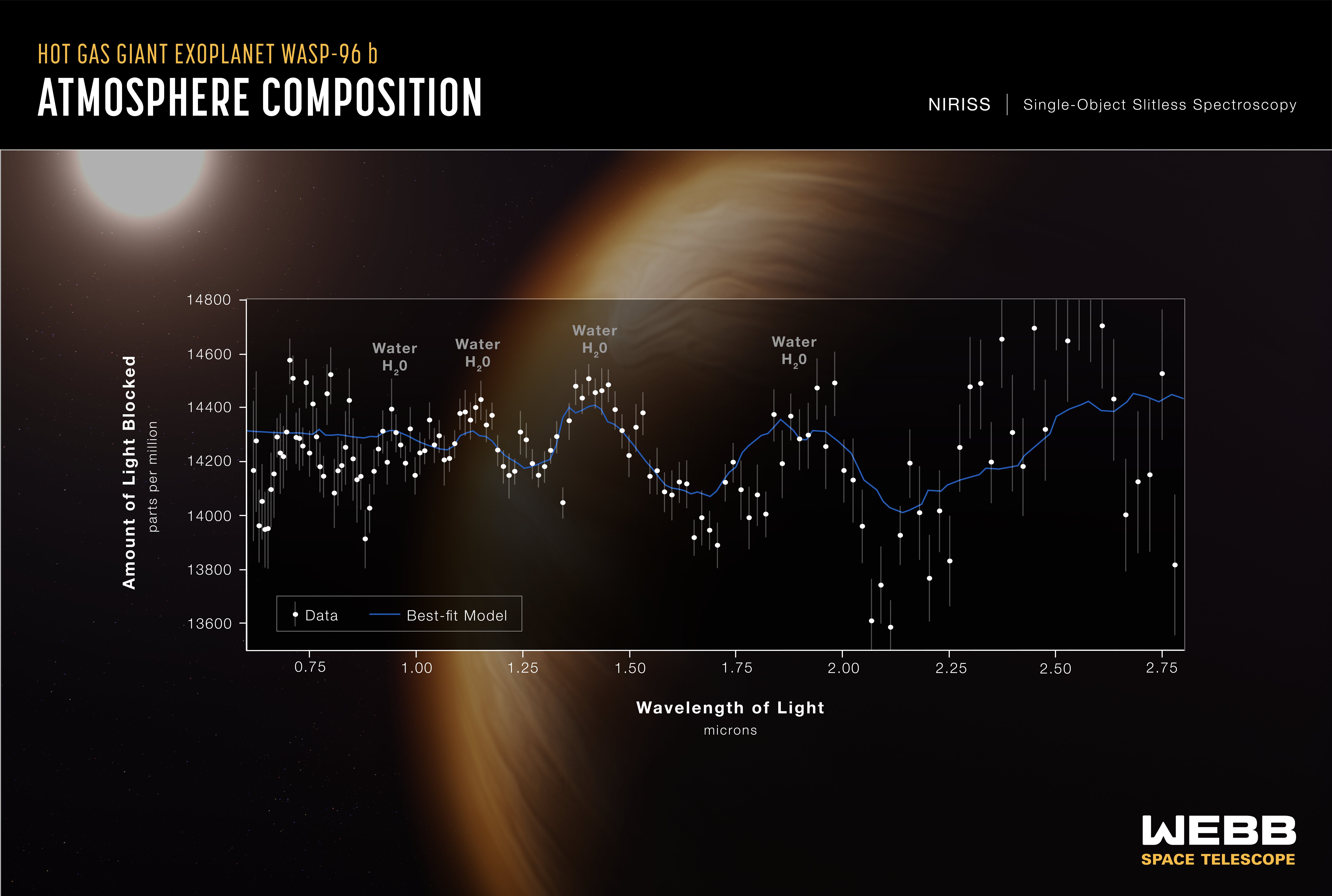
Image number 1 of today's reveals shows the atmosphere of a hot exoplanet called WASP-96 b. Read more here>
Starting soon! Here's the schedule for the day.
Today's the day space fans have been waiting for. Here's what to expect as NASA unveils the first science-quality images from the James Webb Space Telescope:
9:45 a.m. EDT (1345 GMT): Opening remarks from NASA leadership.
10:30 a.m. EDT (1430 GMT): Individual release of each new image.
12:30 p.m. EDT (1630 GMT): NASA officials and scientists will hold a news conference.
You can watch all of these events here at Space.com, and we'll be sharing live updates throughout the day.
The big reveal of James Webb Space Telescope images is today!
An avalanche of images from the magnificent James Webb Space Telescope is set to be unleashed onto the world today after a taster glimpse into the deepest universe was unveiled on Monday (July 11) by U.S. President Joe Biden.
Scientists and space enthusiasts alike have been virtually star-struck by Webb's sharp gaze and the plethora of distant objects the telescope revealed. But the best is yet to come during the official image release that is set to commence at 10:30 a.m. EDT (1430 GMT) today (July 12), which you can watch here at Space.com courtesy of NASA.
The space agency has previously hinted which celestial objects space fans can look forward to seeing in these images. On Friday (July 8), the agency announced that the reveal will include views of the Carina and Southern Ring nebulas, as well as Stephan's Quintet of closely packed galaxies. Also on the agenda is observations of an exoplanet called WASP-96 b, although JWST won't be offering an image of the distant world. Instead, scientists will share a spectrum of the planet, which splits light by wavelength, offering insight into the chemical composition.
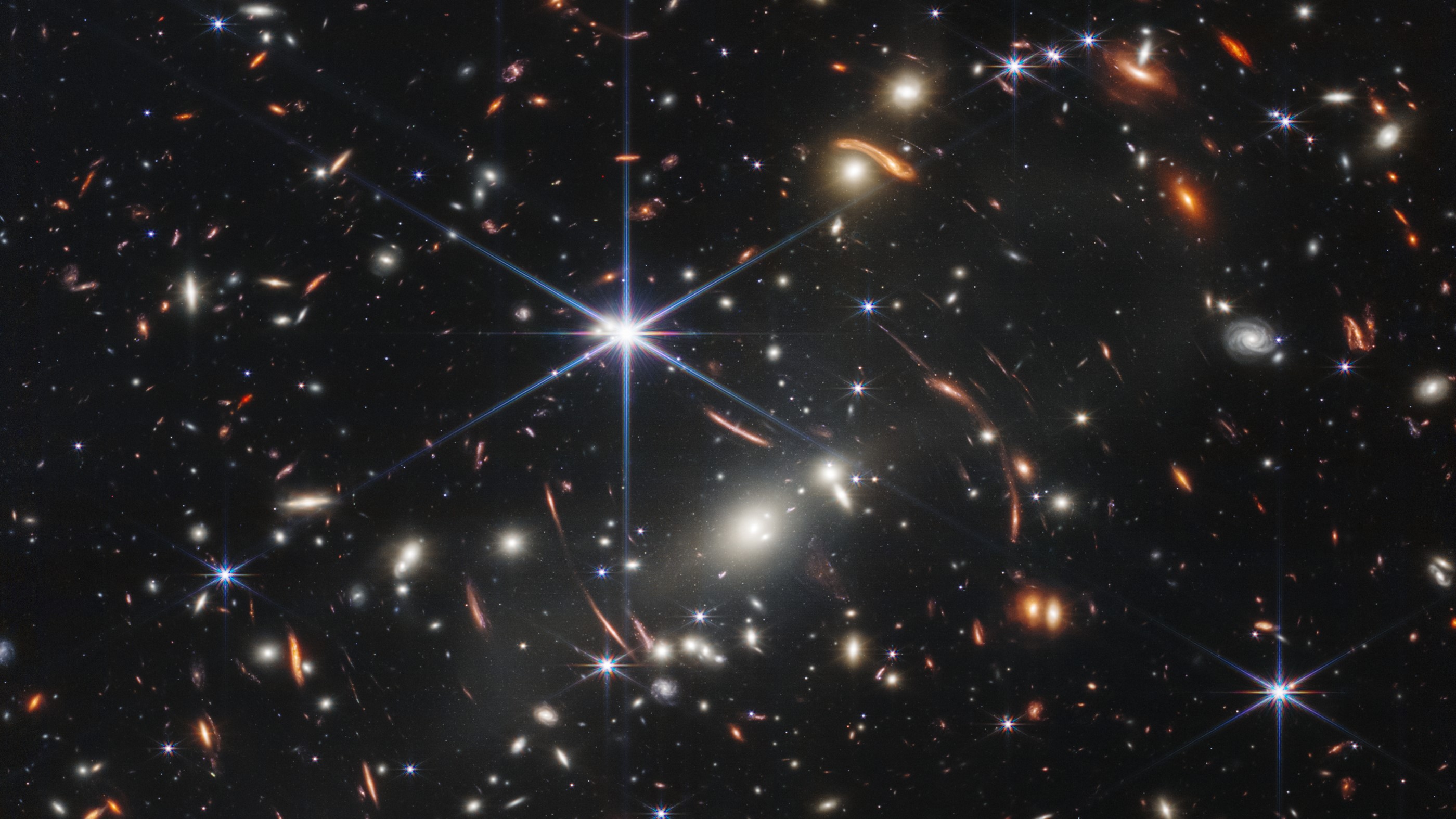
President Biden unveils JWST's 1st science image
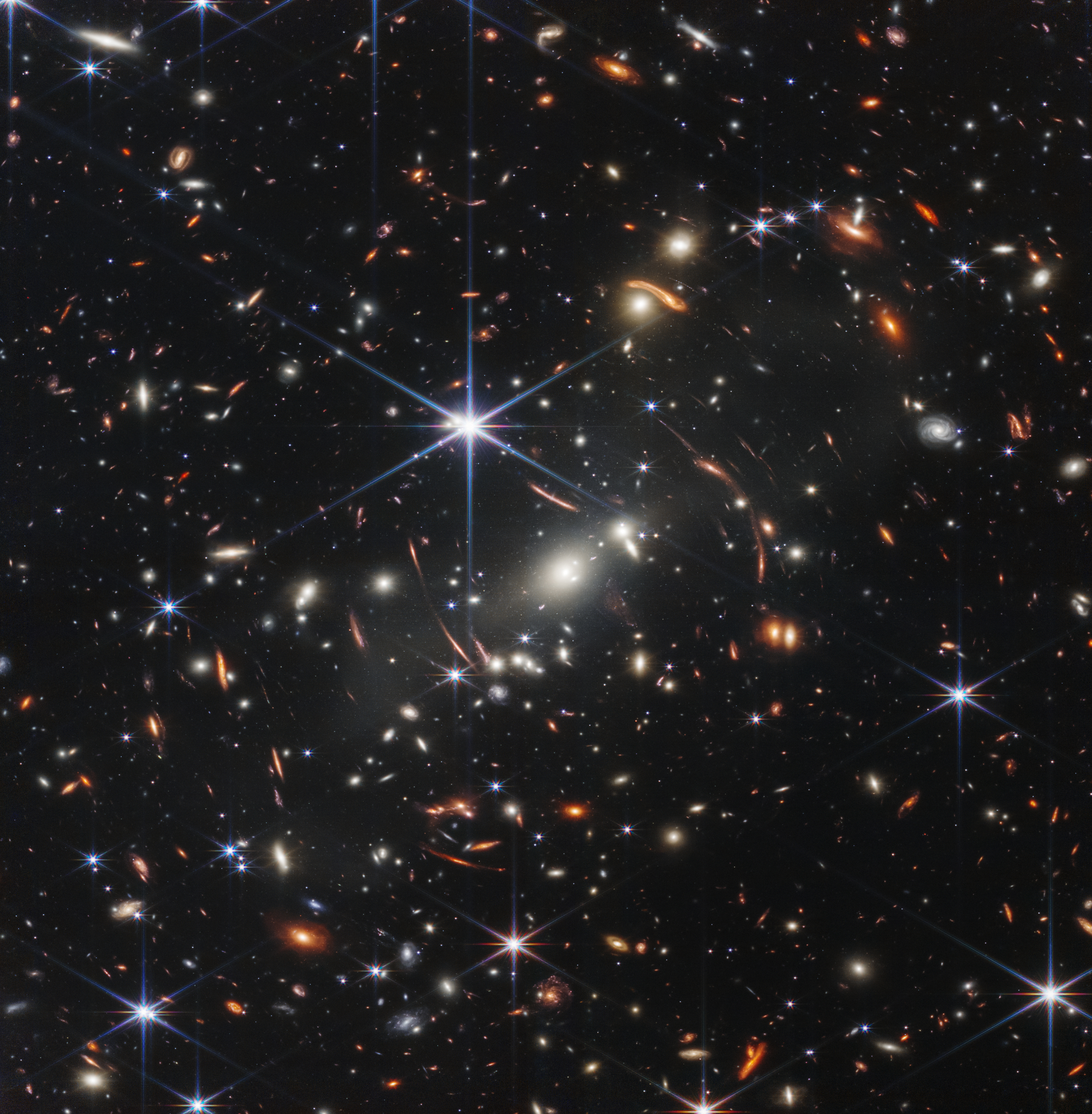

Today (July 11), U.S. President Joe Biden and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson revealed the first science-quality image taken by the agency's $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope. The shot, known as Webb's First Deep Field, shows an amazingly sharp ultra-deep view of the universe, capturing a galaxy cluster called SMACS 0723 as it appeared 4.6 billion years ago. Read more here>
This is just the beginning for the Webb mission, which is now ready to begin its highly anticipated science mission. NASA will reveal a raft of other science-quality Webb photos during an event on Tuesday morning (July 12). You can watch it here at Space.com.
Take a video tour of Webb's first targets
On Friday, NASA released the list of objects that will star in the first science-quality images from the James Webb Space Telescope, which are being released Monday evening and Tuesday morning. Tour them in this video!
President Biden to unveil first Webb image from White House today
President Joe Biden will unveil the first image from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, Monday July 11, directly from the White House, NASA announced.
You can watch the Monday reveal live here on Space.com at 5 p.m. EDT (2100 GMT) , courtesy of NASA, or directly on NASA TV.
The Monday release will be the first time the public will get a glimpse of a full-color, science-grade image from the James Webb Space Telescope, the most complex and expensive observatory ever built.
Announced on Sunday, July 10, the event comes less than 24 hours ahead of the main release of the first science-grade images from the observatory, which is scheduled to begin at 9.45 a.m. EDT (1345 GMT).
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson will provide remarks, and the image will simultaneously be released to the public via NASA's website, NASA said in a statement.
Previously, the space agency released a series of engineering images that provided a fascinating preview of the potential of the telescope, which images the cosmos in infrared wavelengths and can thus see much more distant objects than the Hubble Space Telescope.
The engineering images, scientists said, kept exceeding expectation, confirming that after years of delays and cost-overruns, the high-tech observatory is set to live up to the expectations and revolutionize our understanding of the universe.
Here are the subjects of Webb's first science images
NASA has unveiled a list of celestial objects that will feature in Tuesday's release of the first science-quality images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope. From nebulas to an exoplanet and more, see the full list here>
Surprise! We'll know more about Webb's first science photos tomorrow
We'll know a smidge more about the subjects of the James Webb Space Telescope's first science-quality images a bit earlier than expected. NASA has decided to release on Friday (July 8) a list of the targets that will be depicted in the observatory's first data release, scheduled for July 12, according to a statement.
We'll be back tomorrow to give you the rundown on that list!
Another stunning preview
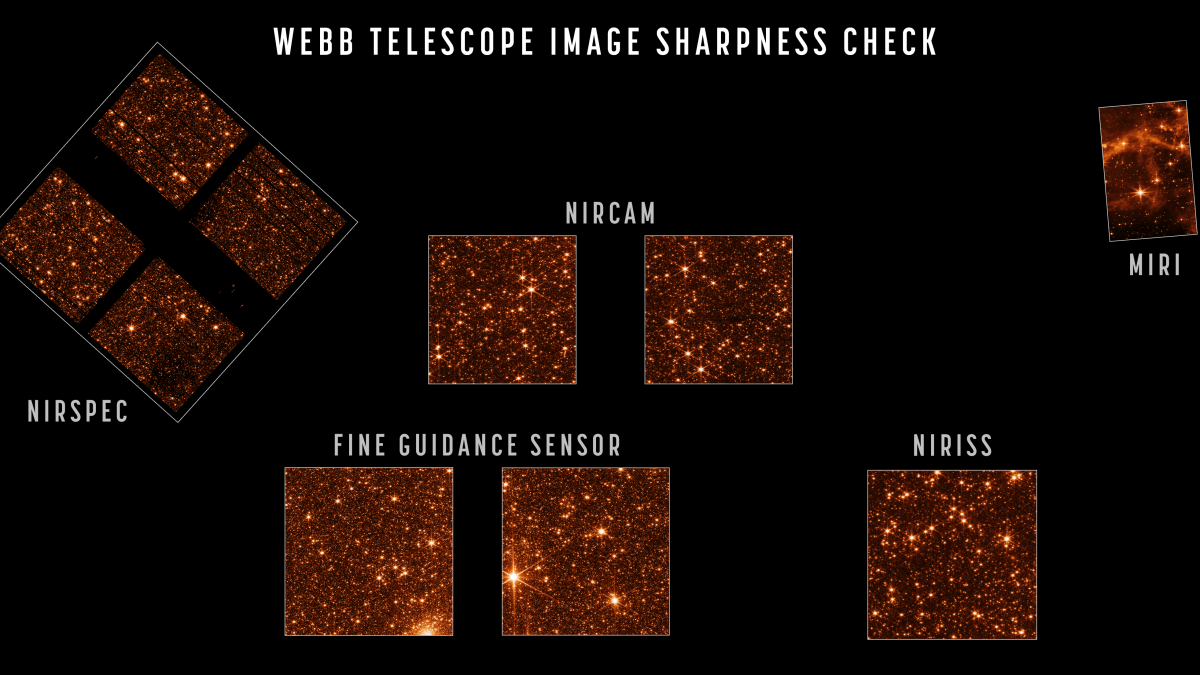
It's another teaser for just how much we have to look forward to on Tuesday (July 12) when NASA unveils the first science-quality images from the James Webb Space Telescope. (Watch live here.) On Wednesday (July 7), NASA released an engineering image taken by the observatory's Fine Guidance Sensor — not a science tool but an engineering instrument that keeps the telescope pointing properly. Still, the new image is currently the deepest ever view of the universe and promises good things to come from the observatory. Read more>
"This is really only the beginning."
During a media event held on Wednesday (June 29), scientists hailed the James Webb Space Telescope images that NASA will release on July 12. Agency officials hinted at what some of those images will be, scientists discussed what they hope to learn from the observatory's early work, and engineers recounted tense moments from the long path to having an operational telescope in space. Read more>
Listen live!
NASA officials will discuss preparations for the first science-quality images from the James Webb Space Telescope during a media teleconference today that you can listen to live beginning at 10 a.m. EDT (1400 GMT) in the window above, courtesy of NASA.
Webb's first instrument is ready for science!
The first of the James Webb Space Telescope's four instruments has been declared ready for science. The Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph instrument, or NIRISS, is designed to help scientists study the atmospheres of exoplanets, among other science tasks. Read more>
Meanwhile, space fans around the globe are counting down to July 12, when NASA has said it will unveil the first science images from the observatory. You'll be able to watch the announcement live on Space.com, of course, and stay tuned for more coverage.
Webb suffers first micrometeoroid impacts
The James Webb Space Telescope has suffered its first few micrometeoroid impacts, according to a NASA statement. The observatory has experienced four small impacts as well as one larger strike that hit one of the 18 primary mirror segments. However, the agency said that it does not expect meaningful changes to the timeline for first science-quality images from the mission or to the observatory's overall scientific legacy. Read more>
Mark your calendars!
NASA has announced that it will unveil the first science-quality images from the James Webb Space Telescope on July 12. We don't yet know what celestial objects those images will show — but they should be incredible. "These images will be the culmination of decades of dedication, talent, and dreams — but they will also be just the beginning," Eric Smith, Webb program scientist at NASA, said in a statement. Read more>
Webb tracked an asteroid for the first time
The James Webb Space Telescope has successfully tracked an asteroid, an important testing milestone that proves the observatory can monitor objects within our solar system that appear to be moving quite quickly. Read more>
Webb is in the homestretch of commissioning
NASA offered an update on the commissioning of the James Webb Space Telescope on Monday (May 9), which highlighted a test image taken by its Mid-Infrared Instrument, or MIRI. The agency compared the new image, showing part of the neighboring Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy, with one taken by NASA's previous infrared observatory, the retired Spitzer Space Telescope. Read more>
NASA will update on Webb's final prep stages
The James Webb Space Telescope is entering its final commissioning phase before beginning science operations this summer. The last phase will focus on testing the instruments aboard the observatory and is expected to take about two months.
NASA personnel will update the public about the telescope's progress so far and what remains to be done during a news conference on Monday (May 9) at 11 a.m. EDT (1500 GMT), which you can watch here on Space.com courtesy of the agency or directly at the agency's website.
Webb is fully aligned and the views are stunning!
The three-month process of aligning the James Webb Space Telescope's instruments and mirrors is finally complete, according to a NASA statement released today (April 28). The agency shared sample images that, while small, showcase the sharp focus of the instrument and offer a tantalizing look at what's to come. Read more>
Webb cools down
In a new update, NASA revealed that the James Webb Space Telescope is almost fully-cooled.
Webb observes in infrared light, which we know best as heat. To make sure its observations aren't contaminated by any heat from the scope itself, Webb has to be extremely cold. In a new blog post, NASA shared that the space telescope is very close to its final temperature.
Webb's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) is now cooled to under 7 kelvins (-447 degrees Fahrenheit (-266 degrees Celsius) and so Webb's instruments are all at their operating temperatures. Now, the scope's mirrors just need to reach their final cooled-down temperatures.
Webb meets crucial temperature milestone
The James Webb Space Telescope's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) finally reached the super-cold temperature needed to operate as designed. Because the instrument targets infrared light, which manifests as heat, the instrument must remain under 7 degrees Kelvin, which is equivalent to minus 447 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 266 degrees Celsius). And after a complicated, careful cooling process, that milestone has been reached, according to NASA. Read more>
James Webb Space Telescope most heat-sensitive instrument cooling to absolute zero
The James Webb Space Telescope continues to cool down to its operating temperature of minus 369.4 degrees Fahrenheit ( minus 223 degrees Celsius) as it prepares to take its first scientific images of the distant universe this summer. One of the telescope's four instruments, the Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI), needs some extra help from a dedicated cryocooler as it needs to get to an even colder temperature of minus 447 degrees F ( minus 266 degrees C), only 12 degrees F (7 degrees C) above absolute zero, the temperature where the motion of atoms stops.
Just one alignment left
The James Webb Space Telescope has just one step of its seven-phase alignment process left to complete, NASA announced on April 1. The remaining step requires that the observatory's most heat-sensitive instrument, the mid-infrared instrument or MIRI cool even farther. That should occur in the next few weeks, NASA said, at which point mission personnel can begin calibrating the observatory's instruments. Read more>
Europe's Gaia observatory spies James Webb Space Telescope (photo)
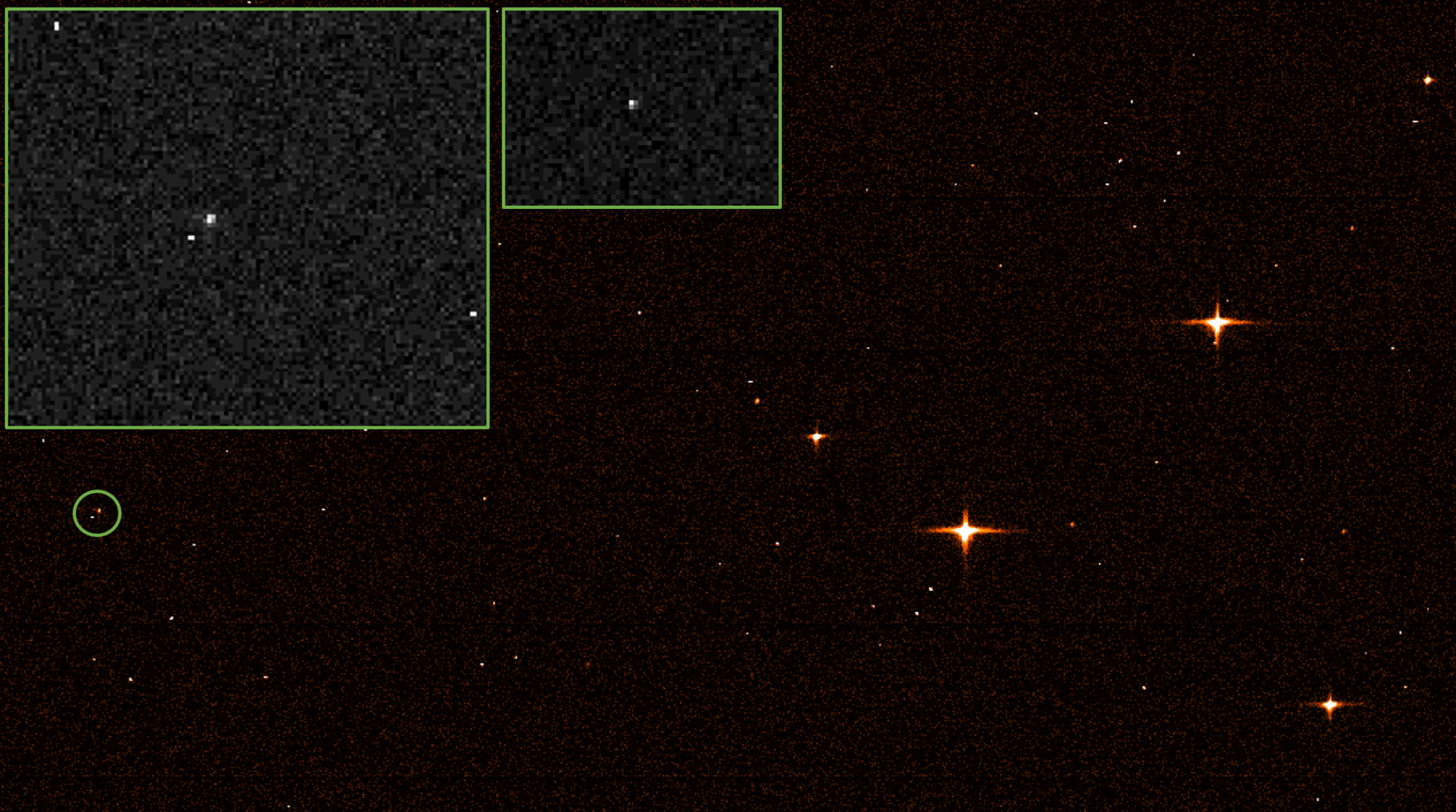

Europe's star-mapping Gaia space observatory managed to snap an image of NASA's $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope on Feb. 18, when the duo were about 620,000 miles (1 million kilometers) apart, we learned today (March 16).
You can't see much of Webb — it appears as a faint speck against a field of stars — but spotting the scope at all is a real achievement. Read our full story here.
James Webb Space Telescope notches "fine phasing" alignment milestone

The James Webb Space Telescope keeps checking off boxes on the way toward the start of science operations this summer.
The Webb team has aligned the $10 billion scope's 18 primary mirror segments and focused them on a single star, NASA officials announced today (March 16). More fine-tuning work remains, but it's a huge milestone for the mission and for NASA.
"More than 20 years ago, the Webb team set out to build the most powerful telescope that anyone has ever put in space and came up with an audacious optical design to meet demanding science goals," Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, said in a statement today. "Today we can say that design is going to deliver."
Read the ful story here.
NASA promises Wednesday Webb update and new image
NASA will update the public on Wednesday about progress aligning the James Webb Space Telescope's primary mirror. The golden mirror is made up of 18 hexagonal segments that must be in perfect alignment for the observatory to capture sharp images.
And it sounds like that process is going well: NASA has promised a new image as well. "Participants will share progress made in aligning Webb’s mirrors, resulting in a fully focused image of a single star," NASA officials wrote in a statement.
The NASA briefing will begin on Wednesday (March 16) at 12 p.m. EDT (1600 GMT) and you can watch live here at Space.com or directly via the agency's YouTube. Speakers will include:
- Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters in Washington
- Lee Feinberg, Webb optical telescope element manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland
- Marshall Perrin, Webb deputy telescope scientist, Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore
- Jane Rigby, Webb operations project scientist, Goddard
- Erin Wolf, Webb program manager, Ball Aerospace in Broomfield, Colorado
Webb telescope to study quasars, Kuiper Belt

As the James Webb Space Telescope continues its checkout tests in deep-space, scientists continue to eagerly await the flood of science discoveries they hope to make with the $10 billion space observatory.
Our latest updates on the Webb space telescope's mission have to do with the Kuiper Belt and quasars, targets both near (in astronomical scales) and far that Webb will observe to better understand the universe.
First, the Kuiper Belt, which is home to icy objects leftover from the formation of the solar system. As contributing writer Elizabeth Howell writes today, some of Webb's earliest tasks will be to observe brilliant quasars at the heart of distant galaxies to study how these distant objects (powered by black holes billions of times the mass of our sun) shaped the early universe. You can read the full story here.
More closer to home is the Kuiper Belt, the stomping grounds for Pluto and its biggest moon Charon, which will be a target for Webb. As contributing writer Stefanie Waldek reports, another one of Webb's early science goals will be to observe Pluto and some other objects in the Kuiper Belt at the fringe of the solar system to track them over time and learn about their surface chemistry and why there is such a diverse range of objects there.
"Using Webb, we will be able to get information about surface chemistry that might be able to give us some clues into why there are these different populations in the Kuiper Belt," Heidi Hammel, a Webb interdisciplinary scientist for solar system observations, said in a statement.
Webb instrument work continues
NASA engineers are working on the fourth stage of the long process to align the mirrors of the James Webb Space Telescope, according to a new statement from the agency.
The observatory's Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) instrument has finished initial check-out and its three key mechanisms have successfully been characterized, the statement noted. The instrument will allow Webb to study the "fingerprint" of light of up to 100 galaxies at a time, giving scientists crucial information about mass, temperature and chemical composition.
We're also highlighting more of the research that Webb will execute once science observations begin, including studying strange "sub-Neptunes" and evaluating how the activity of stars might affect nearby planets.
Nearly halfway through mirror alignment


The James Webb Space Telescope team just completed the third of seven planned steps to align the 18 segments of Webb's big mirror.
During the second stage, called "segment alignment," the team corrected the positions of Webb's primary mirror segments and updated the alignment of the secondary mirror to bring the 18 individual images into focus. They then stacked the 18 images to produce one unified image. "After future alignment steps, the image will be even sharper," NASA officials said in a statement Friday (Feb. 25).
Webb instrument work continues smoothly
As the James Webb Space Telescope continues the slow commissioning phase, work is going smoothly, according to a NASA statement published Thursday (Feb. 24). That update notes details about progress in several instruments, including filter wheel calibration for the Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS) and wheel tuning for the Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam). Engineers are also working to precisely align the 18 hexagonal segments that make up the observatory's massive golden mirror.
Science observations are not expected to begin until this summer, but there's plenty of science to get excited about during the wait. That science includes plans to contribute to the Event Horizon Telescope's observations of the black hole at the center of the Milky Way and a program to observe star formation currently hidden by layers of dust.
Sharpening sight
The first image NASA shared from the brand new James Webb Space Telescope showed a star warped over 18 different images due to inconsistencies in the mirror's alignment. Just a week later, a new image still shows one star 18 times, but now the sparkle forms a sort of cosmic snowflake as the observatory's image has sharpened. Read more>
Science sneak peek: interstellar asteroids
While James Webb Space Telescope engineers continue aligning the observatory's segmented golden mirror, scientists are looking ahead to the research the telescope will begin conducting this summer. Overall, the observations will range from our own solar system to the very earliest days of the universe.
One example of what astronomers hope to do with Webb? Study any interstellar objects that come rushing through our solar system. To date, scientists have spotted two: 'Oumuamua in 2017 and Comet Borisov in 2018. But the James Webb Space Telescope is more powerful than anything in the sky during those two visits, plus it has the capacity to observe in infrared, a key skill. Read more>
It's a lock!
The James Webb Space Telescope's Fine Guidance Sensor has successfully locked onto a star for the first time, according to a NASA statement. The instrument plays a crucial role facilitating observations, since it keeps the telescope pointing toward the proper target. Read more>
Before science observations can begin, however, the observatory still needs to finish aligning the 18 hexagonal segments of its golden primary mirror, a process that the Fine Guidance Sensor also supports. Although Webb has begun gathering observations and shared its first images last week, those will show the same star multiple times until the mirror segments are properly aligned.
Webb mission team ecstatic over first images
Today (Feb. 11), NASA revealed that the James Webb Space Telescope has captured its first images of starlight.
And, while the mission team is still cautiously looking ahead as there is much work to be done before the scope is fully operational and ready to begin science observations, they are ecstatic.
"After all these years, to actually see data when we're in zero gravity in space, it is emotional," Lee Feinberg, the Webb optical telescope element manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, told Space.com today during a news conference
However, "We still are being a little cautious, because we still have things that we have to get through ... but I will definitely say when I went home Saturday night, two days later [after the image was taken], I know my wife said to me it was the first time she'd seen me smile since December," he added.
Read more about the team's excited response and Webb's thrilling milestone here.
See Webb's first view of space!
NASA has unveiled Webb's first image. The photo, as seen above, shows a star called HD 84406 as seen through each of the observatory's 18 golden mirror segments as scientists continue to work to align the mirror to produce a single, ultra-crisp image of the universe.
The agency also posted a video sharing the story behind the image:
But that's not all the excitement for today! NASA has also released an annotated version of the same image, plus a "selfie" taken by the observatory of its own golden mirror. See those images and read more here>
And don't forget to listen to NASA scientists talk about the new images live right now (11 a.m. EST/1600 GMT)! You can listen here at Space.com.
First Webb images available tomorrow, NASA says
NASA will release some of the first images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope on Friday (Feb. 11) at 10:30 a.m. EST (1530 GMT), according to an agency update. While these images are an important milestone in the observatory's commissioning, don't get your hopes up for the next great view of the universe: These are images taken during the mirror alignment process and are strictly utilitarian.
In addition, NASA will offer an update on its progress aligning the 18 mirror segments of Webb's massive primary reflector. The teleconference will begin at 11 a.m. EST (1400 GMT) and will be available to listen to on NASA TV or here at Space.com.
Speakers will include:
- Lee Feinberg, Webb optical telescope element manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland
- Marshall Perrin, Webb deputy telescope scientist, Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore
- Marcia Rieke, principal investigator for the NIRCam instrument and regents professor of astronomy, University of Arizona in Tucson
Webb is painted black - but why?
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is finally at its home in space where it's preparing to observe the cosmos. But to do this, it has to stay ultra-cold. (Webb's "cool side" is minus 388 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 233 degrees Celsius).)
Webb observes infrared light, aka heat, which means that to ensure that observations aren't affected by any additional warmth the scope has to stay super cold. To keep Webb cold enough, the mission team painted its radiator (which helps to radiate heat away from the telescope) and components an ultra-black color.
Read more about Webb's paint job and why it has to stay so cold here.
"First light" images coming soon
NASA could be releasing the first images from the James Webb Space Telescope in the next few days, NASA's Webb program director Greg Robinson said in an agency town hall meeting today (Feb. 8). But don't expect these first images to be pretty.
"So the beautiful, very clear images that we expect to see, you'll see those in the summer sometime approximately six months after launch," Robinson said. "Sometime next few days, you will see some of the first images that are not so clear ... the purpose of those is to align the mirrors and make sure the entire system is working," he added. "We are in that process right now. We just recently started it. So stay tuned over the next few days on those."
Telescope alignment begins
The James Webb Space Telescope mission team has begun the three-month process of aligning the telescope, NASA officials announced today (Feb. 3).
"This milestone marks the first of many steps to capture images that are at first unfocused and use them to slowly fine-tune the telescope," NASA officials wrote in an update today. "This is the very beginning of the process, but so far the initial results match expectations and simulations."
Read the full story: Alignment of James Webb Space Telescope begins
James Webb Space Telescope's exoplanet plan, instruments on
NASA flight controllers are have switched on the four main instruments aboard the James Webb Space Telescope as they prepare to snap the first images of a target star that will be used to align the observatory's 18-segment main mirror.
The instrument activation began last week. Here's our full report from senior writer Tereza Pultarova.
Meanwhile, with Webb's commissioning underway, scientists are now eyeing a future of amazing astronomy with the huge space observatory. One scientist, the Ph.D. candidate Louis-Philippe Coulombe of the University of Montreal, wrote in an op-ed that he is eager to see how Webb will help map the atmosphere of exoplanets, something the observatory should be able to do better than any space telescope to date.
James Webb Space Telescope waking up
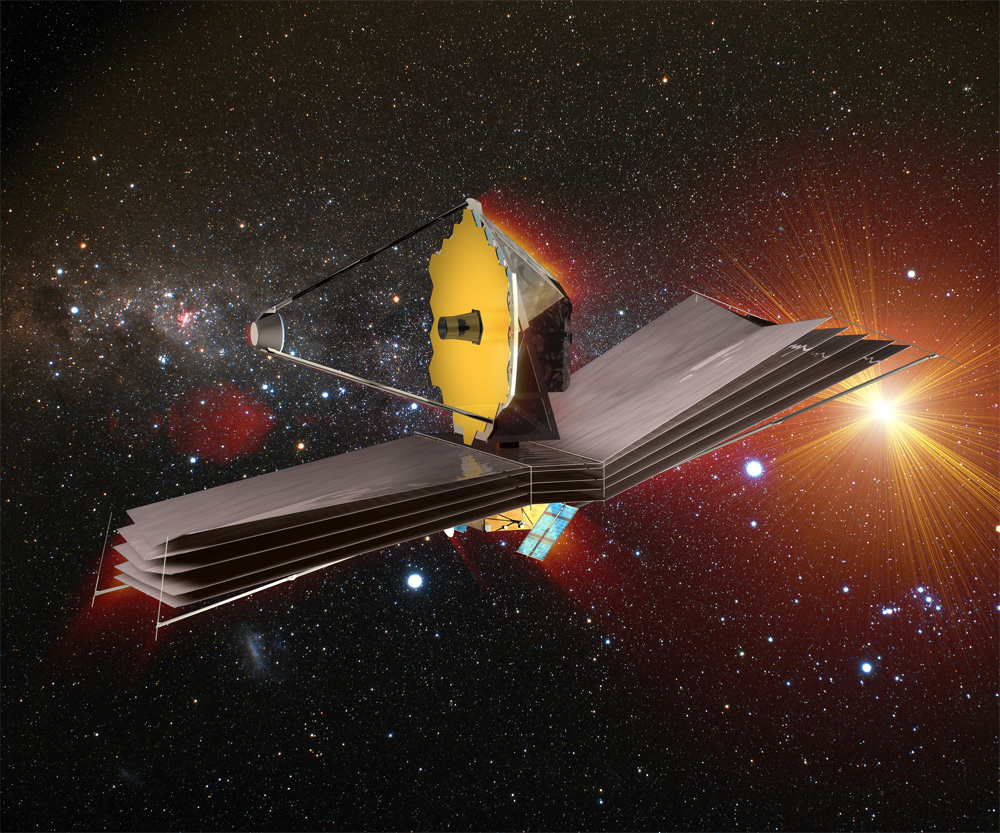
The James Webb Space Telescope is beginning to wake up.
In a town hall press conference on Friday (Jan. 28), scientists with NASA's Webb Space Telescope mission outlined the work so far to commission the observatory at its new home at the Earth-sun Lagrange point 2. During that virtual briefing, Webb scientists outlined the activation sequence for Webb's main instruments, as well as the months-long mirror alignment and focusing work that is underway now.
Read our full story from Elizabeth Howell on Webb's commissioning work from the briefing.
Meet Webb's 1st target star: HD 84406
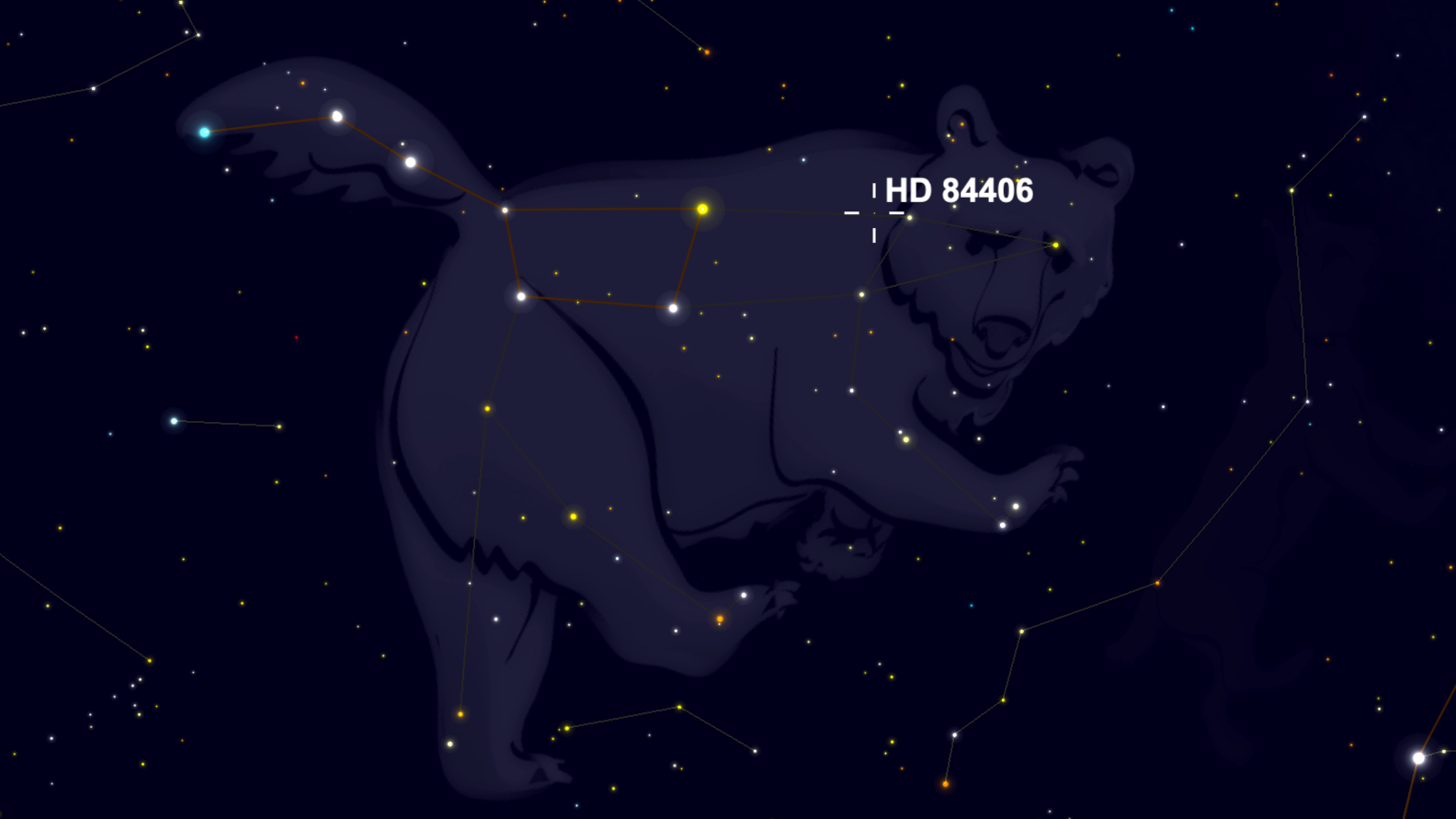
Scientists with NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have picked the first star they will aim at with the new observatory and it's in a very familiar place.
The star, called HD 84406, is located in the constellation Ursa Major, the Big Bear, which is home to a star pattern you may know better as the Big Dipper.
Webb scientists will use the star to focus each of the 18 mirror segments of Webb's primary mirror. HD 84406 is a sun-light star about 260 light-years from Earth, and may need binoculars to see clearly.
Here's our full story on HD 84406, the first target of the James Webb Space Telecope.
Also this week, Bill Ochs, NASA's Webb telescope project manager, thanked the mission team for its amazing work and dedication to get the observatory to its L2 observing spot. Ochs quoted Jimmy Buffett as he hailed the team, changing some key lyrics.
Hello, instruments!
According to an emailed statement from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), Webb will begin turning on its science instruments today (Jan. 28). That will include the Fine Guidance Sensor, which will guide the observatory's mirrors through the delicate alignment process to turn 18 small individual views into one massive view of the universe.
In the meantime, consider reading this op-ed from Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA's associate administrator for science, celebrating the vast team behind the James Webb Space Telescope.
"We did it. We did it, and you can see that speck of light in the sky because of an incredible team with extraordinary tenacity," Zurbuchen wrote. Read more>
Scientists relieved (and thrilled) after Webb's trek

With the James Webb Space Telescope now at its final destination, scientists can let out a deep sigh of relief. After just over a month in space (and decades in development), Webb is now at its observing site.
"We're a month in, and the baby hasn't even opened its eyes yet. But that's the science that we're looking forward to," Jane Rigby, Webb operations project manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, said during a media teleconference on Monday.
You can read Rigby's reaction and those of her Webb telescope colleagues in this update from today's teleconference by contributing writer Elizabeth Howell.
Space.com Senior Writer Chelsea Gohd has this account of Webb's arrival at L2 with comments from NASA chief Bill Nelson and others.
The James Webb Space Telescope is "home"
Today (Jan. 24), the James Webb Space Telescope arrived in orbit around L2, the second sun-Earth Lagrange point, its final destination after a long almost million-mile (1.5 million kilometers) journey from Earth.
To learn more about Webb's arrival at L2, check out this article on Space.com here.
Webb arrives at L2!
The James Webb Space Telescope has arrived!
Webb has completed the mid-course correction burn (MCC2), an insertion burn that has guided it into its orbit around its final home in space, NASA announced in a blog post today (Jan. 24).
Beginning at 2 p.m. EST (1900 GMT), the space telescope fired its onboard thrusters for about five minutes (297 seconds) to complete this burn maneuver. The burn added just about 2.6 miles per hour (1.6 meters per second) (a walking pace, NASA noted), to Webb's speed as the craft sailed into a halo orbit around its destination: L2, the second sun-Earth Lagrange point.
🏠 Home, home on Lagrange! We successfully completed our burn to start #NASAWebb on its orbit of the 2nd Lagrange point (L2), about a million miles (1.5 million km) from Earth. It will orbit the Sun, in line with Earth, as it orbits L2. https://t.co/bsIU3vccAj #UnfoldTheUniverse pic.twitter.com/WDhuANEP5hJanuary 24, 2022
L2, which lies just about a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) from Earth opposite the sun, is a gravitationally stable point that Webb will orbit as it works. Webb will spend the next few weeks in its new home cooling down before taking about five months to prepare its science instruments to get to work.
"Webb, welcome home!" NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said in the blog post. "Congratulations to the team for all of their hard work ensuring Webb’s safe arrival at L2 today. We’re one step closer to uncovering the mysteries of the universe. And I can’t wait to see Webb’s first new views of the universe this summer!"
Join NASA live at 3 p.m. EST (2000 GMT) here to learn more about the successful arrival and what's next for Webb.
Insertion burn starting!
The James Webb Space Telescope has begun its mid-course correction burn (MCC2), the insertion burn that will ease it into its halo orbit around its ultimate home in space: L2, the second Lagrange point.
The #NASAWebb L2 Mid Course Correction Burn (MCC2) is ongoing: https://t.co/xpsH2rVmMX#UnfoldTheUniverse pic.twitter.com/8Yi2q9Mi8eJanuary 24, 2022
Lagrange points are gravitationally stable points in space, and L2 is located almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from Earth on the opposite side of the sun. This vantage point will help Webb to stay cold, which is crucial for its science instruments to work as planned.
Join NASA experts LIVE at 3 p.m. EST (2000 GMT) to hear about Webb's progress and new home at L2.
About to begin insertion burn!
Webb is about to fire its thrusters to get to its ultimate destination!
Today (Jan. 24), the James Webb Space Telescope makes its arrival at its new home in space, in orbit around L2, the second sun-Earth Lagrange point which lies on the opposite side of Earth as the sun.
To get into orbit around L2, Webb is beginning what is known as the mid-course correction burn (MCC2), an insertion burn that will ease the space telescope into its operating orbit, a halo orbit, around L2.
Webb will begin MCC2 at 2 p.m. EST (1900 GMT) and, at 3 p.m. EST (2000 GMT), NASA officials will be updating the public and answering questions live right here.
Today is the day!

Nearly a month after its stunning Christmas Day launch, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is due to arrive in orbit around L2 today (Jan. 24).
At about 2 p.m. EST (1900 GMT), the mission team will direct the observatory to fire its thrusters for about five minutes, completing the long journey of nearly 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers).
NASA will not be broadcasting the burn live, but scientists will be talking about what's next for the observatory during a 3 p.m. EST (2000 GMT) broadcast and the agency will hold a media teleconference at 4 p.m. EST (2100 GMT) as well. You can watch both events live on Space.com.
Although arrival in orbit marks the last major milestone in the observatory's deployment, the telescope isn't quite ready to do science. The mission team still needs to precisely align the 18 golden mirror segments into one vast reflector and to calibrate the observatory's instruments.
NASA has said to expect the James Webb Space Telescope to begin science operations this summer.
James Webb Space Telescope 1 day from L2

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is one day away from arriving at its final destination for its ambitious science mission: a gravitationally stable point in space known as the Earth-sun Lagrange point 2, or L2.
As of 8 a.m. EST (1300 GMT), the Webb Space Telescope was about 17,310 miles (27,854 kilometers) away from the L2 location, and about 893,897 miles (1,438,484 km) from the Earth. The L2 location is nearly 1 million miles from Earth on the opposite side of the Earth from the sun.
Webb is expected to enter orbit around the L2 point on Monday, Jan. 24. To do so, it will fire its thrusters at 2 p.m. EST (1900 GMT) on Monday for a few minutes to push it the final distance into L2 orbit.
NASA is expected to host a live webcast of the L2 arrival insertion burn and follow it up with a NASA Science Live program to discuss the event at 3 p.m. EST (2000 GMT). At 4 p.m. EST (2100 GMT), NASA will hold a press teleconference on the event to discuss the next steps for the space telescope.
L2 on Monday
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is just a few days away from its arrival at its home in space: L2, or the second Lagrange point, gravitationally stable points in space. L2 is positioned on the side of Earth opposite the sun.
While NASA had previously expected Webb to arrive at L2 on Jan. 23, 29 days after its Dec. 25 launch, Webb is now expected to begin its mid-course correction burn (MCCB), or insertion burn, into an orbit around L2 on Monday (Jan. 24).
You'll be able to watch a live broadcast with scientists and engineers operating the space telescope on Monday at 3 p.m. EST (2000 GMT).
Next stop, L2.
Webb's next major milestone will be its arrival in orbit around a point in space called the Earth-sun Lagrange point 2, or L2. This video explains where L2 is and why the observatory will camp out in orbit around it.
Mirror deployment is complete
Just in from the @NASAWebb team: All 18 primary mirror segments and the secondary mirror are now fully deployed!Congratulations to the teams that have been working tirelessly since launch to get to this point. Soon, Webb will arrive at its new home, L2!#unfoldtheuniverse pic.twitter.com/QsIyr5AWiiJanuary 19, 2022
The 18 primary mirror segments of the James Webb Space Telescope are fully deployed, according to a tweet from NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. The observatory has one deployment milestone outstanding, a final course correction burn. Read more>
Fast forward to Webb's first look
NASA is continuing to adjust the individual mirror segments of the James Webb Space Telescope as the observatory continues its trek to orbit nearly 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from Earth. In the meantime, we're looking ahead to the big moment: What will the observatory look at first? Read more>
Time to adjust those mirrors
NASA has confirmed that the team behind the James Webb Space Telescope have begun the process of aligning the observatory's mirrors, which were stowed for launch. The preliminary adjustments will take about 10 days, according to a mission timeline, although NASA expects to spend about three months to completely align the panels into a working telescope. Read more>
Onto Webb's mirror segments
According to a NASA timeline, the team behind the James Webb Space Telescope will likely begin moving the 18 individual segments of the observatory's hexagonal golden mirror out of their launch configurations on Wednesday (Jan. 12).
This process is slow and finicky, and is expected to take about 10 days. Each of the 18 primary mirror segments is held in place by seven different actuators that can adjust their position and curvature super precisely. But even once this process is complete, the observatory team will need to spend about three more months getting the honeycomb of mirrors to work together to produce one sharp image.
Webb has been in space for 18 days now and is more than 82% of the way to its final destination. The observatory will orbit a point called the Earth-sun Lagrange point 2, or L2, which is located nearly 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from Earth on the side opposite the sun. The observatory has covered more than 740,000 miles (1.2 million km) and has 160,000 miles (250,000 km) more to go.
You can track the telescope's location, temperature and deployment via NASA.
Webb keeps trekking out to space
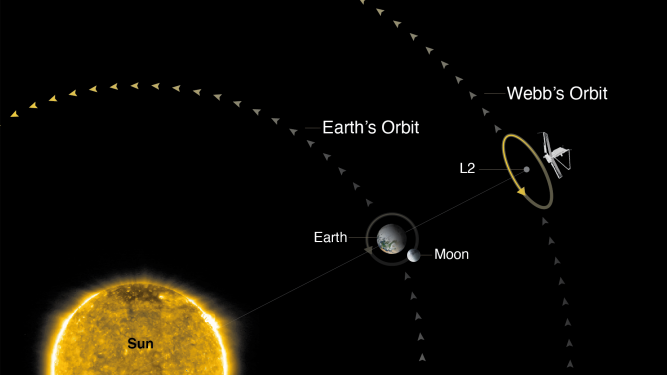
NASA has again delayed beginning work on aligning the individual mirror segments of the James Webb Space Telescope, according to an agency timeline, with that project now scheduled to begin Wednesday (Jan. 12). The process will take several days and moves the 18 individual hexagons of the golden primary mirror out of their launch configuration.
In the meantime, Webb continues its long journey out to Earth-sun Lagrange point 2, or L2. The observatory is currently 80% of the way to L2 and has traveled nearly 725,000 miles (1.16 million kilometers) away from Earth. To follow Webb's journey, consult NASA's tracking website for the observatory, which also tracks the deployment process.
Webb work continues
Adjustments to the 18 golden mirror segments of Webb's primary mirror are due to begin tomorrow, Jan. 11, according to the deployment timeline provided by NASA. That process is expected to take several days and marks the observatory's transition from deployment into commissioning.
Meanwhile, the observatory continues its trek out to its station orbiting Earth-sun Lagrange point 2, or L2, which is located about 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from Earth on the side opposite the sun. As of today (Jan. 10), the telescope is more than 78% of the way to orbit, having traveled more than 700,000 miles (1.1 million km) from Earth, according to NASA's observatory tracker.
Mirror alignment to begin for Webb Space Telescope
With the James Webb Space Telescope now fully deployed, work is expected to begin today to start aligning the 18 individual mirrors that make up the observatory's primary mirror. It is not a fast process.
Full story: The James Webb Space Telescope is fully deployed. So what's next?
"This operation is a multi-day multi-step activity to activate and move each of its 18 primary mirror segments (which are adjustable) out of their launch configuration, NASA wrote in a deployment guide. "The primary mirror segments and secondary mirror are moved by six actuators that are attached to the back of each mirror piece. The primary mirror segments also have an additional actuator at its center that adjusts its curvature. The telescope's tertiary mirror remains stationary."
The primary mirror is Webb's main light collection surface. It will reflect light to the tertiary mirror located on booms in front of the telescope, which then bounces the light into Webb's instruments.
Each of the 18 segments of the primary mirror is plated in a shiny, but ultra thin, layer of gold. If left in launch position, they would act as individual telescopes with images that would be fuzzy and unclear. Once aligned, the mirror segments will act as one giant mirror 21.3 feet (6.5 meters) across, the largest ever in space.
NASA has estimated that it could take up to 120 days after launch for Webb's mirror alignment work to be complete. The first photos from Webb are not expected until about five months after launch once commissioning ends. -- Tariq Malik
Here's a look at how Webb's focusing works:
James Webb Space Telescope deployment success
An elated mission team for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope confirmed that the space observatory is in great shape after a deployment phase that was 100% successful.
"It is a fully deployed telescope ready to perform fantastic science to expand our knowledge," said John Durning, Webb Deputy Project Manager of NASA Goddard.
Up next for the Webb team is a five-month commissioning phase to calibrate the telescope's optics and adjust its mirrors. Webb is currently making its way to its final observing site nearly 1 million miles (1.6 km) from Earth and is due to arrive around Jan. 23.
To enter orbit around its Lagrange 2 point, Webb will have to perform a short maneuver, but it is expected to go well.
You can read our wrap story on today's Webb mirror deployment success here. -- Tariq Malik
NASA Webb Space Telescope press conference underway
NASA's post-deployment press conference is underway now and you can watch it live in the video window at the top of this page.
NASA is holding two panels, one on the deployment's success and the other on what's next for the Webb Space Telescope.
Here's a rundown of the speakers for the briefing:
Panel on Webb Space Telescope deployment success
Bill Ochs, Webb Project Manager, NASA Goddard
Mike Menzel, Mission Systems Engineer, NASA Goddard
Scott Willoughby, Vice President and Program Manager, Webb, Northrop Grumman
Vince Heeg, Deputy Program Manager, Northrop Grumman
Panel on what's next for James Webb Space Telescope
John Durning, Webb Deputy Project Manager, NASA Goddard
Lee Feinberg, Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager, NASA Goddard
Jane Rigby, Webb Operations Project Scientist, NASA Goddard
Heidi Hammel, Vice President for Science, Space Telescope Science Institute
Success! Webb Space Telescope primary mirror latched
Congratulations, @NASAWebb! You are fully deployed! 🥳Stay tuned over the coming months as the space telescope reaches its destination of Lagrange point 2 and prepares to #UnfoldTheUniverse: pic.twitter.com/qg6jmVRCsHJanuary 8, 2022
James Webb Space Telescope mission engineers confirmed that the observatory's starboard primary mirror wing successfully latched into place at 1:17 p.m. EST (1817 GMT), marking an end to a two-week process that was NASA's most-complicated deployment in space telescope history.
Cheers erupted at Webb's mission operations center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, as the mission team now prepares for an arduous three-month process to align and calibrate the $10 billion space telescope.
"Today, NASA achieved another engineering milestone decades in the making!" NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said on Twitter. "While the journey is not complete, I join the Webb team in breathing a little easier and imagining the future breakthroughs bound to inspire the world."
NASA will hold a press conference at 2:30 p.m. EST (1930 GMT) for today's successful deployment. You'll be able to watch that live here at start time.
Latching underway for Webb telescope mirror
James Webb Space Telescope engineers have passed the halfway mark in latching the observatory's starboard mirror wing in place.
The latching process began shortly after 10:30 a.m. EST (1530 GMT) and was expected to take around two hours to complete.
Webb Space Telescope mirror fully deployed!
It's official, the primary mirror of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is completely deployed, the final step of its unprecedented two-week deployment phase that began with a Dec. 25 launch.
"I just feel this kind of glow in my chest right now just seeing that mirror deployed all together," NASA scientist Michelle Thaller said in a live webcast as the Webb mission team applauded and shared high-fives.
Webb space telescope starboard mirror in motion
The Webb Space Telescope's mission operations team has commanded Webb to deploy its starboard mirror wing.
It should take 4 to 5 minutes for the mirror segment to swing into place, after which it will take a few hours to latch into place.
Launch locks released from Webb mirror
The four launch locks securing the Webb Space Telescope's starboard mirror wing in place have successfully been unlocked, freeing the mirror segment for its final move.
A series of motors successfully worked to unlock the launch locks. They were the final critical movies of 178 mechanism firings that were vital to go smoothly for Webb's deployment over the last two weeks, NASA says. Those actions were non-redundant, if one failed it would have doomed the Webb Space Telescope.
"178 out of 178, congratulations," Webb's Mission Operations Manager just said.
The mirror segment is expected to begin slowly moving soon, with major movement to begin in about 20 minutes. Once in place, it will take about two hours to latch it securely in place. -- Tariq Malik
Final mirror unfolding begins for Webb Space Telescope
NASA has begun unfolding the final mirror wing for the James Webb Space Telescope. You can watch it in the live video feed at the top of this page.
Telescope controllers are working to send commands that will remove the launch locks on Webb's starboard mirror wing. Today's mirror unfolding will swing three final mirror segments into place to complete the 18-segment primary mirror deployment, the final step for Webb's two-week deployment phase.
Here's a closer look at the primary mirror of James Webb Space Telescope
Webb Space Telescope final deployment underway
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope mirror deployment webcast is underway. You can watch it above here hosted by NASA scientist Michelle Thaller.
NASA to webcast Webb final mirror deployment
Update for 9 a.m. EST: NASA's live webcast appears delayed. Once it begins, it will appear on this page.
It's a major day for the James Webb Space Telescope. Two weeks after its Dec. 25 launch, The Webb space telescope is scheduled to unfold its final mirror segment today, Jan. 8, today.
NASA will webcast the deployment of the Webb's starboard primary mirror segment live, with a livestream beginning no earlier than 9 a.m. EST (1400 GMT). You'll be able to watch that live on this page once it begins.
Today's mirror deployment will use motors to swing Webb's starboard primary mirror wing, which consists of three mirror segments, into its final position. It will then be latched into place.
"Upon completion, Webb will have concluded its major deployment sequence," NASA officials wrote in an update on Friday after Webb's port mirror wing was deployed.
After today's mirror deployment, NASA will hold a press conference to begin no earlier than 1:30 p.m. EST ( 1730 GMT). -- Tariq Malik
Live webcast delayed to Saturday
The Virtual Telescope Project's live webcast of the James Webb Space Telescope in deep space has been postponed until Saturday (Jan. 8), because clouds above the observatory Italy did not clear up in time to see it today. The webcast is scheduled to begin at 4:30 p.m. EST (2130 GMT).
The weather forecast for Saturday's observation looks more promising, Gianluca Masi of the Virtual Telescope Project told Space.com in an email.
Virtual Telescope Project JWST webcast delayed
Astrophysicist Gianluca Masi of the Virtual Telescope Project near Rome, Italy will broadcast live views of the distant James Webb Space Telescope today, beginning at 5:30 p.m. EST (2230 GMT). The webcast was originally scheduled to begin an hour earlier, but clouds are currently blocking the view.
You can tune in live in the window above, courtesy of the Virtual Telescope Project.
Read more: Watch the James Webb Space Telescope soar through space in this livestream today!
1st mirror wing deployed
The James Webb Space Telescope unfolded the first of two wing segments on its hexagonal gold-coated primary mirror on Friday (Jan. 7). NASA received confirmation of the successful deployment at approximately 2:11 p.m. EST (1911 GMT), agency officials wrote in a blog post.
Full story: James Webb Space Telescope has unfolded 1st wing of massive golden mirror
Nope, we’re not just winging it! But we did successfully deploy and latch the first of our two primary mirror wings. 😎These side panels, folded back for launch, each hold 3 of Webb’s 18 mirror segments. Next up: our final wing! https://t.co/xnaWZXYiSx #UnfoldTheUniverse pic.twitter.com/mBQ0S7eB2wJanuary 7, 2022
Webb's main mirror deployment has begun!
The James Webb Space Telescope has begun unfolding the left side panel of its golden primary mirror, according to a NASA statement published just before 9:30 a.m. EST (1430 GMT). The panel holds three of the hexagonal mirror segments the observatory uses to catch light.
During the deployment, team members will unlatch the wing from its stored position, then motors will unfold the panel in a process expected to take about five minutes. Then, the team will spend about two hours latching the panel into place, according to the statement.
The team is expected to repeat the process tomorrow (Jan. 8) on the right side of the observatory, which will mark the last major unfolding from the spacecraft's launch position. That event will be livestreamed beginning around 9 a.m. EST (1400 GMT), NASA has stated.
Webb main mirror deployment begins today
The James Webb Space Telescope will begin its final major unfolding events today with the first of two primary mirror deployments.
Today, Webb is expected to unfold and secure its port primary mirror wing, which contains three of the space telescope's 18 hexagon-shaped mirror segments.
"Webb's final series of major deployments is planned to start tomorrow, Jan. 7, with the rotation into position of the first of two primary mirror wings," NASA wrote in an update on Jan. 6. "The second primary mirror wing – Webb’s final major spacecraft deployment – is planned for Saturday, Jan. 8."
Webb's two primary mirror wings, port and starboard, each have three mirror segments. They were folded back behind the central mirror face during launch in order to fit inside the payload fairing of Webb's Ariane 5 rocket.
In other Webb news, the European Space Agency released a stunning HD video of the James Webb Space Telescope captured just after it separated from its Ariane 5 rocket. You can watch that video of Webb here. It is the last view of the space telescope we'll ever see.
Why is it the last view? The James Webb Space Telescope doesn't have onboard cameras.
Webb Mirror deployment webcast update
This is an update to note that NASA's webcast of the James Webb Space Telescope's mirror deployment will actually occur on Saturday, Jan. 8, at a time still to be determined based on NASA's latest live broadcast schedule.
Webb's flight controllers plan to deploy the the telescope's aft radiator as soon as today before proceeding with the port and starboard mirror deployments on Friday and Saturday. Sorry for any confusion, space fans! -- Tariq Malik
James Webb Space Telescope to deploy port mirror wing

The James Webb Space Telescope is expected to begin unfolding its primary mirror today, Jan. 6, starting with the port side.
In what could be a two-day process, Webb will unfold first the port side and then the starboard side wings of its 18-segment primary mirror, which is made up of shiny gold hexagons. There are three mirror segments on each wing.
Each of the wings were folded for launch in order to fit inside the payload fairing of Webb's Ariane 5 rocket.
While the mirror unfolding process is scheduled to take two days, it could occur faster. Webb's mission operations team has been running ahead of schedule for several key steps.
NASA will webcast today's Webb mirror deployment on NASA TV. A time has not been released for the webcast's start. Once we have more information, we'll share that here. -- Tariq Malik
James Webb Space Telescope secondary mirror latched securely
The secondary mirror of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is now securely latched into place, marking a successful end to today's deployment step. NASA's webcast has ended. You can read our full story by senior writer Tereza Pultarova here.
Deploying the mirror is the latest critical step for the Webb space telescope. The secondary mirror will focus light from the main mirror into the observatory's optics.
Over the next few days, Webb will deploy its aft radiator, followed by folding out the two side segments, or wings, of its main mirror. Those steps will mark the final major deployment stages of the telescope.
Engineers will still have to move each of the 18 primary mirror segments out of their launch configuration so that they can be calibrated for observations. Once that is complete (slated for 15 days after launch), the next major step will be Webb's arrival into orbit around its L2 point.
Webb space telescope secondary mirror deployed
NASA reports that the secondary mirror of the James Webb Space Telescope has successfully unfolded and is now in position.
Mission operations controllers are now working to drive latches into place to secure the mirror in its deployed configuration. Here's a look of how the operation went:
NASA Webb mirror deployment webcast begins
NASA's live webcast of the James Webb Space Telescope's secondary mirror deployment has begun! You can watch live in the window above.
NASA to Webbcast secondary tescope mirror deployment
Update: NASA's webcast will now begin at 10:20 a.m. EST (1520 GMT).
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope will deploy its secondary mirror today and you'll be able to follow the milestone live in a webcast today beginning at 10:20 a.m. EST (1520 GMT).
During this step, Webb will unfold a series of booms that hold the secondary mirror out in front of the observatory's main multi-segmented mirror. You'll be able to watch the live webcast on this page once it begins, and you can watch it directly from NASA here.
"Webb's secondary mirror is at the end of the Secondary Mirror Support Structure (SMSS)," NASA wrote in a deployment description. "As it is deployed, its long booms will swing the secondary mirror out in front of the primary mirror. The secondary mirror plays an important role in reflecting the light from the primary mirror to where the instruments sit, behind the primary mirror."
On Monday, Webb completed its huge sunshield deployment. Here's a look at what's ahead this week for the James Webb Space Telescope this week.
Listen to NASA's sunshield briefing
Today's live broadcast of the Webb telescope sunshield and deployments media teleconference did not air live on NASA TV as the agency said it would — but you can now listen to a recording of the briefing on YouTube.
NASA briefing coming soon...
NASA officials will hold a media teleconference at 12:45 p.m EST (1745 GMT) today to discuss the recently completed deployment of the James Webb Space Telescope's sunshield and go over next steps for the observatory.
You can listen to the teleconference live in the window above, courtesy of NASA TV, or directly via nasa.gov/live.
James Webb Space Telescope sunshield tensioning complete!
NASA has just confirmed that the fifth and final layer of the James Webb Space Telescope's heat shield has been successfully tensioned, marking the end of the sunshield deployment work that began last week.
"This is an historic day," NASA scientist Michelle Thaller said during a live webcast. "The first major phase of the deployment of the sunshield has been compete."
Our wrap story on the event will be posted shortly.
NASA webcast for Webb sunshield tensioning
Update: NASA's Webb sunshield tensioning webcast is under way. Watch live above for the critical milestone for the James Webb Space Telescope.
It's Day 2 of sunshield tensioning for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope and the space agency will webcast live views from Webb's mission operations center in Baltimore, Maryland today starting at 9:30 a.m. EST (1430 GMT). You'll be able to watch that live here in the window above at start time.
NASA did not state how long the webcast will last, but the agency does have another event scheduled for 11:25 a.m. EST from the International Space Station, so it likely won't last beyond that.
Webb's sunshield tightening is the final step in the intricate unfurling of the space telescope's tennis court-sized shield to protect it from sunlight and keep it cool enough for science. It involves using a series of motors to position and tighten the five ultra-thin layers of Webb's reflective sunshield.
The process began on Monday, Jan. 3, with Layer 1 tightening and was expected to end as soon as Wednesday, Jan. 5. However, NASA is way ahead of schedule. As of late Monday, three of the five sunshield layers have been successfully tightened, the agency said in an update on Twitter.
The layers start coming and they don’t stop coming…Layers 2 and 3 are now complete! Tensioning for the final two layers of Webb’s 5-layer sunshield is planned for tomorrow. More: https://t.co/rD9IOD9gX4 #UnfoldTheUniverse pic.twitter.com/BaQKwd2MuOJanuary 4, 2022
Webb space telescope in good health, tensioning beginning
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is in good health and will begin tensioning its huge sunshield today, its mission team said today.
In a media teleconference, NASA officials said Webb will begin tightening the tension on the 1st layer of the five-layer sunshield on Webb today after two days of rest and power system optimization.
Two issues occurred over the New Year's Day holiday weekend.
First, Webb's solar arrays were not generating as much power as they could due to their factory settings. At no point was the space telescope in need of power, but NASA rebalanced the arrays so that they can now work at their peak efficiency.
Second, the motors used to tension Webb's sunshield were not staying cool enough as flight controllers preferred. They commanded Webb to change its orientation in space in a way that will keep its motors cooler during the deployment phase.
With both of those fixes in, Webb appears to be doing well in its deployment.
The tensioning process for Webb's sunshield should take at least three days, NASA officials said.
NASA to hold press conference on Webb deployment
NASA will hold a media teleconference at 11:30 a.m. EST (1630 GMT) today, Jan. 3, and you can listen to it live here, courtesy of NASA TV. You can also watch directly from NASA here.
This teleconference will update the public on the James Webb Space Telescope's deployment after its sunshield was deployed on Dec. 31.
NASA paused deployment activities on Saturday, Jan. 1, to give its team a rest. The team then spent Sunday studying Webb's power systems before proceeding with the final steps for sunshield deployment.
James Webb Space Telescope tension could begin today
After a day of delay, NASA James Webb Space Telescope flight controllers are expected to begin the sunshield tightening process on the new space observatory today, Jan. 3.
The process, which could take at least two days, was initially slated to begin yesterday, but NASA opted to stand down and instead study Webb's power systems to make sure they were working properly after a week in space.
The sunshield tightening process involves activating a series of motors on Webb that will separate, and then tighten, the five layers of the space telescope's gossamer sunshield, which is blocks out sunlight from the infrared observatory's sensitive instruments so it can better study the universe. -- Tariq Malik
NASA delays Webb sunshield tensioning
NASA flight controllers have delayed today's planned tensioning of the James Webb Space Telescope's sunshield in order to work on the observatory's power systems.
"This will ensure Webb is in prime condition to begin the next major deployment step in its unfolding process," NASA officials wrote in an update today (Jan. 2).
Read our full story by Senior Writer Meghan Bartels.
The sunshield tensioning process will now begin no earlier than Monday, Jan. 3, and is expected to take at least two days. Flight controllers made the decision earlier today in order to optimize the power systems on the Webb space telescope.
"Specifically, the team is analyzing how the power subsystem is operating now that several of the major deployments have been completed," NASA wrote in the update. "Simultaneously, the deployments team is working to make sure motors that are key to the tensioning process are at the optimal temperatures prior to beginning that operation."
Webb's step-by-step deployment process is designed in such a way that it can be stopped and started along the way as required, according to NASA officials. The flight control team wants to use some extra time to better understand how Webb is behaving in space, and how it is differing from simulations based on computer testing on the ground.
“Nothing we can learn from simulations on the ground is as good as analyzing the observatory when it’s up and running,” said Bill Ochs, NASA's Webb project manager at the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, said in the update. "Now is the time to take the opportunity to learn everything we can about its baseline operations. Then we will take the next steps." -- Tariq Malik
Webb ratchets up the tension today
It's time to raise the tension on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope.
After taking New Year's Day off on Saturday to rest up after a long Friday night unfolding Webb's massive sunshield, the mission team aims to begin tensioning the shield's five layers today to lock them in place.
It should take at least two full days to lock Webb's sunshield in place, which marks the final step in its weeklong deployment process. The process involves Webb separating the five layers of its sunshield, which unfolded in a single group and then tensioning them so they are tightly secured for the space telescope's lifetime.
NASA expects to complete the sunshield tightening step on Monday, Jan. 3, and will then hold a press teleconference to update the public on the space telescope's status. - Tariq Malik
Taking a rest day
The team overseeing the deployment of the James Webb Space Telescope are taking today (Jan. 1) off, according to a NASA statement. Yesterday's procedure, deploying the two booms that support the width of the observatory's massive sunshield, ran later into the day than personnel had hoped. And the next step is even more daunting: a two-day process of separating the five delicate layers of the vast sunshield.
That work will begin tomorrow (Jan. 2), the statement noted, and is expected to take two days to complete. Read more>
James Webb unfurls its sunshield!
The James Webb Space Telescope successfully unfurled its massive sunshield on Friday (Dec. 31), notching a huge milestone in its long and complex deployment campaign. Read our full story about it here.
The sunshield, which will help keep Webb's optics and instruments cool enough to detect faint heat signals from the early universe, unfolded via two "mid-booms," which were extended over two roughly three-hour stretches on Friday.
The boom extension activities were delayed slightly while Webb team members checked to make sure the sunshield's protective cover had fully rolled up as needed. But everything worked out just fine.
"Today is an example of why we continue to say that we don’t think our deployment schedule might change, but that we expect it to change," Keith Parrish, Webb observatory manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, said in a blog post update Friday night.
"The team did what we had rehearsed for this kind of situation — stop, assess and move forward methodically with a plan," Parrish said. "We still have a long way to go with this whole deployment process."
Next up is tensioning of the sunshield's five layers, which could be complete as early as Sunday (Jan. 2). After that, the Webb team will shift their focus to mirror deployment.
Sunshield halfway unfurled!
The James Webb Space Telescope has successfully deployed its sunshield port mid-boom, unfurling half of the huge membranous structure.
"The deployment of the 5 telescoping segments of the mid-boom began around 1:30pm ET and reached full deployment at 4:49 pm," mission team members said via Twitter today (Dec. 31). "Webb's deployment steps are all human-controlled, so the schedule can change. The team plans to deploy the starboard mid-boom tonight."
There was indeed a schedule change today: The mid-boom deployments were supposed to happen earlier, but Webb's handlers took extra time to make sure the sunshield's protective cover had fully rolled up as planned, mission team members explained in another tweet.
Sunshield deployment is one of the riskiest, most complex activities the $10 billion observatory will perform during its time in space. So keep your fingers crossed that everything goes well tonight and over the weekend, when the team plans to bring the deployed shield's layers up to the proper tension.
James Webb Space Telescope to deploy sunshield booms
It's a big day for the James Webb Space Telescope.
Today is the day the huge space observatory will deploy the two mid-booms on it port and starboard side that will extend its sunshield out to its full width. The port boom will be extended first, followed by the starboard boom. Motors will drive both events.
Each mid-boom will deploy with its five sunshield membrane layers attached. If it goes smoothly, Webb will spend the next two days tightening the tension of the sunshield so it's not loose.
Wondering why it takes so many steps to deploy Webb's sunshield? Our Senior Writer Mike Wall has the full story here today.
Webb deploys flab, removes sunshield covers
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope successfully completed its two critical deployments for today, the space agency announced.
In back-to-back updates, NASA officials confirmed that the Webb space telescope successfully deployed its aft momentum flap and retracted the protective membrane covers on its gossamer sunshield, a major step in the weeklong work to unfurl the shield.
Read the full story from Senior Writer Chelsea Gohd here.
The membrane covers protected Webb's sunshield, which will be as large as a tennis court when deployed, during launch. You can see an animation of how the cover retraction went in space above.
Here's a close-up graphic below of the aft momentum flap, which is designed to steady Webb against the push of solar wind against its huge sunshield. -- Tariq Malik
2 deployment steps for Webb telescope today
It's been five days since NASA's James Webb Space Telescope launched into space on the observatory has two steps planned for today to continue its ultra-complicated deployment.
Today, Webb is expected to unfold a aft momentum flap, a three-panel structure at the bottom rear of the telescope designed to offset some of the pressure from the solar wind on Webb's massive sunshield. The flap should help Webb conserve fuel during its mission life as it limits the extra push on the telescope from the solar wind.
Later, Webb is expected to retract the sunshield membrane covers that have been protecting its thin sunshield layers since launch. The step will require a series of release devices to be activated that will then retract and roll up the membrane covers (two per sunshield pallet, fore and aft) to uncover the sunshield itself.
When deployed, the five-layer sunshield will be about the size of a tennis court. But there are 50 distinct steps to get it into place.
You can explore exactly how Webb is unfolding at NASA's Deployment Explorer website here. -- Tariq Malik
JWST extends its Deployable Tower Assembly
The James Webb Space Telescope has successfully completed the deployment of the tower assembly that separates the two main halves of the spacecraft.
The observatory's Deployable Tower Assembly took a little over 6.5 hours to extend, creating about 4 feet (1.2 meters) of space between the mirror assembly and the spacecraft's bus, which houses its electronics and propulsion systems, NASA officials said in a statement.
"This creates enough distance to allow the sensitive mirrors and instruments to cool down to the necessary temperatures to detect infrared light," NASA said in the statement. "This gap will also provide room for the sunshield membranes to fully unfold."
Read the full story here
Correction: This post was updated to correct the distance of space created by the tower deployment, it is 4 feet, not 2 feet.
Next up: Deployable Tower Assembly
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has begun extending its Deployable Tower Assembly, according to an agency update. The process, which began shortly after 9 a.m. EST (1400 GMT), will take at least six hours and creates space for the observatory's sunshield to deploy.
Good news: Webb has plenty of fuel for years of science

According to a NASA update, the James Webb Space Telescope may have enough fuel to more than double its minimum lifetime thanks to the precision of its launch and the two trajectory corrections the spacecraft has made to date.
"The Webb team has analyzed its initial trajectory and determined the observatory should have enough propellant to allow support of science operations in orbit for significantly more than a 10-year science lifetime. (The minimum baseline for the mission is five years.)" agency officials wrote in an update posted Dec. 29.
However, NASA emphasized that it is not providing a new mission timeline for the long-awaited observatory. "Consequently, Webb will have much more than the baseline estimate of propellant — though many factors could ultimately affect Webb's duration of operation," officials wrote in the statement. Read more>
Webb's sunshield unfolds some more
The James Webb Space Telescope has successfully completed deploying both pallet structures of its sunshield, notching another milestone in the five-day-long process of unfurling the massive sunshield.
After deploying the forward pallet earlier today, the aft pallet finished deploying at approximately 7:27 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Dec. 28 (0027 GMT on Dec. 29).
"While the actual motion to lower the forward pallet from its stowed to its deployed position took only 20 minutes, and the lowering of the aft pallet took only 18 minutes, the overall process took several hours for each because of the dozens of additional steps required," NASA officials said in a statement.
"These include closely monitoring structural temperatures, maneuvering the observatory with respect to the sun to provide optimal temperatures, turning on heaters to warm key components, activating release mechanisms, configuring electronics and software, and ultimately latching the pallets into place."
Sunshield deployment has begun!
The James Webb Space Telescope has begun deploying its massive sunshield, a vital component of the observatory. The spacecraft unfolded its Forward Unitized Pallet Structure, which supports the sunshield, on Tuesday (Dec. 28). Read more>
Webb has crossed the moon's orbit
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is now farther from Earth than the moon's orbit, according to an agency update posted late Monday (Dec. 27). The spacecraft also completed its second of three trajectory correction burns. Next up, the observatory will begin deploying its massive sunshield. Read more>
Webb telescope maneuver planned
It's day three of NASA's "29 days on the edge" for the James Webb Space Telescope and today's main goal is to perform the second of three mid-course correction burns to refine Webb's path to its new home at Lagrange point 2, or L2, nearly 1 million miles (1.6 million km) from Earth.
Latest story: James Webb Space Telescope successfully deploys antenna
Webb performed its first, and biggest, course correction burn on Saturday, Dec. 25, after launching into space. The third burn will occur on day 29 to enter its final orbit around the L2 point.
Here's how NASA describes today's planned burn on its deployment guide:
"This burn fine-tunes Webb's trajectory after launch. The duration of the burn will depend on Ariane 5 launcher performance.
"There are three mid-course correction (MCC) maneuvers: MCC-1a, MCC-1b, and MCC-2. This is the second. The first burn, MCC-1a, is the most important and the only other time-critical operation aside from solar array deployment during Webb’s commissioning period.
"The second, MCC-1b, is a shorter burn performed before the sunshield deployment is scheduled to start. The final maneuver, MCC-2, performed 29 days after launch, is designed to insert Webb into the optimum orbit around L2.
Antenna deployment successful
A day after launch, the James Webb Space Telescope continues to travel away from Earth and set itself up for observations in the months to come.
Beginning on Sunday (Dec. 26) at about 10 a.m. EST (1500 GMT), the spacecraft deployed and tested a key antenna in a process that took about one hour, according to a NASA statement. The antenna will be responsible for twice-daily science data dumps to Earth.
In addition, the spacecraft's temperature sensors and strain gauges began work overnight. The next stage in the telescope's deployment, according to NASA, will be a second course-correction burn scheduled to occur about two days after launch.
Crucial burn complete, NASA says
The James Webb Space Telescope successfully executed a vital burn to correct its trajectory, according to a NASA statement. The burn began at 7:50 p.m. EST (0050 GMT) and lasted for 65 minutes, according to the agency. The maneuver also marked the last step of the mission's deployment that needed to be executed at a specific time; from now on, mission personnel can adapt the deployment timeline as needed. Read more>
Presidential congratulations
Congratulations @NASA and all who made today’s launch of the James Webb telescope possible. Webb is a shining example of the power of what we can accomplish when we dream big. We've always known that this project would be a risky endeavor, but with big risk comes big rewards.December 25, 2021
President Joe Biden offered his congratulations on the successful launch of the James Webb Space Telescope the evening of its flawless launch. "Congratulations @NASA and all who made today's launch of the James Webb telescope possible," Biden wrote in a tweet. "Webb is a shining example of the power of what we can accomplish when we dream big. We've always known that this project would be a risky endeavor, but with big risk comes big rewards."
Where is NASA's James Webb Space Telescope?
It's been just over 7 hours since NASA's James Webb Space Telescope launched into space and the space telescope is currently more than 67,800 miles (109,110 kilometers) away and climbing as it makes its way toward its destination: Lagrange Point 2.
Full story: NASA's James Webb Space Telescope launches on epic mission to study early universe
More: 'It's truly Christmas': James Webb Space Telescope's yuletide launch has NASA overjoyed
In photos: The Christmas launch of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope
You can track the Webb space telescope with NASA's Where is Webb website online, which uses real-time telemetry from the spacecraft to present a precise picture of where the space telescope is and at what stage its deployment is in.
It will take about 29 days for Webb to reach L2 nearly 1 million miles (1.6 million km) from Earth, and about six months before it will be ready to begin snapping images of the universe.
The next milestone for Webb will be a mid-course correction burn, a maneuver in deep space to fine-tune the space telescope on its path to L2.
'It's truly Christmas!' NASA on JWST launch
NASA chief Bill Nelson called today's successful launch of the James Webb Space Telescope a "good day for Earth" as NASA and its partners celebrate the successful beginning of a $10 billion mission.
Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA's associate administrator for science missions, said it's a Christmas to remember.
"What am amazing day," Zurbuchen said. "It's truly Christmas with all the presents and everything and we have a space mission."
Post-launch press conference for JWST
With NASA's James Webb Space Telescope successfully launched, the space agency and its partners will hold a press conference soon to celebrate the successful liftoff.
The press conference is expected to begin by 9 a.m. EST (1400 GMT) and should include the heads of agencies who built James Webb, as well as leading mission scientists.
You can watch it live in the window above. Meanwhile, here's a look back at today's successful launch.
James Webb Space Telescope launch a success
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is successfully in space and beginning its monthlong trek to its L2 home about 1 million miles from Earth.
Full story: NASA's James Webb Space Telescope launches on epic mission to study early universe
"It's a great day for planet Earth," NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said after the launch. "We are going to discover incredible things that we never imagined."
The accolades are pouring in from the space agencies who worked together to put the space telescope together with a series of interviews on NASA TV.
Spacecraft separation and solar array deploy
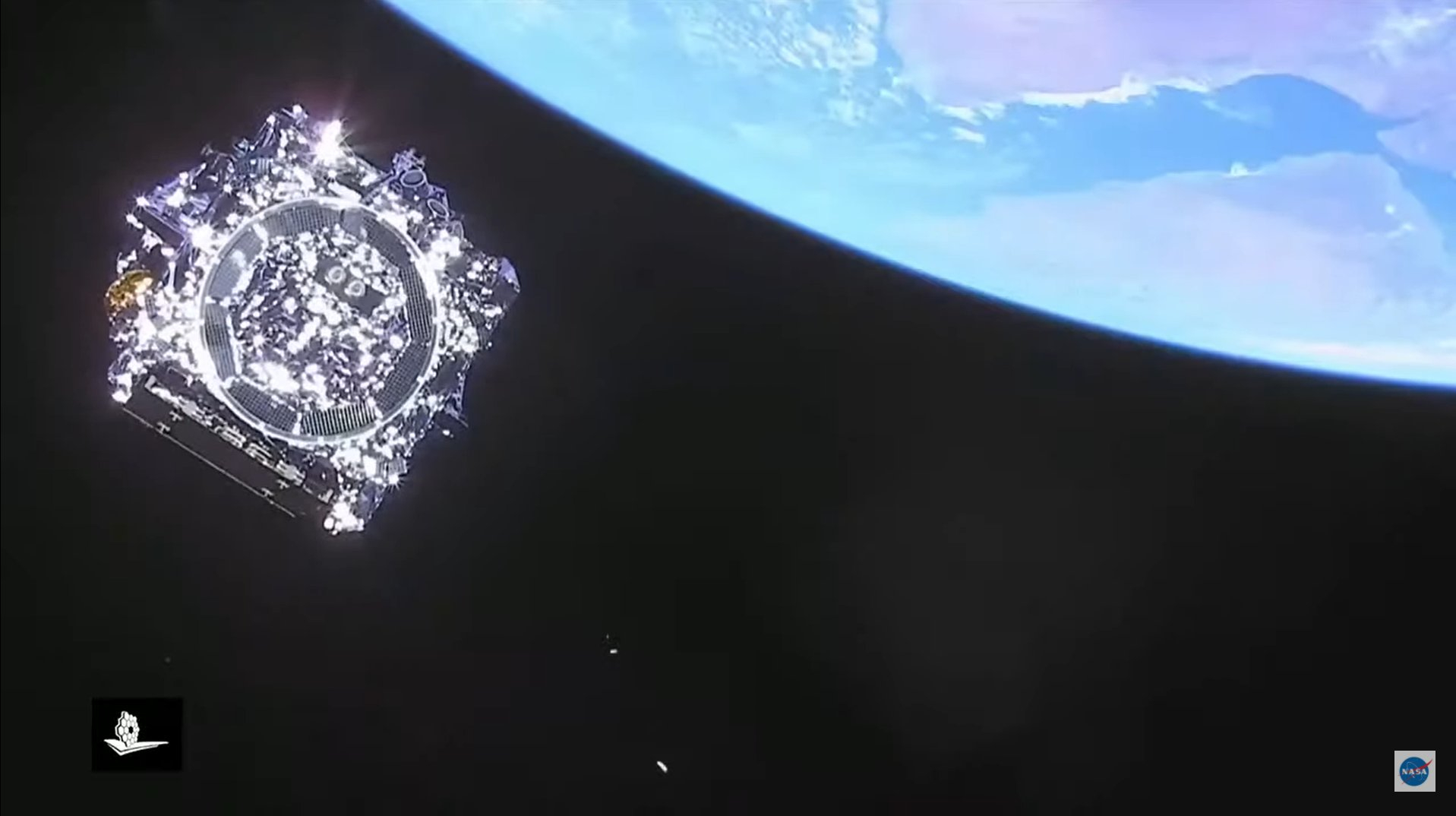

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has successfully separated from its Ariane 5 rocket and deployed its solar array to mark a flawless trip into space after today's launch.
A camera on Webb's Ariane 5 rocket upper stage beamed live views of the event, with solar array deployment occurring a bit early.
'Go, Webb, go!" rang cheers from Arianespace launch control at the Guiana Space Center in French Guiana.
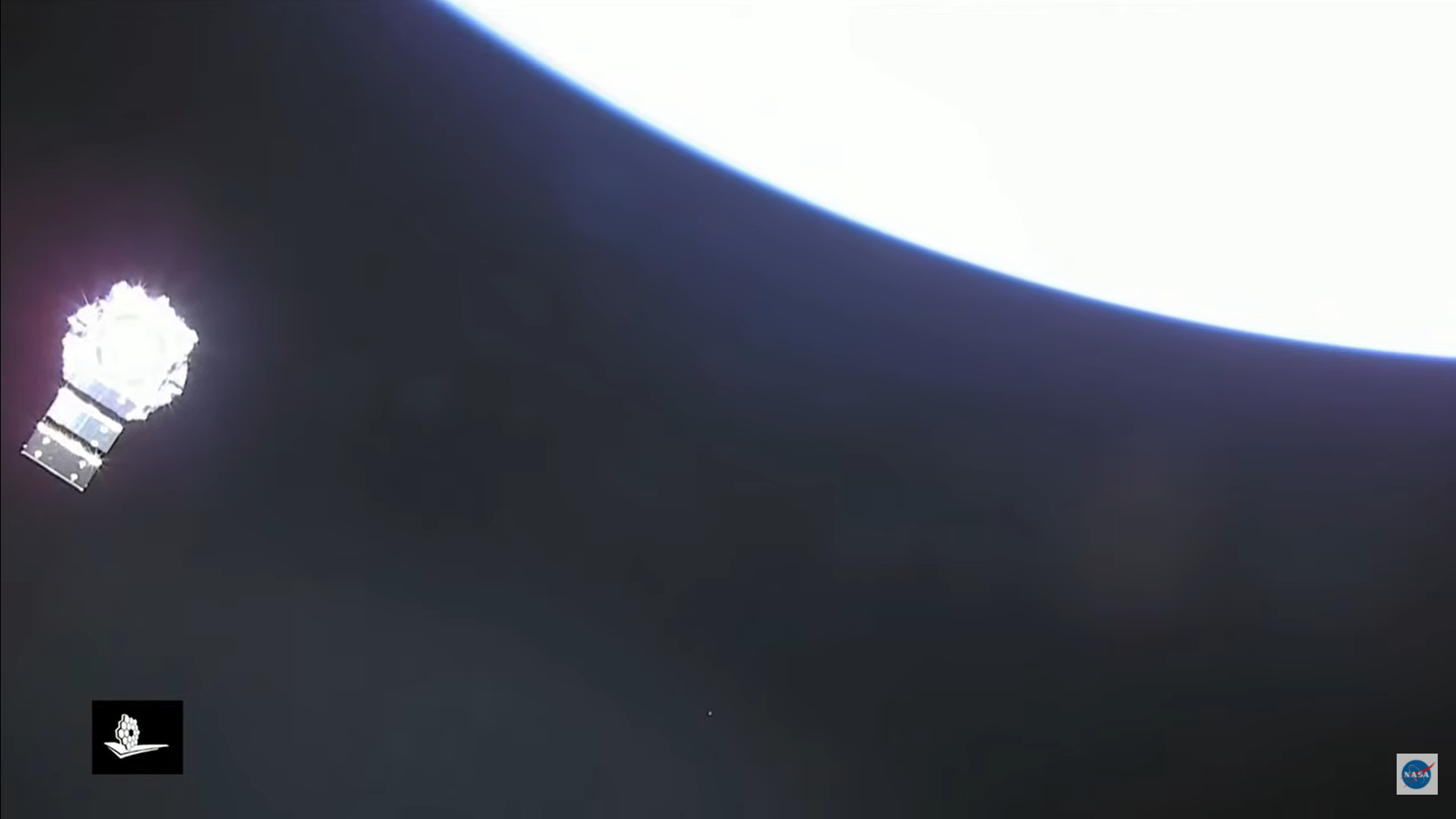

2nd stage shutdown
2nd stage shutdown: The Ariane 5 upper stage engine carrying NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has shut down as planned.
James Webb Space Telescope on track during ascent
The Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA's James Webb Space Telescope continues its 2nd stage burn to carry the telescope into space.
"Very quiet now in the room," NASA spokesperson Rob Navias says of launch control. Officials with NASA, Arianespace and their partners are watching telemetry carefully, he says.
So far, all systems are working as expected.
"Today's countdown was as flawless as you can imagine," Navias said. "Everything fell together on this Christmas Day to send a new present to the world's astronomers."
4 minutes of powered flight remain.
Upper Stage separation and ignition
Stage Separation: The Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has jettisoned its main stage and ignited its upper stage to continue powering the James Webb Space Telescope into orbit.
View of James Webb Space Telescope on Ariane 5
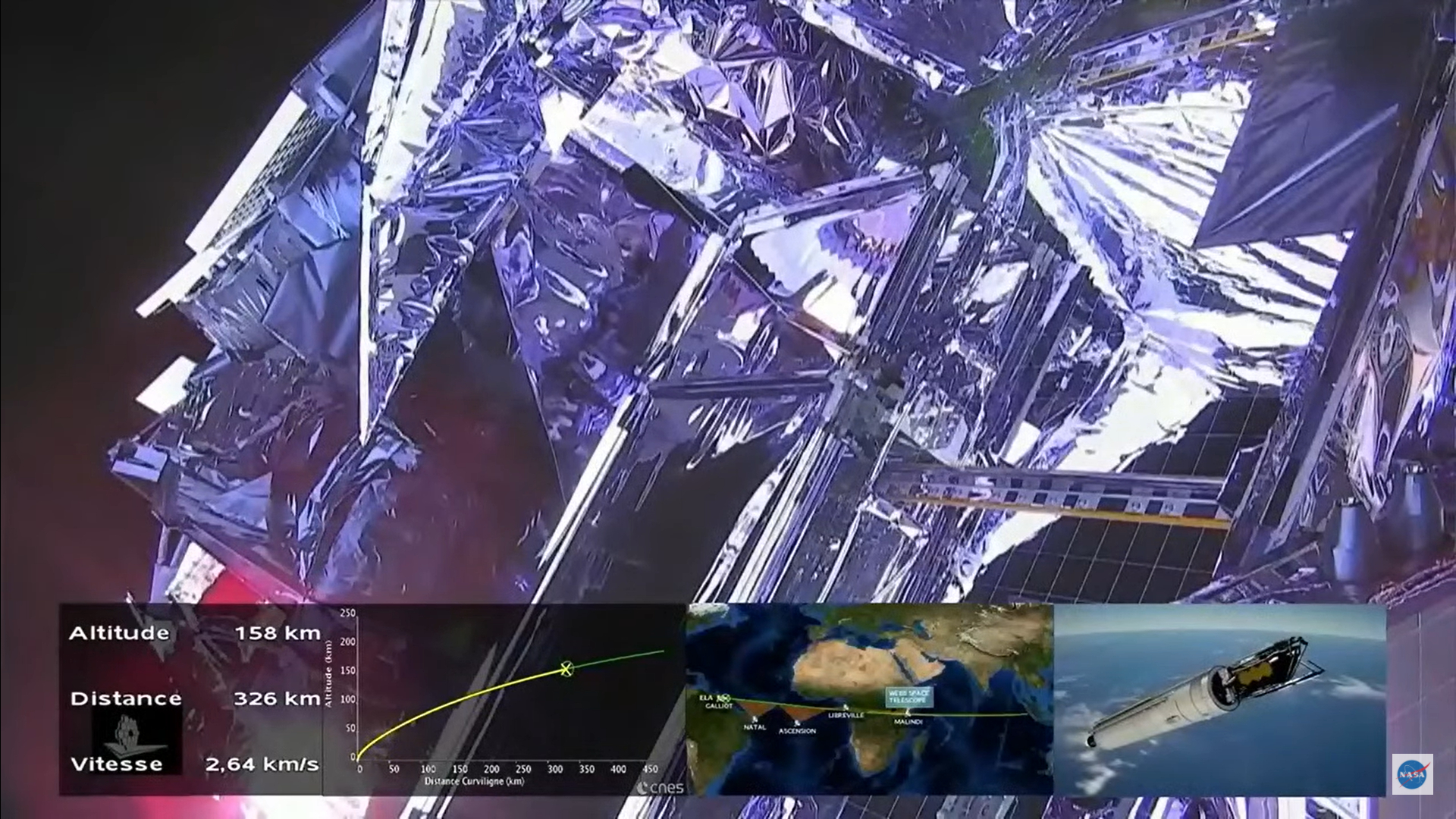
A camera aboard today's Ariane 5 rocket launch has captured a view of the James Webb Space Telescope folded up for launch.
You can see that image above here.
Webb continues its ascent on its Ariane 5.
Stage separation for Ariane 5, Fairing separation
Stage separation: The 2 strap on boosters for the Ariane 5 rocket carrying the James Webb Space Telescope have separated as planned.
The rocket has also jettisoned its payload fairing.
"All parameters normal," Arianespace reports.
Liftoff for the James Webb Space Telescope!
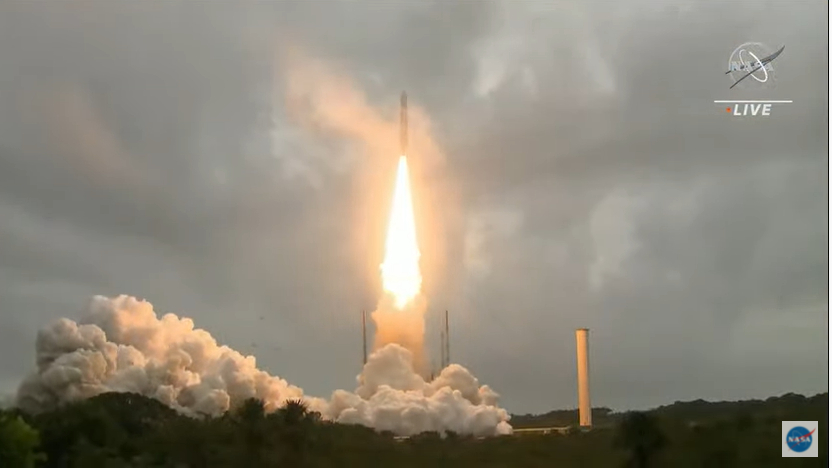

LIFTOFF! NASA's James Webb Space Telescope launches on a mission to seek out the earliest light of the universe
James Webb Space Telescope in final countdown
The Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is now in its final automated launch countdown sequence.
A final launch weather check reveals good conditions for launch, Arianespace reports.
Less than 3 minutes remain until launch.
JWST launching 53 years after Apollo 8 Christmas broadcast
NASA spokesperson Rob Navias took a moment in today's James Webb Space Telescope launch broadcast to remind viewers Webb is launching on Christmas Day, 53 years after NASA's Apollo 8 crew beamed a Christmas Eve message to Earth from the moon. In that Christmas broadcast in 1968, the Apollo 8 astronauts read from the Bible's Book of Genesis to mark the holiday.
"Today, more than a half century later. we're just minutes away from another Genesis, the genesis of a new era of discovery," Navias said. "The launch of the James Webb Space Telescope is at hand."
James Webb Space Telescope on internal power
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is on internal battery power for today's launch, a major milestone head of launch. NASA spokesperson Rob Navias says the observatory will remain on internal battery power until its solar arrays deploy about 30 minutes after liftoff.
It's a cloudy day in Kourou for today's launch, but Navias says all systems are still green.
"Don't let those clouds fool you, we are go for launch," Navias said.
T-30 minutes to James Webb Space Telescope launch
The James Webb Space Telescope is less than 30 minutes from launch for today's Ariane 5 liftoff.
NASA spokesperson James Webb Space Telescope Rob Navias at the launch site reports all systems are green for launch so far, with liftoff on track for a 7:20 a.m. EST (1220 GMT) ignition.
Fueling complete for James Webb Space Telescope
Fueling is now complete! 👍Our #Ariane5 is sitting tight @EuropeSpacePort with its passenger: @NASAWebb/@ESA_Webb!#VA256 #WebbFliesAriane pic.twitter.com/LPs5y7xg0NDecember 25, 2021
Arianespace reports the fueling process for the Ariane 5 rocket is now complete for today's launch of the James Webb Space Telescope.
NASA launch webcast live for JWST launch
Merry Christmas, space fans, it's launch day for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope.
After months of delays, the new Great Observatory is ready to launch at 7:20 a.m. EST (1220 GMT) atop an Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. NASA's live launch webcast has begun for this Christmas launch, a rare event for NASA.
NASA is kicking off its webcast with its epic trailer for the James Webb Space Telescope mission, which uses the words of famed astronomer Carl Sagan.
'Go' for fueling
The Ariane 5 rocket that will launch the James Webb Space Telescope will begin fueling up for liftoff soon, according to the brief update just aired on NASA TV.
"Within the last hour mission controllers ... received a comprehensive weather briefing and we were told conditions were 'go' for the start of the loading of 175 tons of propellant into the core or first stage of the Ariane five rocket," a NASA spokesperson said in the update on NASA TV.
"150 tons of liquid oxygen and 25 tons of liquid hydrogen will soon be flowing into the first stage tanks of the Ariane 5. This process will take about two hours to complete. About an hour from now some 15 tons of propellant will be loaded into the second stage, or upper stage, of the Ariane 5 — another two-hour process, which should be complete around one hour and 22 minutes before launch."
Go for fueling! 😊Get ready for our Flight #VA256 with @NASAWebb/@ESA_Webb on board #Ariane5!#VA256 #WebbFliesAriane pic.twitter.com/LxZ5ASoszqDecember 25, 2021
NASA to provide Webb telescope update
NASA officials are about to give a status update on the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope. You can watch it live in the window above, courtesy of NASA TV, or directly via YouTube.
Just one day left
The James Webb Space Telescope is still on track for a Christmas Day launch, after spending the night of Dec. 23 on the launch pad in Kourou, French Guiana. Arianespace, which built the Ariane 5 rocket carrying the observatory, has confirmed that the weather forecast looks promising for the Saturday launch attempt. "Latest weather forecast just arrived and we are still good to go for tomorrow!" the European launch provider wrote in a statement posted to Twitter.
Webb is on the launch pad!
The Ariane 5 rocket carrying the James Webb Space Telescope made the two-hour trek out to the launch pad at Kourou, French Guiana, on Thursday (Dec. 23). See more photos
Roll-out is coming!
Let the roll-out to the launch pad begin for @ariane5 and #Webb! 🚀The doors of the assembly building have opened @EuropeSpacePort #WebbFliesAriane #JWST #VA256 📸 ESA - S. Corvaja pic.twitter.com/iMfgce4yLiDecember 23, 2021
The James Webb Space Telescope and its Ariane 5 rocket will begin the slow march to the launch pad at Kourou, French Guiana, in advance of the mission's Saturday morning launch at about 10 a.m. EST (1500 GMT) on Dec. 23.
Christmas Day launch still on track for JWST
The target launch date for the @NASAWebb/@ESA_Webb is confirmed on December 25, as early as possible within the following launch window: pic.twitter.com/aGB1ABzML5December 22, 2021
Arianespace, the European company responsible for launching the James Webb Space Telescope, confirmed in a tweet on Wednesday (Dec. 22) afternoon that they were still targeting Christmas Day (Saturday, Dec. 25) for the launch of the massive observatory.
The rocket, an Ariane 5, will roll out to the launch pad at Kourou, French Guiana, on Thursday morning (Dec. 23), the company noted.
High winds delay launch to Christmas
However, due to adverse weather conditions at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana, the flight #VA256 to launch the James Webb Space Telescope –initially scheduled for December 24– is being postponed.December 21, 2021
Arianespace has announced that due to upper-level winds, it will not attempt to launch the James Webb Space Telescope on Friday (Dec. 24). The next launch opportunity will be Saturday (Dec. 25) beginning at 7:20 a.m. EST (1220 GMT).
NASA Webb Space Telescope prelaunch briefing
With the clocking steadily ticking toward a Christmas Eve launch for the James Webb Space Telescope, NASA and its partners will hold a prelaunch teleconference for the mission today, Dec. 21, at 2 p.m. EST (1900 GMT) and you can watch it live.
The webcast will be broadcast on NASA Live and simulcast in the audio player at the top of this page.
Speaking during today's prelaunch press conference will be:
- NASA Administrator Bill Nelson
- NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy
- Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters in Washington
- Greg Robinson, Webb program director, NASA Headquarters
- Jérôme Rives, vice president, Ariane 5 Business Unit, Arianespace, Paris, France
- Amber Straughn, Webb deputy project scientist for communications, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland
Three days until launch!
With three days to go before the James Webb Space Telescope launches, NASA has released a mission trailer paired with archival audio of the iconic astronomer Carl Sagan. "If we crave some cosmic purpose, then let us find ourselves a worthy goal," Sagan said. Watch the full trailer above.
And learn about the incredible engineering behind the most complex space observatory ever built with a deep dive into the telescope that "is not allowed to fail" in this new feature story.
What will the James Webb Space Telescope tell us about dark matter?
The world's most powerful space telescope is about to launch, and scientists think it could reveal incredible new information about dark matter.
The James Webb Space Telescope is set to launch on Dec. 24. from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana. By observing primarily in infrared, the massive telescope will be able to peer back farther than ever into the cosmos, revealing new information about our early universe. However, additionally, scientists think that the scope could utilize the phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, from Einstein's general theory of relativity, to indirectly "observe" evidence of dark matter.
It's Launch Week for James Webb Space Telescope

It's launch week for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope and as the days count down to its Christmas Eve launch on Dec. 24, we're taking a look at the science promised by the huge new space observatory.
Today's feature: James Webb Space Telescope vs. Hubble: How will their images compare?
Space.com senior writer Chelsea Gohd takes a look at the fundamental differences between the iconic Hubble Space Telescope, which can capture images in visible light, and the James Webb Space Telescope, which is solely an infrared observatory, but one so sensitive it's designed to peer back closer to the birth of the universe than ever before.
Dec. 24 launch date confirmed for Webb space telescope
NASA and its partners officially confirmed Dec. 24 as the launch target for the new James Webb Space Telescope. Liftoff is set for 7:20 a.m. EST (1220 GMT) from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana.
Read our full story on the confirmed launch date here.
NASA confirmed the launch target today in a blog post, stating that the Webb space telescope is packed inside its nosecone and attached to its Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket.
"The James Webb Space Telescope is confirmed for the target launch date of Dec. 24, at 7:20 a.m. EST," NASA wrote. "Late yesterday, teams at the launch site successfully completed encapsulation of the observatory inside the Ariane 5 rocket that will launch it to space. Webb’s launch final readiness review will be held on Tuesday Dec. 21 and, if successful, roll-out is planned for Wednesday, Dec. 22."
Launch date confirmation coming Saturday
The James Webb Space Telescope is still tentatively scheduled to launch on Dec. 24, but the launch date won't be officially confirmed until tomorrow (Saturday, Dec. 18), according to Arianespace CEO Stéphane Israël.
"Final encapsulation operations ongoing," Israël tweeted late Friday. "Target launch date is December 24 at 12:20 am UTC. Confirmation Saturday."
Final encapsulation operations ongoing. Need a few more hours to complete them. Target launch date is December 24 at 12:20 am UTC. Confirmation Saturday. Go @NASAWebb/@ESA_Webb! Go #Ariane5! Go! 🎅🚀#WebbFliesAriane #VA256 pic.twitter.com/15wvWpaD3RDecember 17, 2021
NASA, ESA discussing Webb space telescope launch date
NASA and the European Space Agency are discussing their options today (Dec. 17) on when to launch the multibillion-dollar James Webb Space Telescope.
Earlier this week, the two agencies and their partners delayed the Webb telescope's Dec. 22 launch after a data cable issue prevented communications between the observatory and equipment with its Ariane 5 rocket. The launch is currently targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, but that launch date could change.
NASA and ESA have both said they will announce a firmer launch date by then end of the day today, Dec. 17. The faulty data cable on Webb was fixed yesterday afternoon and engineers were expected to perform final tests before making a decision on whether to close up the space telescope inside its clamshell-like payload fairing.
The Webb space telescope is NASA's next "Great Observatory" and set to launch on an Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket from Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana.
The mission has been delayed several times in recent months, from an October launch target to late December due to launch preparation issues.
Data cable fixed on James Webb Space Telescope
Just in from the Webb launch site: The team has fixed the connection issue and @NASAWebb is in the midst of its final scheduled aliveness test before launch. We’ll provide an additional update on the status of encapsulation and the launch date tomorrow. pic.twitter.com/ehFVzfeeCIDecember 16, 2021
Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA's associate administrator for science missions, announced on Twitter today that the launch team for the agency's James Webb Space Telescope has fixed the data cable connection issue that has delayed the space observatory's launch. A new launch date will be announced on Friday, Dec. 18.
"Just in from the Webb launch site: The team has fixed the connection issue and @NASAWebb is in the midst of its final scheduled aliveness test before launch," Zurbuchen wrote on Twitter. "We'll provide an additional update on the status of encapsulation and the launch date tomorrow."
The Webb Space Telescope is currently targeted to launch no earlier than Dec. 24, two days later than planned due to the data cable issue.
Faulty cable caused JWST launch delay
A faulty communications cable is responsible for the James Webb Space Telescope's latest delay, according to the European Space Agency.
In a press conference today (Dec. 16), ESA officials said a faulty data designed to deliver data from the Webb space telescope and its rocket and launch pad equipment was not working properly.
"It's an interface issue in the electrical network connecting the observatory and the ground support equipment," Daniel Neuenschwander, ESA director of space transportation, said in the briefing. "It's a cable located in the launch table, which is experiencing some intermittent losses of data."
JWST packed for flight
On Saturday, Dec. 11, Arianespace packed NASA's James Webb Space Telescope for launch, installing the space telescope atop its Ariane 5 rocket for a planned launch from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana.
The actual launch date for the Webb space telescope is still uncertain, as NASA and Arianespace have delayed its launch (initially set for Dec. 22) to no earlier than Dec. 24. An update on launch plans for Webb is expected by Friday, Dec. 17, according to NASA.
NASA and Arianespace originally aimed to launch the Webb space telescope on Oct. 31 and have delayed it repeatedly due to integration and other issues. Watch this space for updates on a new firm launch date for the James Webb Space Telescope.
JWST launch delayed to Dec. 24

The James Webb Space Telescope is now scheduled to launch no earlier than Christmas Eve (Dec. 24), NASA announced today.
"The James Webb Space Telescope team is working a communication issue between the observatory and the launch vehicle system," NASA officials said in a statement. "This will delay the launch date to no earlier than Friday, Dec. 24. We will provide more information about the new launch date no later than Friday, Dec. 17."
James Webb Space Telescope ready to launch
After years of development and billions of dollars, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is nearly ready to launch.
Follow JWST's last days on Earth and its future as a new Great Observatory for NASA, the European Space Agency, Canadian Space Agency and the world in our live coverage here.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.