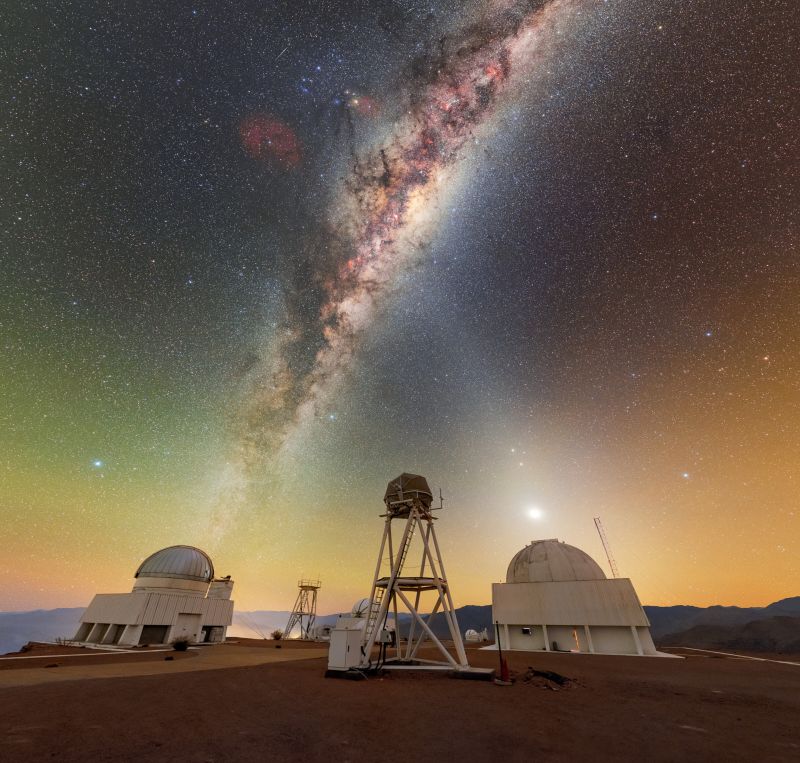
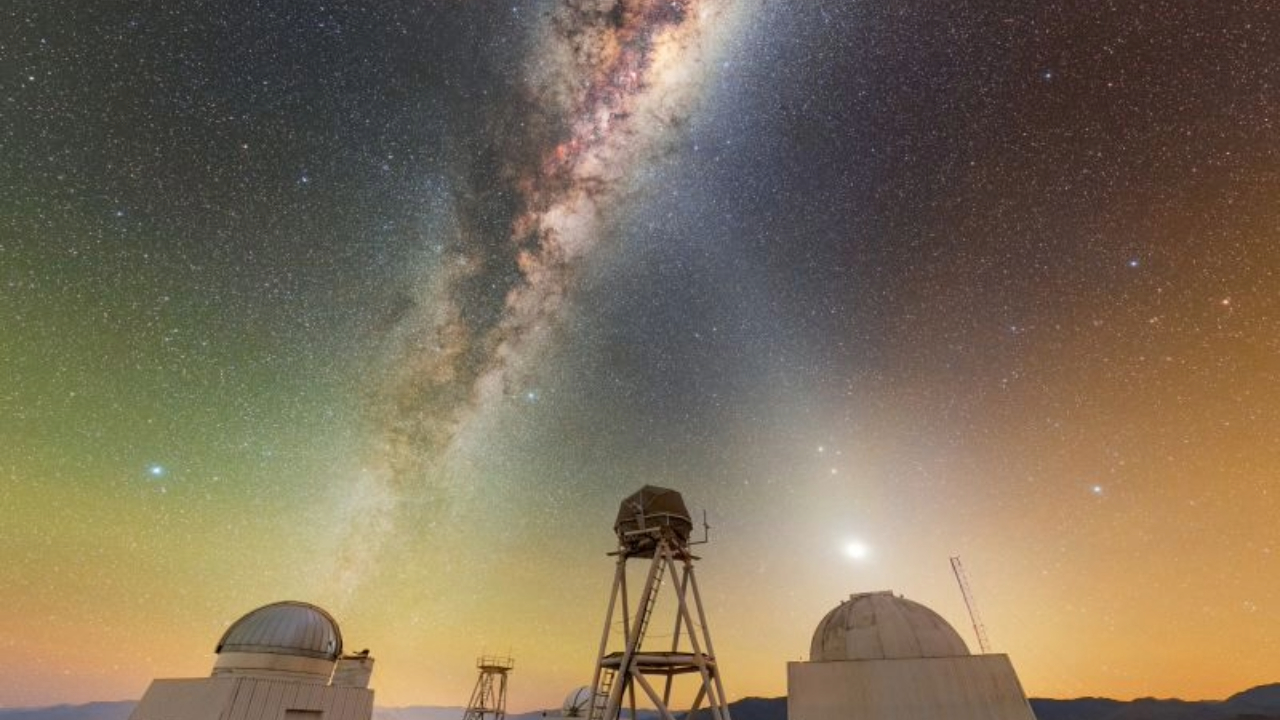
Milky Way and zodiacal light glow above telescopes in Chile | Space photo of the day for Aug. 15, 2025
The unique zodiacal light phenomenon made an x-shape in the night sky for stargazers.

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
Recently, the Chilean night sky was illuminated by the glow of the Milky Way galaxy as it was seen above the domes of telescopes at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO), a facility of the National Science Foundation's (NSF) NOIRLab.
What is it?
A cone of zodiacal light intersects the iconic Milky Way, creating an x-shape in the night sky. NOIRLab highlighted this x-shape in a recent LinkedIn post, saying: " X marks the spot at Cerro Tololo!"
Zodiacal light extends in a triangular shape from Earth's horizon along the ecliptic, the apparent annual path of the sun across the sky, serving as the baseline for positions of the planets and zodiac constellations. This special light is the reflection of sunlight off particles and dust in the solar system.
Astronomers can study zodiacal light to map the distributions and possible origins of cosmic dust, revealing further insights about the processes happening in our solar system.
Where is it?
This image was taken at the CTIO facility, around 310 miles (500 km) north of Santiago, Chile at an elevation of 7,200 feet (2200 meters). Its location allows it to avoid light pollution from urban areas.
Why is it amazing?
As a major astronomical research facility, the CTIO hosts nearly 40 telescopes at it site, which offers exceptionally clear dark skies to peer deep into space. These telescopes are used for many different projects, from studying near-Earth asteroids to space debris to exoplanets.
CTIO's mission is to provide world-class observing capabilities to the global astronomical community, supporting key discoveries while helping us to further understand more about our universe.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Want to learn more?
You can read more about telescopes based in Chile and night sky photography.
Kenna Hughes-Castleberry is the Content Manager at Space.com. Formerly, she was the Science Communicator at JILA, a physics research institute. Kenna is also a freelance science journalist. Her beats include quantum technology, AI, animal intelligence, corvids, and cephalopods.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.