Northern lights chances rise for Christmas as space weather remains unsettled
Fast solar wind and a possible glancing blow from a coronal mass ejection could spark auroras over Christmas.

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
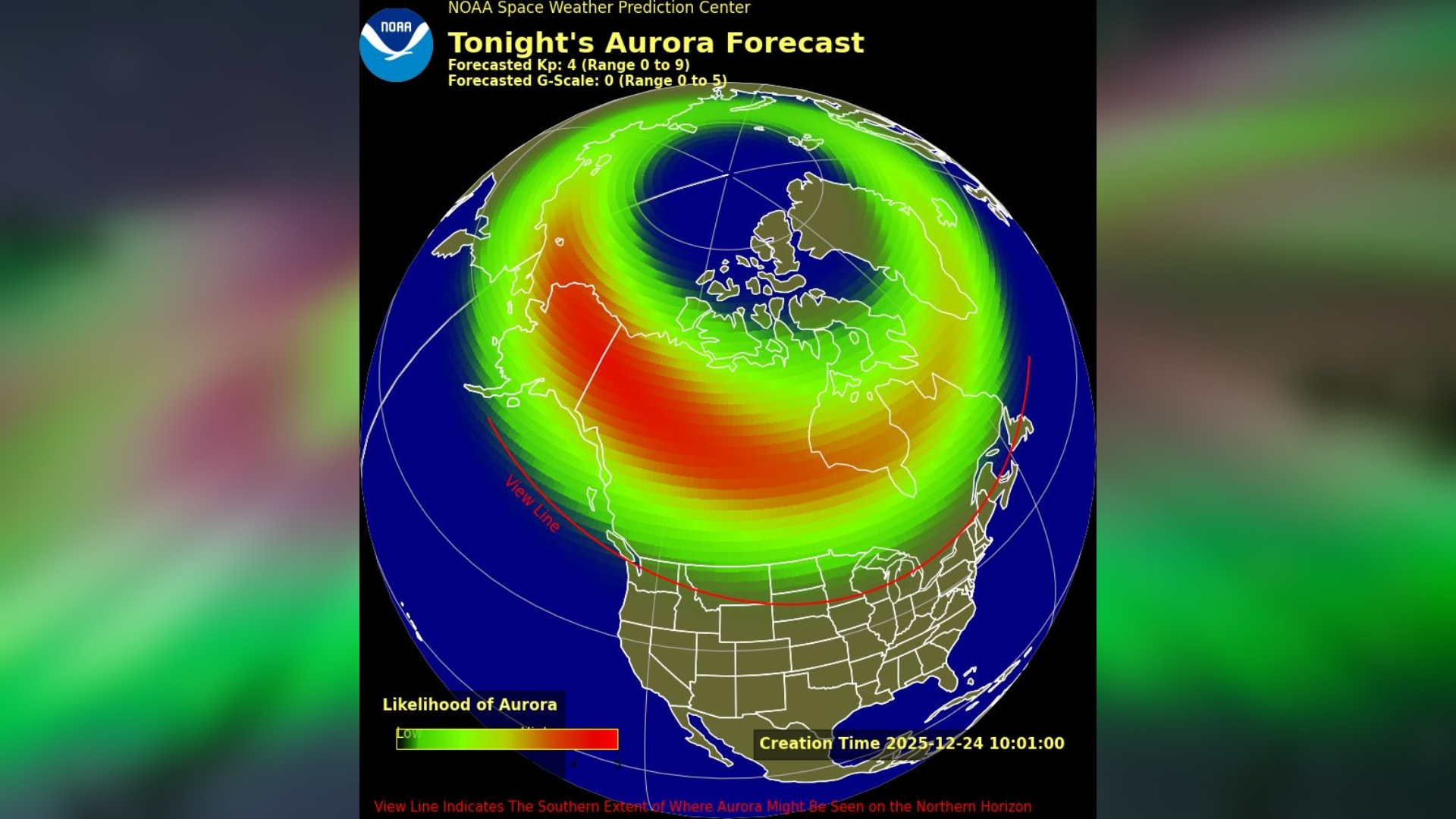
If you're hoping for a festive skywatching surprise, Christmas week is shaping up to be more active than usual in space. Fast solar wind from a large coronal hole on the sun has already triggered minor (G1) geomagnetic storms and forecasters say unsettled conditions could persist into Christmas.
While this isn't likely to be a major aurora event, conditions are more unsettled than background levels, raising the odds for festive auroras, especially at high latitudes. The best chances will be limited to high-latitude regions, including Alaska, northern Canada, Scandinavia, and far northern Scotland.
Behind the unsettled conditions is a stream of unusually fast solar wind flowing from a large coronal hole on the sun. According to NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center, solar wind speeds peaked near 500 miles (800 kilometers) per second earlier this week and are now averaging around 430 miles (700 km) per second, still about twice as fast as typical background solar wind — helping to drive the recent G1 geomagnetic storms.
Article continues belowThese enhanced solar wind conditions are forecast to persist through Dec. 24-25, keeping geomagnetic activity elevated through Christmas Eve into Christmas Day. While storm levels may ease off slightly, there is a possibility of periods of active geomagnetic conditions according to space weather forecasters at NOAA and the U.K. Met Office.
There is also a possible wildcard at play.
According to NOAA, a coronal mass ejection (CME) that left the sun on Dec. 20 could pass close to Earth on Dec. 24, potentially striking our planet with a glancing blow. While no clearly Earth-directed CME has been observed, even a near-miss could briefly enhance aurora activity by disrupting the already disturbed solar wind environment around Earth.
Any aurora enhancement is likely to be limited to high latitudes; for the U.S., this means northern states such as Alaska, Washington, North Dakota and Minnesota. Elsewhere, elevated geomagnetic conditions could see auroras dance for skywatchers in northern Canada, Greenland and parts of Scandinavia.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
To keep informed about when and if you can expect to catch a glimpse of the northern lights from where you live, we recommend downloading a space weather app that provides aurora forecasts based on your location. One option I use is "My Aurora Forecast & Alerts," available for both iOS and Android. However, any similar app should work well.
I also use the "Space Weather Live" app, which is available on iOS and Android, to get a deeper understanding of whether the current space weather conditions are favorable for aurora sightings. Want to capture the perfect photo? Our how to photograph auroras guide can help.

Daisy Dobrijevic joined Space.com in February 2022 having previously worked for our sister publication All About Space magazine as a staff writer. Before joining us, Daisy completed an editorial internship with the BBC Sky at Night Magazine and worked at the National Space Centre in Leicester, U.K., where she enjoyed communicating space science to the public. In 2021, Daisy completed a PhD in plant physiology and also holds a Master's in Environmental Science, she is currently based in Nottingham, U.K. Daisy is passionate about all things space, with a penchant for solar activity and space weather. She has a strong interest in astrotourism and loves nothing more than a good northern lights chase!
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.