Blazing 'ring of fire' eclipse seen from space | Space photo of the day for Feb. 20, 2026
ESA's Proba-2 satellite captured a stunning 'ring of fire' annular solar eclipse from orbit — a view few on Earth could see.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
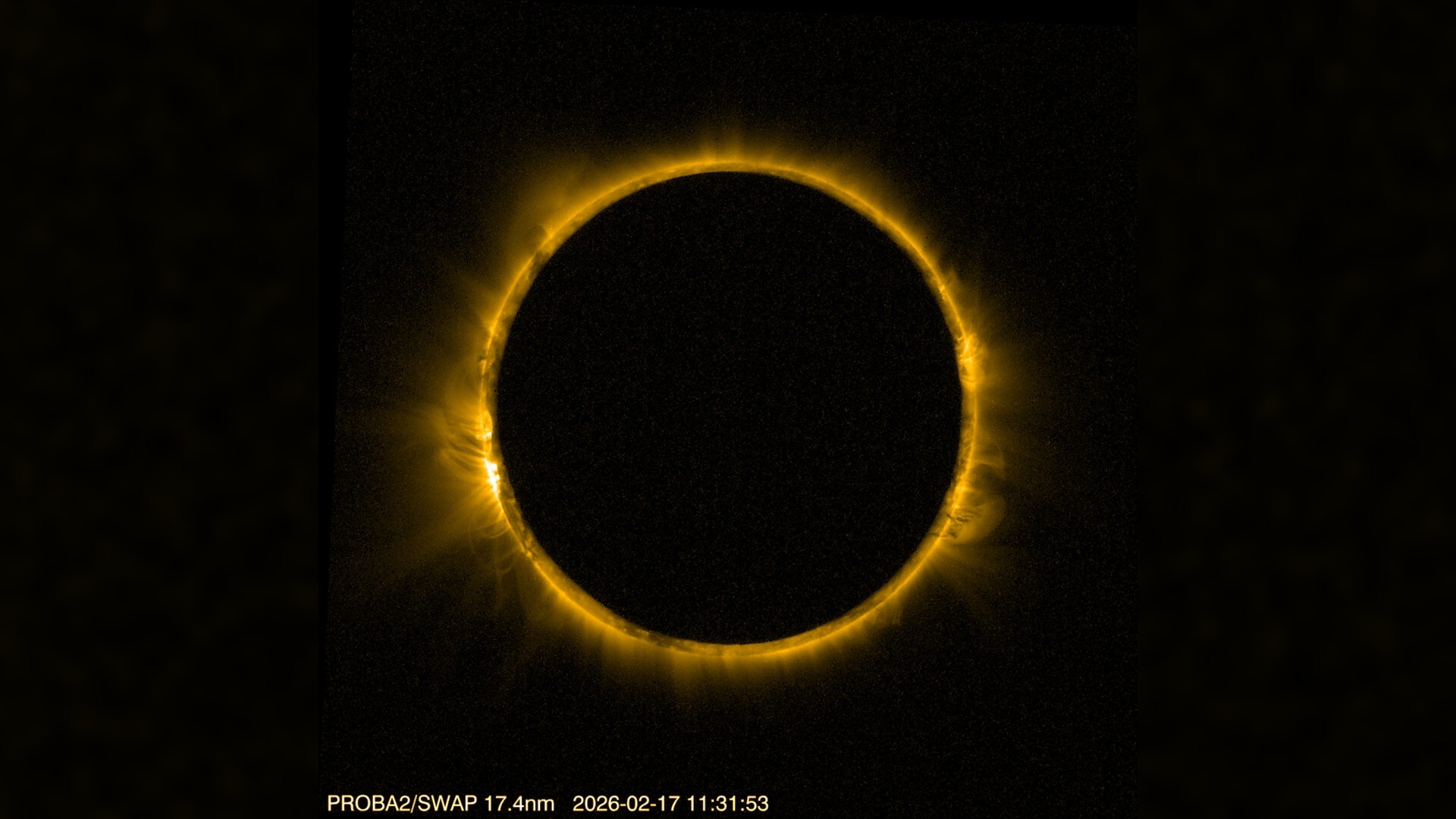
On Feb. 17, 2026, the moon slipped directly between Earth and the sun, creating a spectacular 'ring of fire' visible to very few people on Earth, but ESA's Proba-2 had had the best seat in the house.
From its vantage point in orbit, the satellite was able to witness the annular solar eclipse in striking detail — not once, but four times during its orbit, including a perfect 'ring of fire' at 6:31 a.m. EST (1131 GMT) when the moon occulted just over 93% of the sun's disk.
The stunning image was captured with Proba-2's SWAP instrument, which views the sun in extreme ultraviolet light, revealing details of the sun's corona — the outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere.
What is it?
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes in front of the sun while positioned farther from Earth during its slightly elliptical orbit. Because the moon appears a bit smaller in the sky at that distance, it doesn't completely cover the sun's disk (like we see during a total solar eclipse). Instead, a bright ring of sunlight encircles the moon's silhouette, often called a 'ring of fire'.
While Proba-2 had an unobstructed view from space, on Earth the full annular phase was only visible from remote locations in Antarctica, limiting the spectacle to just a small number of researchers stationed at remote scientific outposts … and a lot of penguins. Observers in the southern tip of Chile and Argentina, along with parts of southern Africa, witnessed a partial solar eclipse instead.
Why is it amazing?
Unlike observers on Earth, Proba-2 wasn't limited to a single view. Thanks to its fast sun-synchronous orbit, the spacecraft crossed the eclipse zone four times and was able to witness the event from several perspectives.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Daisy Dobrijevic joined Space.com in February 2022 having previously worked for our sister publication All About Space magazine as a staff writer. Before joining us, Daisy completed an editorial internship with the BBC Sky at Night Magazine and worked at the National Space Centre in Leicester, U.K., where she enjoyed communicating space science to the public. In 2021, Daisy completed a PhD in plant physiology and also holds a Master's in Environmental Science, she is currently based in Nottingham, U.K. Daisy is passionate about all things space, with a penchant for solar activity and space weather. She has a strong interest in astrotourism and loves nothing more than a good northern lights chase!
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.