Astronomers have detected one of the biggest black hole jets in the sky

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
Luke Barnes, Lecturer in Physics, Western Sydney University
Miroslav Filipovic, Professor, Western Sydney University
Ray Norris, Professor, School of Science, Western Sydney University
Velibor Velović, PhD Candidate, Western Sydney University
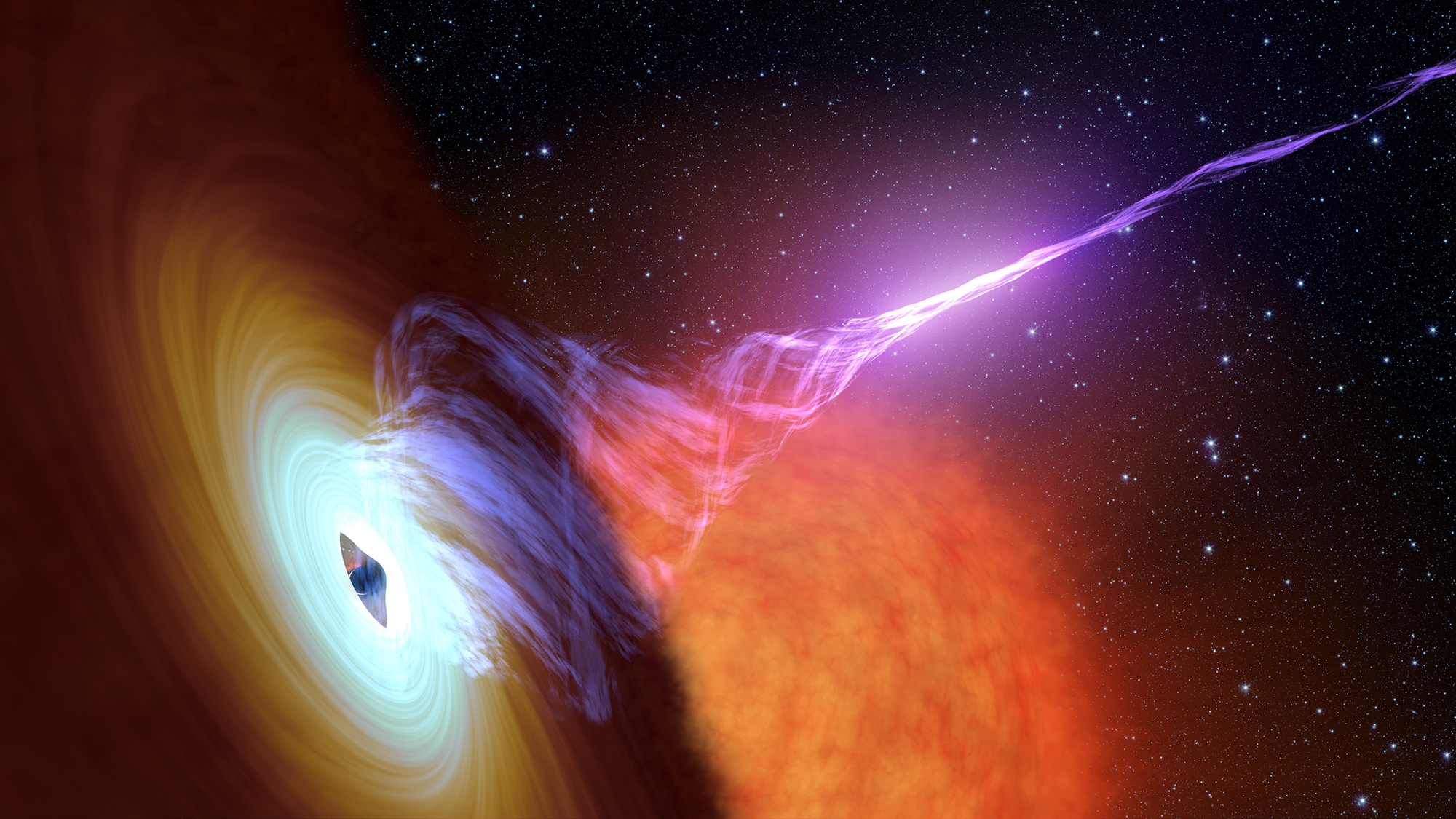
Astronomers at Western Sydney University have discovered one of the biggest black hole jets in the sky.
Spanning more than a million light years from end to end, the jet shoots away from a black hole with enormous energy, and at almost the speed of light. But in the vast expanses of space between galaxies, it doesn't always get its own way.
Related: 8 ways we know that black holes really do exist
Taking a closer look
At a mere 93 million light-years away, the galaxy NGC2663 is in our neighborhood, cosmically speaking. If our galaxy were a house, NGC2663 would be a suburb or two away.
Looking at its starlight with an ordinary telescope, we see the familiar oval shape of a "typical" elliptical galaxy, with about 10 times as many stars as our own Milky Way.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Typical, that is, until we observed NGC2663 with CSIRO's Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) in Western Australia — a network of 36 linked radio dishes forming a single super-telescope.
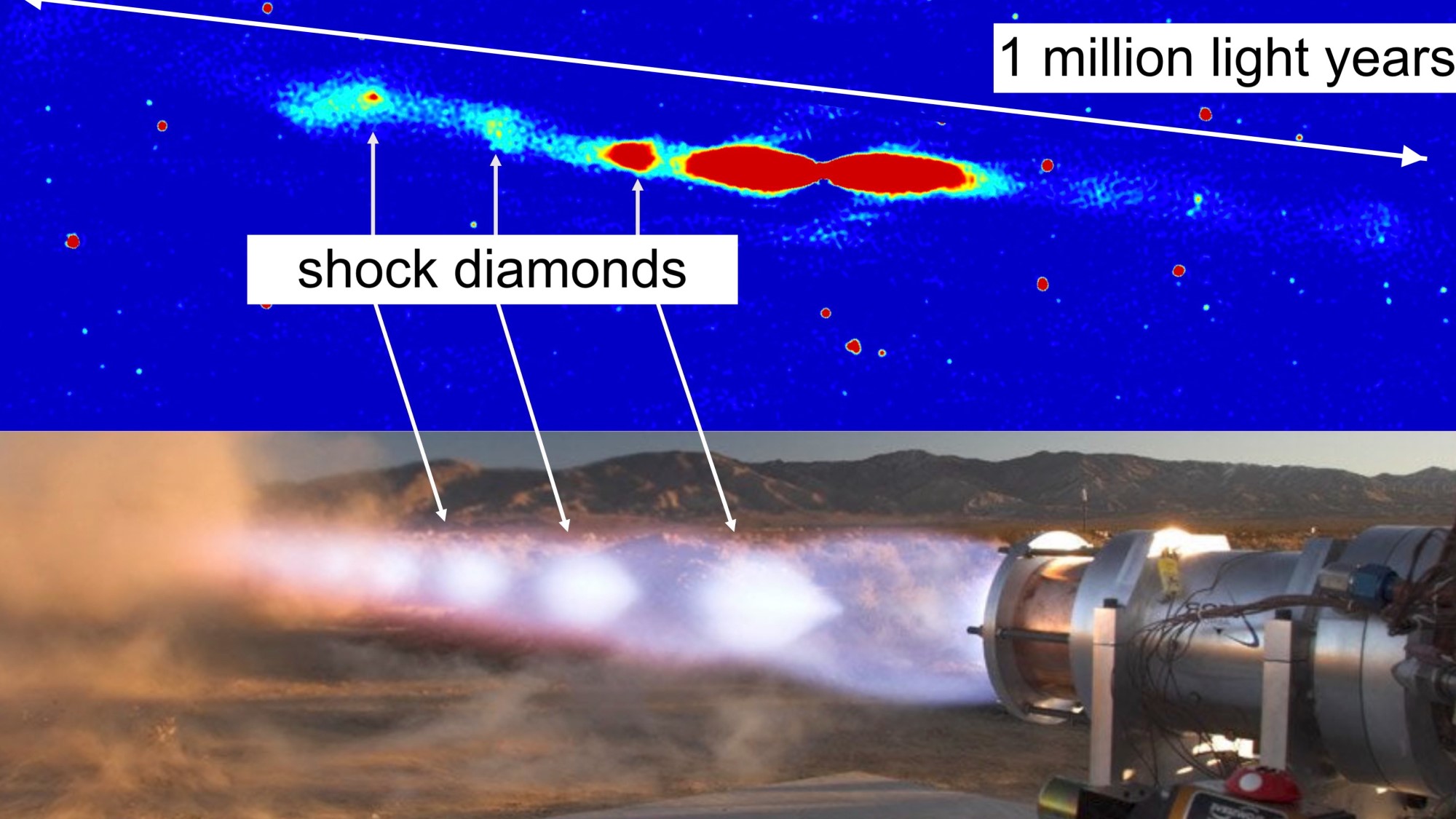
The radio waves reveal a jet of matter, shot out of the galaxy by a central black hole. This high-powered stream of material is about 50 times larger than the galaxy: if our eyes could see it in the night sky, it would be bigger than the moon.
While astronomers have found such jets before, the immense size (more than a million light years across) and relative closeness of NGC2663 make these some of the biggest known jets in the sky.
Read more: Like a spinning top: wobbling jets from a black hole that's 'feeding' on a companion star
Shock diamonds
So, what did we see, when the precision and power of ASKAP got a "close-up" (astronomically speaking!) view of an extragalactic jet?
This research is led by doctoral student Velibor Velović of Western Sydney University, and has been accepted for publication in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (preprint available here). Our Evolutionary Map of the Universe (EMU) survey sees evidence of the matter between galaxies pushing back on the sides of the jet.
This process is analogous to an effect seen in jet engines. As the exhaust plume blasts through the atmosphere, it is pushed from the sides by the ambient pressure. This causes the jet to expand and contract, pulsing as it travels.
As the image below shows, we see regular bright spots in the jet, known as "shock diamonds" because of their shape. As the flow compresses, it glows more brightly.
Biggest one yet
As well as in jet engines, shock diamonds have been seen in smaller, galaxy-sized jets. We've seen jets slam into dense clouds of gas, lighting them up as they bore through. But jets being constricted from the sides is a more subtle effect, making it harder to observe.
However, until NGC2663, we've not seen this effect on such enormous scales.
This tells us there is enough matter in the intergalactic space around NGC2663 to push against the sides of the jet. In turn, the jet heats and pressurizes the matter.
This is a feedback loop: intergalactic matter feeds into a galaxy, galaxy makes black hole, black hole launches jet, jet slows supply of intergalactic matter into galaxies.
These jets affect how gas forms into galaxies as the universe evolves. It's exciting to see such a direct illustration of this interaction.
The EMU survey, which is also responsible for identifying a new type of mysterious astronomical object called an "Odd Radio Circle," is continuing to scan the sky. This remarkable radio jet will soon be joined by many more discoveries.
As we do, we'll build up a better understanding of how black holes intimately shape the galaxies forming around them.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Follow all of the Expert Voices issues and debates — and become part of the discussion — on Facebook and Twitter. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the publisher.

Velibor Velović is completing the last year of his Ph.D. at Western Sydney University. He focuses particularly on studying the jets formed by active galactic nuclei.