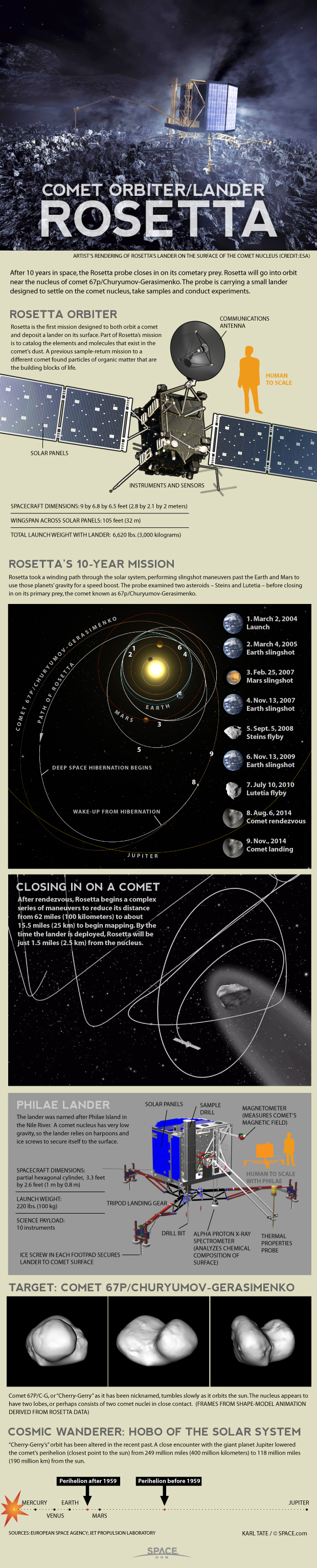
5 Amazing Facts about Europe's Comet-Chasing Rosetta Probe
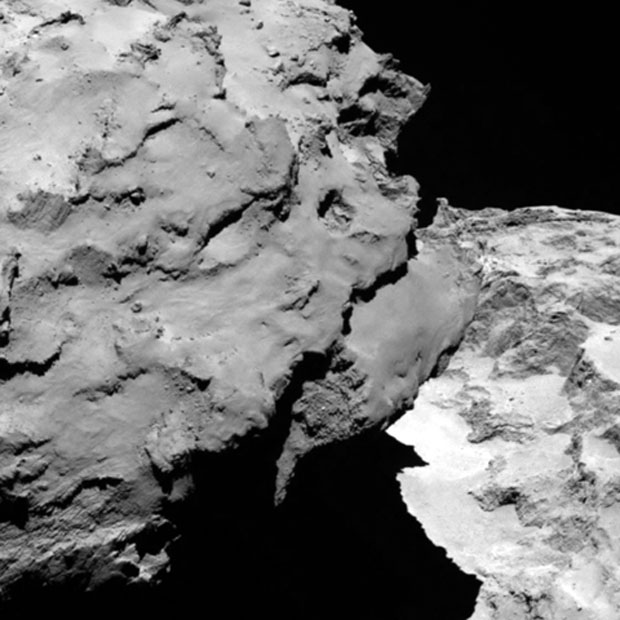

Europe's Rosetta probe made its historic arrival at Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko yesterday (Aug. 6), making Rosetta the first human-built craft ever to rendezvous with a comet with the intention to enter orbit.
Now flying about 62 miles (100 kilometers) from the comet, the Rosetta spacecraft is expected to gather data that will help scientists learn more about comets. Specifically, the findings will shed light on how the ancient, icy wanderers that roam through the solar system formed thousands of years ago.
The European Space Agency-operated spacecraft may also help scientists find answers to some of the most pressing questions in space science today.
"The really big questions here are, 'Where do we come from? Where does the solar system we live in come from? How was it put together? How was it assembled? How did the planets get built up individually, and how did water get to this planet that we live on?'" Mark McCaughrean, senior scientific adviser with the ESA's Directorate of Science and Robotic Exploration, said during a webcast on Aug. 6. [See amazing photos from the Rosetta probe]
"Rosetta is indeed the Rosetta Stone as a mission," McCaughrean added, referencing the Rosetta Stone artifact that helped translate ancient hieroglyphs. "It will unlock this treasure chest as a clue to many comets in our solar system. There are trillions out there. This is a baseline. This is one we can now study in such detail we can rewrite history and begin to understand our own history."
But what are some of the things we already know about the comet? Here are five amazing facts to know about the Rosetta probe and Comet 67P/C-G:
1) This isn't Rosetta's first cosmic rodeo
Rosetta made three flybys of Earth and one of Mars in order to gain enough speed to get past Jupiter and on its way to meet up with the comet, according to ESA. The spacecraft also managed to get some interesting views of the asteroids Steins and Lutetia before going into hibernation in 2011.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"After 10 years, five months and four days traveling towards our destination, looping around the sun five times and clocking up 6.4 billion kilometers [4 billion miles], we are delighted to announce, finally, 'We are here,'" Jean-Jacques Dordain, ESA's director general, said in a statement. "Europe's Rosetta is now the first spacecraft in history to rendezvous with a comet, a major highlight in exploring our origins. Discoveries can start."
2) Rosetta traveled 4 billion miles to Comet 67P/C-G
Although Rosetta and Comet 67P/C-G are flying about 251 million miles (450 million km) from Earth right now, that number is slightly deceiving. Since its launch in 2004, Rosetta has been speeding through the solar system on a circuitous journey to catch up with its comet target.
In total, the Rosetta probe spent a decade traversing about 4 billion miles (6.4 billion km) to make its historic rendezvous with Comet 67P/C-G on Aug. 6. The probe and the comet are now only about 62 miles (100 km) from each other.
3) Rosetta will drop a lander on the comet
At the moment, Rosetta is carrying a special lander poised to launch to the surface of Comet 67P/C-G in November. Rosetta is currently tracking a triangular orbit around the comet; however, it will move into a circular orbit and start getting closer to the surface of the comet as weeks go on, gearing up to release the Philae lander.
Before Philae touches down, mission controllers will scope out a series of potential landing spots for the probe. Once on the surface, Philae will beam back data about the composition of the comet, getting an up-close-and-personal view of the cosmic body.
"Over the next few months, in addition to characterizing the comet nucleus and setting the bar for the rest of the mission, we will begin final preparations for another space history first: landing on a comet," Matt Taylor, Rosetta project scientist, said in a statement. [Best Close Encounters of the Comet Kind]
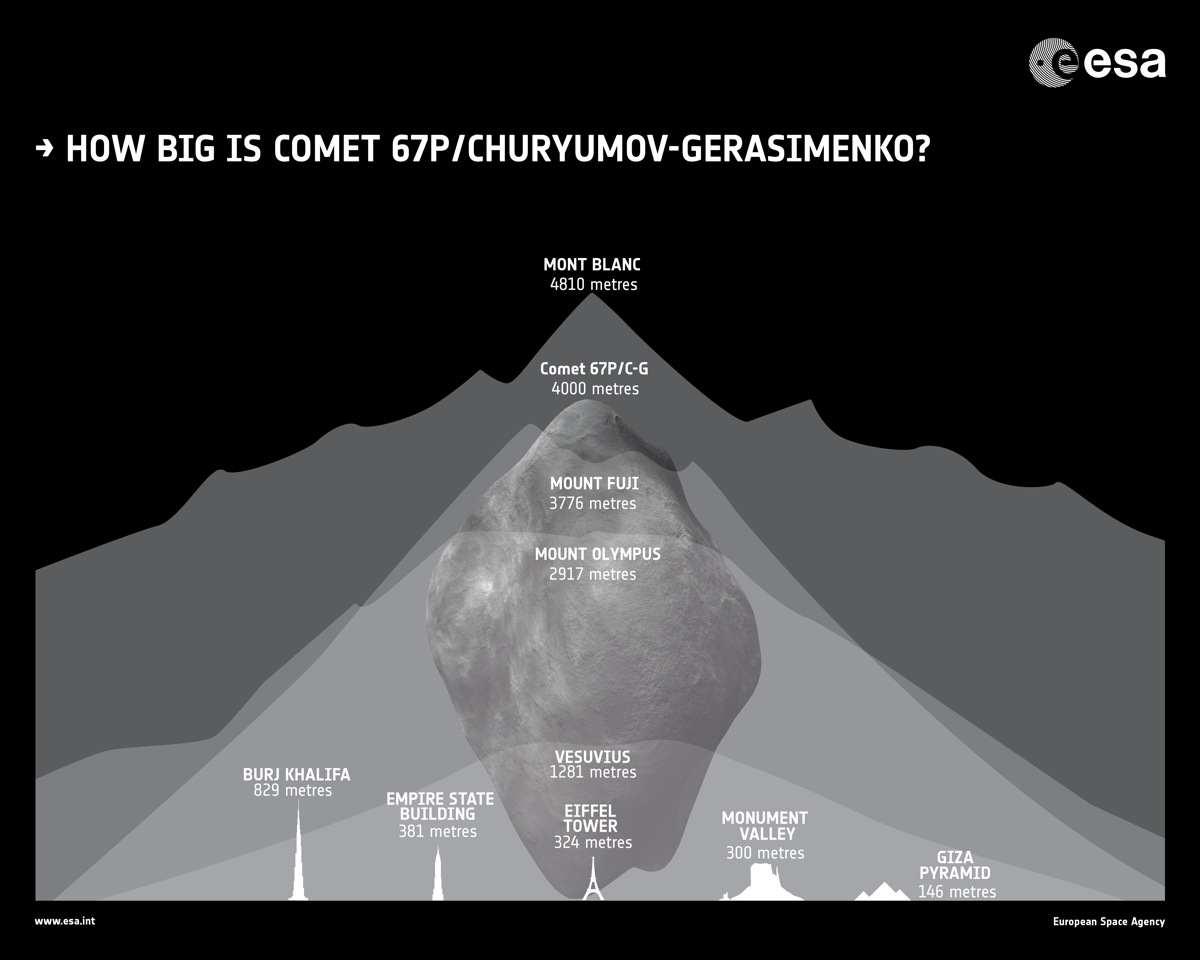
4) Comet 67P/C-G is as big as a mountain
Rosetta's target comet is 2.5 miles wide (4 km), meaning that if it were plopped down on Earth, it would actually be larger that Mount Fuji in Japan, which checks in at about 2.3 miles (3.8 km) high.
The comet's large size is on display in new photos sent back from Rosetta after the probe made its historic rendezvous yesterday. Objects that look like boulders on the comet's surface are actually as large as houses, according to ESA officials.
5) Rosetta's comet is dark and dusty
As it flew toward Comet 67P/C-G, ESA's Rosetta probe collected some interesting data about the object's possible composition. Scientists now think that the comet has patches of ice with a dusty, dark crust covering a good portion of its surface.
ESA scientists are still planning to learn more about the comet's composition using instrumentation as Rosetta gets closer and closer to the celestial object. The VIRTIS instrument on board the spacecraft is designed to create temperature maps of the comet's features, the instrument's principle investigator Fabrizio Capaccioni has said.
The $1.7 billion (1.3 billion euros) Rosetta mission is expected to last until December 2015. Ground controllers monitor the mission from the ESA center in Darmstadt, Germany.
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.

Miriam Kramer joined Space.com as a Staff Writer in December 2012. Since then, she has floated in weightlessness on a zero-gravity flight, felt the pull of 4-Gs in a trainer aircraft and watched rockets soar into space from Florida and Virginia. She also served as Space.com's lead space entertainment reporter, and enjoys all aspects of space news, astronomy and commercial spaceflight. Miriam has also presented space stories during live interviews with Fox News and other TV and radio outlets. She originally hails from Knoxville, Tennessee where she and her family would take trips to dark spots on the outskirts of town to watch meteor showers every year. She loves to travel and one day hopes to see the northern lights in person. Miriam is currently a space reporter with Axios, writing the Axios Space newsletter. You can follow Miriam on Twitter.