DigitalGlobe and Saudi Government Sign Joint Venture on Satellite Imaging Constellation

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
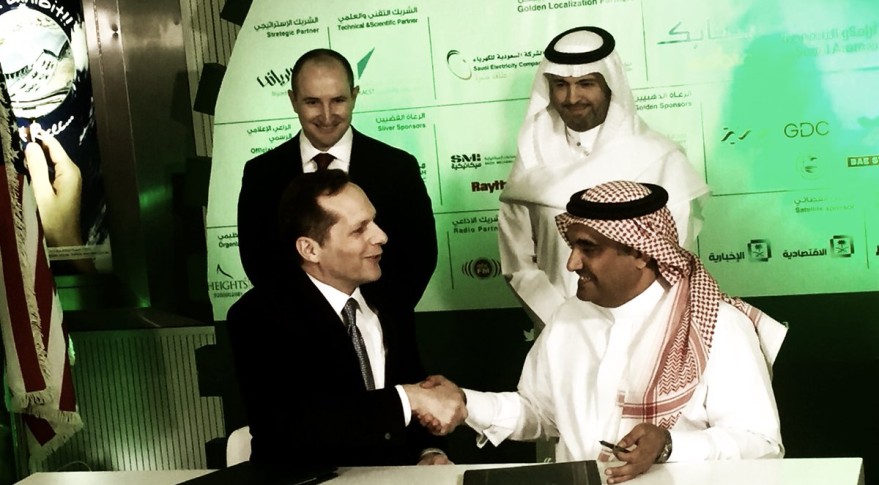
PARIS—Geospatial satellite imagery and services provider DigitalGlobe Inc. on Feb. 21 said it is forming a joint venture with the government of Saudi Arabia to build at least six small optical Earth observation satellites to complement DigitalGlobe's current fleet of large, high-resolution spacecraft.
The satellites, capable of detecting objects of less than 1 meter in diameter, would be launched in 2018 and 2019 and designed for easy operation within DigitalGlobe's existing ground infrastructure, the companies said.
The statement did not disclose the estimated cost of the constellation or detail the two parties' financial commitment. DigitalGlobe's partners in the venture are Taqnia Space, owned by Saudi Arabia's Public Investment Fund; and the King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST), which is already a DigitalGlobe Direct Access Partner receiving imagery directly from DigitalGlobe satellites.
Westminster, Colorado-based DigitalGlobe operates a fleet of large high-resolution satellites whose imagery is sold worldwide. The company's principal customer is the U.S. government, through a large contract renewal yearly, with the U.S. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency.
DigitalGlobe officials have said they would be ordering replacements for their WorldView-1 and WorldView-2 satellites in 2017-2018 but would spend far less on them than what the company paid for the predecessor spacecraft.
DigitalGlobe has not indicated whether the new-generation satellites would be smaller and operate with a constellation-type architecture, which would reduce the time between fly-overs of a given target area; or would retain the higher-resolution capability more associated with larger satellites.
The company's current WorldView-3 and coming WorldView-4 satellites are capable of detecting objects as small as 30 centimeters in diameter. The latter satellite is scheduled for launch late this year.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The joint venture in Saudi Arabia will divide production, sales and marketing responsibility.
KACST will build, integrate and launch the satellites and will own 50 percent of their capacity over Saudi Arabia and "the surrounding region," DigitalGlobe said, without being more specific.
DigitalGlobe will have sales responsibility for the remaining 50 percent inside the KACST region, and 100 percent of the rights to coverage of the rest of the world. The parties will share in the global revenue stream under terms that were not disclosed.
The partnership "offers DigitalGlobe customers a complementary source of data to address new use cases, while expanding the image catalog of DigitalGlobe's Geospatial Big Data platform," DigitalGlobe said, adding that the constellation would be "highly complementary to the next-generation satellite architecture" the company is now designing.
DigitalGlobe said its existing imagery-production capability would be used "to improve the native accuracy of the small-satellite imagery." It was unclear whether the satellites' "native" submetric resolution would be resampled by laying one image atop another to achieve a product with a higher-resolution appearance, or whether the company's existing catalog of higher-resolution imagery would be used to the same end.
The announcement is the latest sign that despite the collapse in the price of the crude oil on which their economies are built, Middle Eastern nations are not scaling back their ambitions to become space-fairing nations in their own right.
Taqnia has signed an agreement with Lockheed Martin Space Systems of Sunnyvale, California, to build a satellite assembly plant on Saudi soil, with the necessary technology transfer occurring in the context of a contract under which Lockheed is building two telecommunications satellites for Riyadh-based Arabsat, a major commercial satellite fleet operator.
The United Arab Emirates, in addition to being home to mobile satellite services provider Thuraya, is investing in the Virgin Galactic small-satellite launch vehicle and space tourism company. The UAE has ordered two high-resolution optical reconnaissance satellites from Airbus Defence and Space and Thales Alenia Space of France. Morocco has made a similar order.
The UAE's new space agency is also planning a Mars probe, to be launched in 2020, and has embarked on its own satellite Earth observation program in collaboration with Satrec Initiative of South Korea. The UAE-built KhalifaSat, with an imager capable of detecting options 70 centimeters in diameter, is scheduled for launch in 2017.
The Egyptian government has said it plans to order a civil/military telecommunications satellite in the coming weeks from French contractors and has expressed an interest in a high-resolution optical satellite reconnaissance capability as well.
"Partnering with the premier commercial satellite imaging firm will help to propel the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia to become a leader in remote sensing and satellite technology," Taqnia Chairman and KACST President H.H. Dr. Turki Bin Saud said in a statement.
This story was provided by SpaceNews, dedicated to covering all aspects of the space industry.
Peter B. de Selding is the co-founder and chief editor of SpaceIntelReport.com, a website dedicated to the latest space industry news and developments that launched in 2017. Prior to founding SpaceIntelReport, Peter spent 26 years as the Paris bureau chief for SpaceNews, an industry publication. At SpaceNews, Peter covered the commercial satellite, launch and international space market. He continues that work at SpaceIntelReport. You can follow Peter's latest project on Twitter at @pbdes.