Destination Moon: Private Spaceflight Companies Eye Lunar Bases
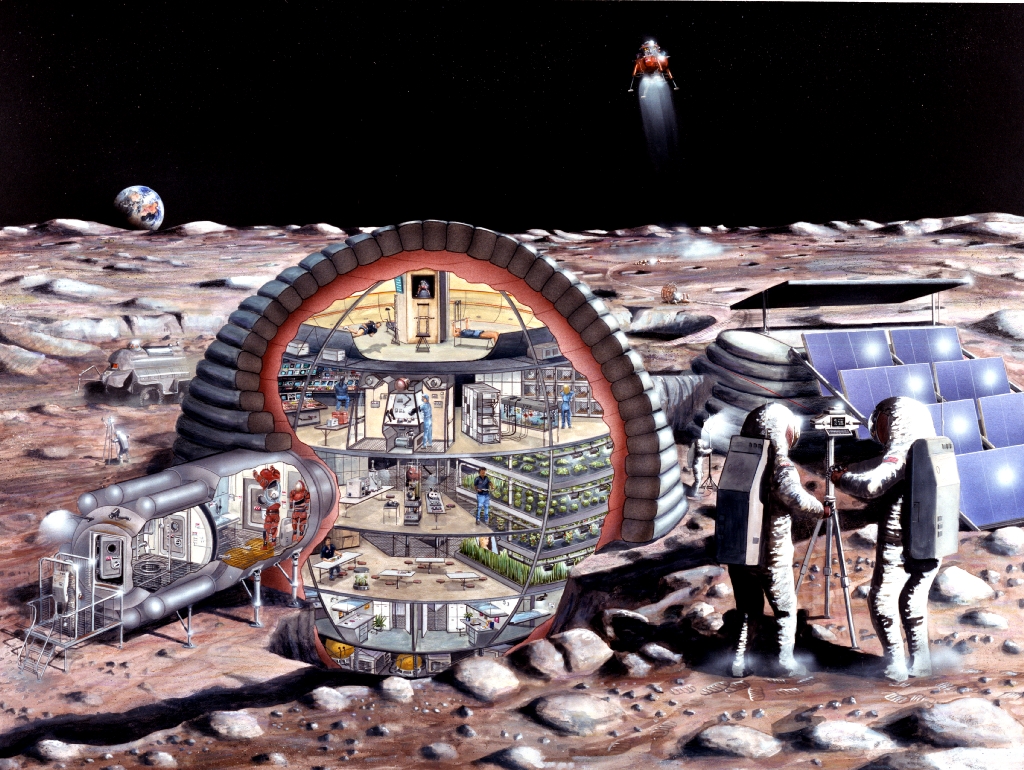
Human exploration of deep space is looking more and more like a tag-team affair, with NASA jetting off to asteroids and Mars while the private sector sets up shop on the moon.
While NASA has no plans to return humans to the lunar surface anytime soon, private industry is eyeing Earth's nearest neighbor intently, said Bigelow Aerospace founder and president Robert Bigelow.
"The brass ring for us is having a lunar base — as a company and in conjunction with other companies, and even other, possibly, foreign entities as well," Bigelow said during a teleconference with reporters today (May 23). "That is an appetite and a desire that we've had for a long, long time." [3D-Printing a Future Moon Base (Gallery)]
Two months ago, NASA tapped Bigelow Aerospace to sound out the private sector's interest and intent in going beyond low-Earth orbit, in an attempt to help map out possible public-private partnerships in deep space.
The Space Act agreement set out a two-phase study approach. Bigelow delivered a draft report of the Phase 1 findings today to NASA human exploration chief Bill Gerstenmaier, who also participated in the teleconference.
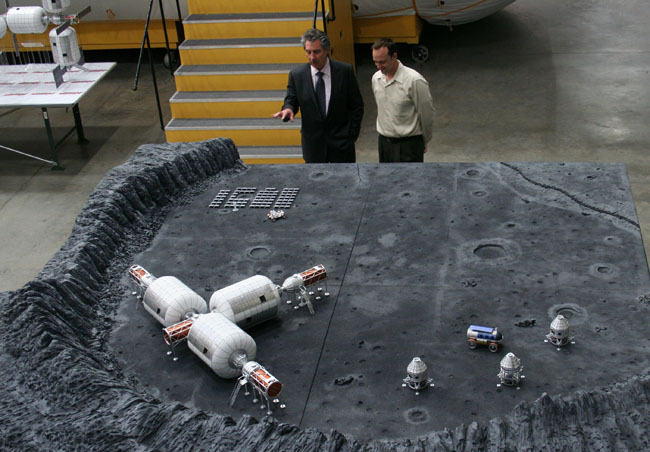
Bigelow Aerospace makes expandable habitat modules designed to house astronauts in space or on the surface of the moon and other bodies. The company has long been an advocate of setting up manned lunar bases, and Bigelow said other firms see the appeal of commercial lunar operations as well.
Golden Spike, for example, aims to begin launching two-person missions to the lunar surface and back by 2020. And several different firms, such as Shackleton Energy Company and Moon Express, plan to mine the moon's resources.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
NASA had been planning on sending astronauts back to the moon until 2010, when President Barack Obama directed the space agency to work instead toward getting to a near-Earth asteroid by 2025, then on to the vicinity of Mars by the mid-2030s.
Gerstenmaier said NASA welcomes private industry's interest in the moon, viewing it as a complement to the agency's plans in deeper space.
"NASA and the government, we focus on maybe deep space, we focus on asteroids. The private sector picks up the lunar activity, and then we'll combine and share with them to see what makes sense," Gerstenmaier said.
"Transportation to the same region is common between us," he added. "Other aspects — life-support — are common between us. We can do lots of co-development between these that actually share what the private sector needs and what the government needs."
Bigelow said he talked to around 20 private companies during the course of the study, including major players such as SpaceX, Boeing and Sierra Nevada Corp.
"You would recognize most of the names," he said.
Gerstenmaier said NASA would release the Phase 1 report to the public after the agency receives the final draft. The Phase 2 portion of the study, meanwhile, is slated to last four months.
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.