Student Engineers Spark Zero-Gravity Fires on Weightless Wild Ride

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
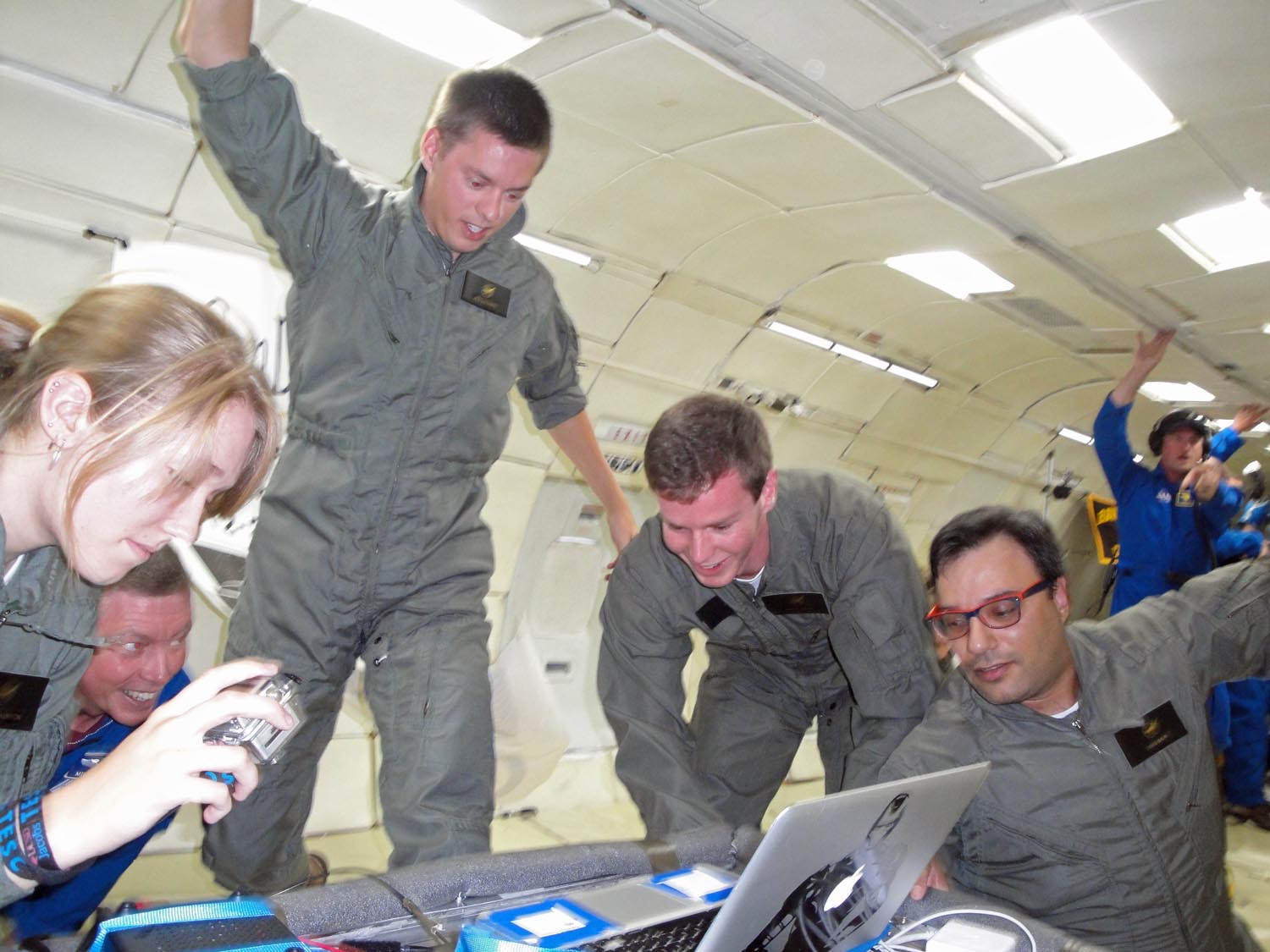
HOUSTON — Gravity, we have defied you. Seven university student teams from across the United States escaped the pull of Earth's gravity — if only for a few seconds — on a NASA microgravity flight to see how fire, liquids and magnets behave in weightlessness.
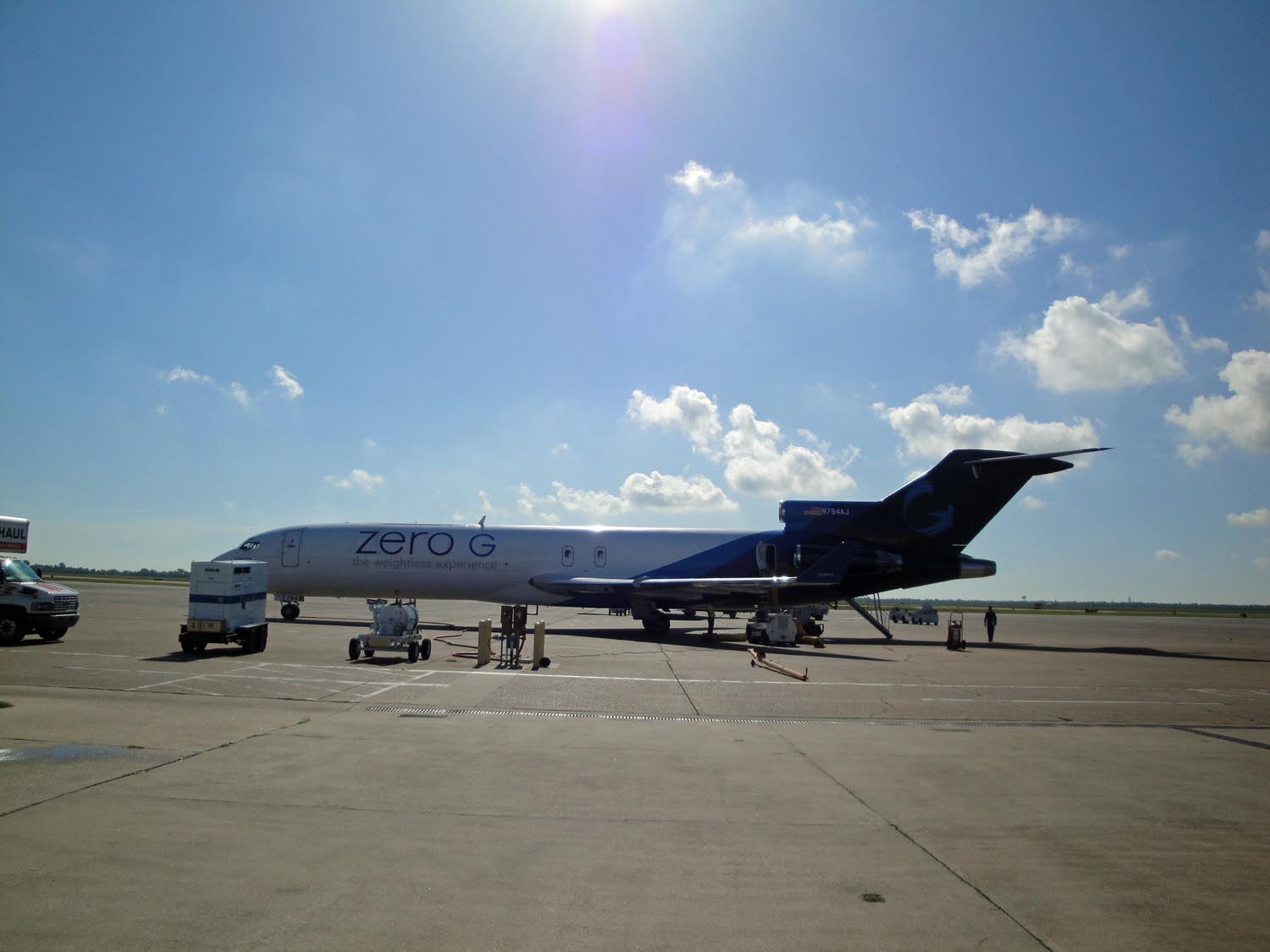
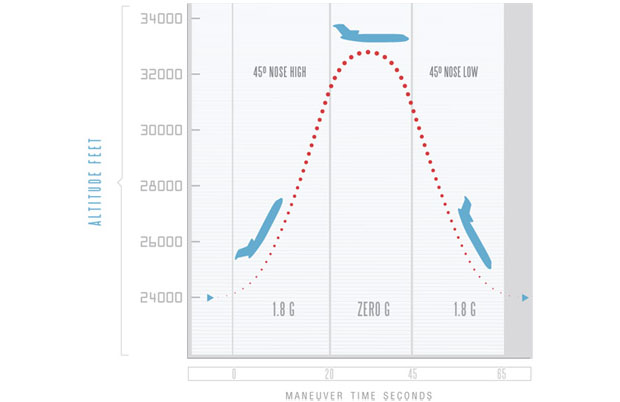
The students flew with NASA's Microgravity University Program Friday (July 19) aboard a Zero Gravity Corporation Boeing 727 jet modified to fly up and down on a parabolic path to create up to 30 seconds of zero gravity, moon gravity or Martian gravity on the downswing followed by periods of "hypergravity" (twice Earth's pull) on the way back up.
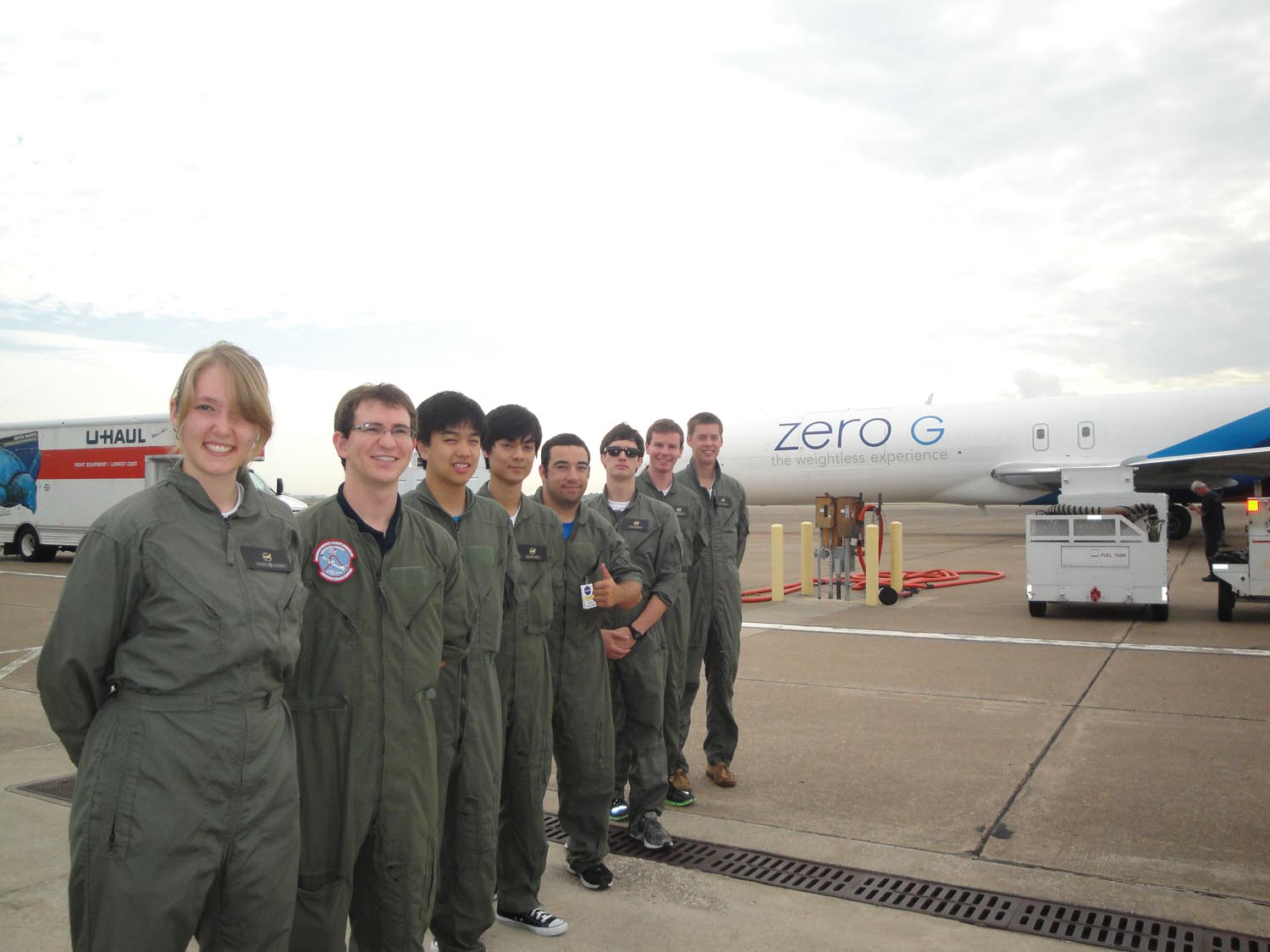
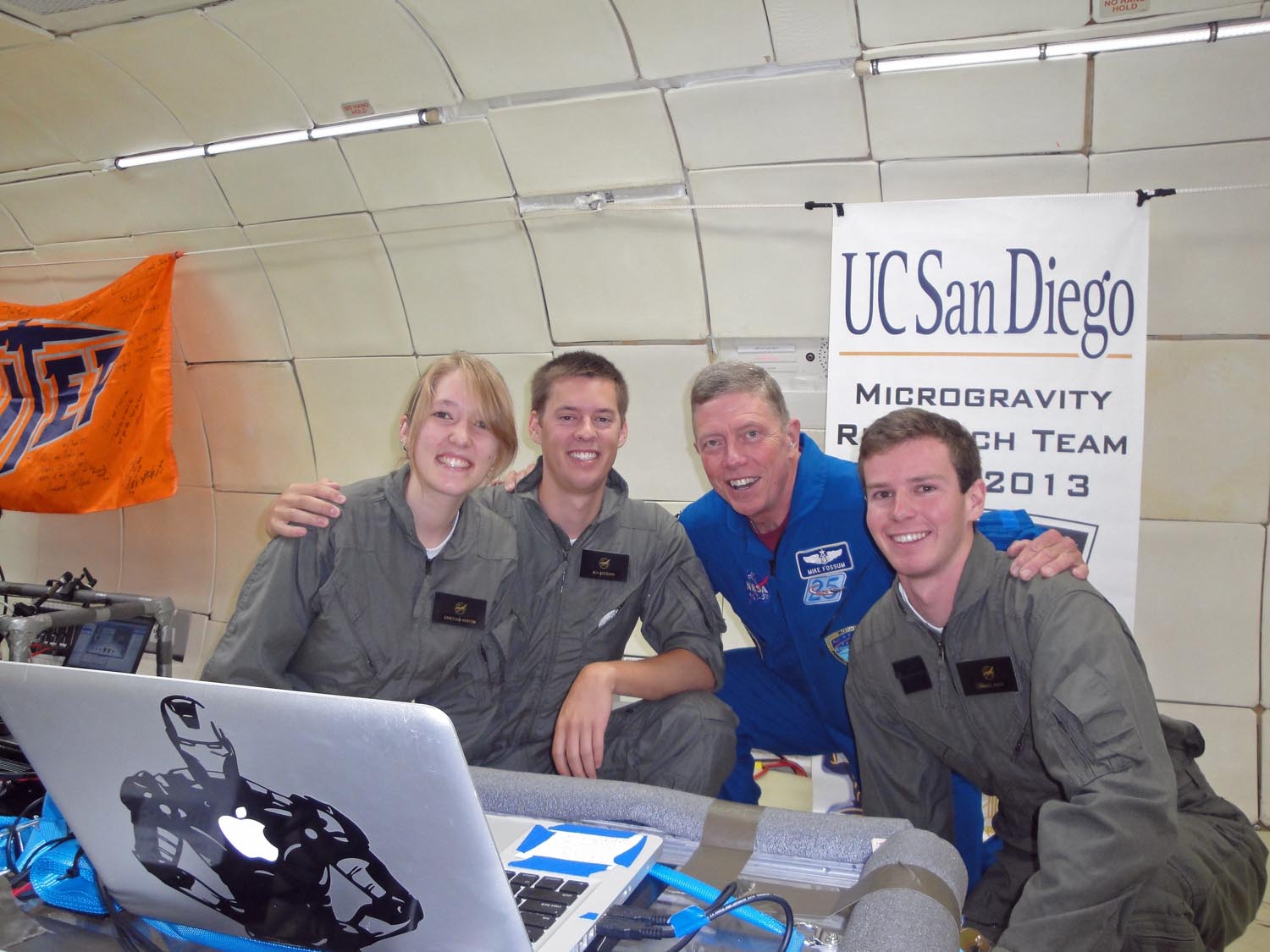
About 34 students, NASA specialists and veteran astronauts Mike Fossum and Cady Coleman flew on ZERO-G's G-Force One jet, which took off from Ellington Field here near NASA's Johnson Space Center. Among the groups was the UCSD Microgravity Team from the University of California, San Diego, which SPACE.com has been shadowing to show how student science is performed in weightlessness without leaving Earth. Offering students and teachers the chance to perform weightless experiments is the goal of NASA's Reduced Gravity Education Flight Program. [Photos: Zero-Gravity Science at NASA's Microgravity University]
Tiny fires + zero gravity = Science
The UCSD Microgravity Team, led by aerospace engineering undergraduate Sam Avery, worked for nearly nine months to create a triple-contained experiment that tested how biofuel fires burn in microgravity. The goal, Avery said, was to learn how large of a fire a single droplet of biofuel creates when ignited in weightless conditions. The experiment was accepted for a NASA weightless flight in October 2012, with the team working ever since to design, fund and then build its flame-inducing box.
During Friday's flight, Avery used a control box covered in switches to issue swift commands to machinery inside the fire box to ignite the biofuel droplet. One switch moved a syringe into place, the next told the syringe to squirt out a tiny blob of fuel onto a set of crosshair-like filaments. Then, another switch moved the igniter into place, setting off the burn. The resulting zero-gravity flame was a rippling blob of pure fire about the size of a small piece of hard candy that glowed in haunting shades of reddish-orange.
"I think that it looked amazing," Avery told SPACE.com. "It was just a big, morphing ball of fire. Every time it was a little bit different."
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Knowing how small biofuel fires behave in weightlessness could help engineers develop more efficient biofuel engines on Earth, as well as better fire countermeasures for astronauts in space. Avery and his team used ethyl alcohol as the fuel source in Friday's weightless flight. The team planned to try butyl alcohol during a second flight, if possible. [6 Everyday Things That Turn Weird in Weightlessness]
A taste of weightlessness
The UCSD team saw a nearly 95 percent success rate in their zero-gravity experiment. The NASA astronauts on the flight, Fossum and Coleman, spent some time observing the UCSD fire experiment. Fossum said it looked remarkably close to the flame experiments he performed during a long-duration mission on the International Space Station.
Avery and his team had hoped to fly two flights this week, with the first flight taking off on Thursday. But bad weather along southern Texas and the Gulf of Mexico delayed that first flight to Friday morning.
In addition to Avery, teammates Jack Goodwin and Daneesha Kenyon flew on the Friday zero-gravity mission. Kenyon observed the experiment and recorded the team's work with a small GoPro video camera, while Goodwin called out the steps for Avery to perform with the control box and a side-mounted valve to vent out the flame vapors.
Who cares about space sickness?
In between experiment runs, the UCSD team and other students enjoyed some fun parabolas and took advantage of the weightlessness to conduct outreach experiments.
For my part, I attempted to show how to put on a SPACE.com t-shirt in weightless conditions and hoped to float some space shuttle toys, but with just 30 seconds of weightlessness, even unfolding the shirt was a challenge. The lesson: Think ahead of what action need to be performed before the onset of weightlessness in order to take advantage of that brief period. But the sensation of floating alone seemed to spark elation in all those aboard, sick or no. [Video: Astronaut Bloopers in Zero-G]
"It's a whole body experience," UCSD aerospace engineering study Jack Goodwin said in a post-flight interview with a NASA video team. "About one-third of the way through, it became natural … you don't have to walk anymore."
Both Avery and Goodwin initially decided to forgo taking a shot of scopolamine, an anti-motion sickness medication offered by NASA for all participants. Ultimately, though, they opted to take the shot just in case. They fared extremely well, floating and laughing during the rare zero-gravity stints that they weren't working. They tackled 2G pushups on the upswing.
Scopolamine, we thank you
Taking the shot, it turns out, was a great choice.
I got through nearly all of the 30 zero-gravity parabolas without any motion sickness from the weightlessness. Near the end, I felt some slight queasiness and whipped out a small plastic bag for the last two weightless periods, just in case. Luckily, I didn't get sick and was able to marvel at Goodwin and Avery as they performed a moon gravity dance with Coleman in one-sixth Earth's gravity, and then again under a one-third Earth gravity parabola mimicking conditions on Mars.
Kenyon, meanwhile, also made it through most of the weightless parabolas but did have to make use of her plastic bag. (All flyers kept them tucked in our flight suit chest pockets to keep them close). She ultimately opted to sit in one of the seats used during takeoff and landing for the remainder of trip.
"Even so, I would 100-percent go again," Kenyon said. "It was such a fantastic experience."
In a post-flight briefing, Coleman and Fossum told the student flyers that they were impressed with the science they saw on the flight. But something else also caught their eye.
"I saw a lot of teamwork and team members not only watching their experiments, but also watching out for one another," Coleman said. "It was really fun."
Real students, real science, real weightlessness
Friday's flight took off at about 9:30 a.m. EDT (10:30 a.m. EDT/1430 GMT) and lasted about two hours. Avery, Goodwin and Kenyon flew on the actual flight while five other team members waited on the ground. The rest of the team at Ellington included Andrew Beeler, Victor Hong, Joshua Siu, Joshua Sullivan, Nico Montoya and their NASA mentor Christina Gallegos.Gallegos is an electrical engineer who works on the Morpheus moon lander prototype at NASA's nearby Johnson Space Center. Other team members remained behind in San Diego.
Some of the remaining team members may fly on Saturday, if the weather allows, in order to collect more data. Beeler, who serves on the team's ground crew to prime the fire experiment for flight, said Friday's experiments managed to burn the needle used to squirt out the biofuel droplet ahead of ignition. [Fires in Space: It's Not What You Know]
"We have never seen this before," he told SPACE.com as he showed the charred syringe needle. "Maybe we'll see how it happened when we go back through the video."
The UCSD Microgravity Team has been supported by several sponsors, including the Canadian biofuel company W2 Energy, the UCSD Jacobs School of Engineering, the California Space Grant Consortium and the Ledell Family Scholarship, Avery said. Altogether, the team raised more than $10,000 to fund the experiment and spent more than 1,000 man-hours building the flame apparatus to NASA specifications. Their mentor at UCSD for the project was engineering professor Forman Williams.
Gallegos, the NASA engineer who served as the UCSD team's mentor on NASA's side, said it was her job to make sure the team knew NASA's regulations and built its flame box to the proper safety specifications. She was slated to fly on the team's second flight to observe the experiment in action.
The UCSD Microgravity Team was just one of seven university teams selected by NASA to fly on the Microgravity University flights this week. Seven other teams of classroom teachers representing grades K-12 also flew on NASA flights this week with the agency's Teach from Space program.
The experiments among the other university teams were varied. The UCSD team was experimenting with two types of biofuels, while a team from Purdue University tested how to remove excess water from fuel cells to improve power systems on satellites and spacecraft.
Another team from West Virginia University studied the effectiveness of spray-cooling on a heated chunk of aluminum to learn how well the method could perform in satellites and spacecraft. And yet another team from the University of Texas, El Paso, was testing how mock Mars and moon dirt combust when mixed with magnesium.
You can see the full list of university teams and their experiment names for this week's NASA Microgravity University here:
- Baldwin Wallace University / John Carroll University: The Stability of Liquid Bridges under Varying Total Body Force
- Purdue University: Water Removal in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
- Rice University Electromagnetic Position Sensing in Microgravity
- SUNY Buffalo: Microgravity Characterization of Zirconia Monolithic Electrokinetic Micropumps
- University of California San Diego: Fiber Supported Droplet Combustion of Bioethanol and Biobutanol
- University of Texas, El Paso: Combustion of Lunar and Martian Regolith Simulants with Magnesium
- West Virginia University: Optimization of Liquid Spray Cooling in a Variable Gravity Environment.
Frank Prochaska, NASA's student campaign manager for the Reduced Gravity Education Flight Program, said the space agency has been organizing the flights for students and teachers for about 18 years.
NASA originally flew microgravity training and research flights aboard its KC-135 "Weightless Wonder" aircraft, which was also known as the "Vomit Comet." The program is based at the Johnson Space Center, with flights originating from Ellington Field. In 2008, NASA began buying weightless flights aboard ZERO-G's G-Force One. ZERO-G has offered commercial weightless flights since 2004.
Before flight, Prochaska urged the college student teams to perform their experiments carefully, but not to overlook the personal impact of where they are: in weightlessness. More people have climbed to the peak of Mount Everest — the world's tallest mountain — than floated in microgravity, he said.
"This is it, this is the pinnacle of your parabola here," Prochaska said. "Don't get so focused on your research that you forget to look around."
NASA's next microgravity flights are scheduled for next week, between July 26 and Aug. 3, as part of the agency's Systems Engineering Education Discovery (SEED) program. The next Microgravity University flights will take off in November, NASA officials said.
In the meantime, Avery and his UCSD teammates are reveling in what appears to have been a successful experiment and an unforgettable experience. The students will take their data back to UCSD, analyze their findings and then write them up in a final report.
"I really feel like this was one of those once-in-a-lifetime type of experiences," Avery said.
Editor's note: Visit SPACE.com next week for more photos and video from the UCSD Microgravity Team's weightless ride. You can learn more about the UCSD Microgravity Team's fire experiment at the team's website here.
Email Tariq Malik at tmalik@space.com or follow him @tariqjmalik and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.

Tariq is the award-winning Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001. He covers human spaceflight, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He's a recipient of the 2022 Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting and the 2025 Space Pioneer Award from the National Space Society. He is an Eagle Scout and Space Camp alum with journalism degrees from the USC and NYU. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast on the TWiT network. To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik.