Winter Stargazing: Orion and Friends Shine Brightly
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
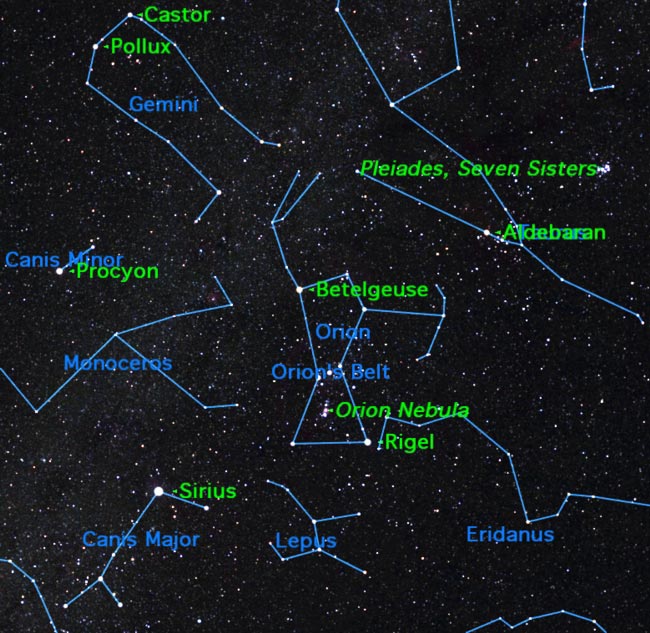
After the Big Dipper, probably the best known grouping of stars in the sky is the constellation Orion.
Lying on the celestial equator, Orion is an "equal opportunity" constellation, visible from all parts of the world except for the extreme polar regions. [Full+story]">See a star map of Orion and nearby constellations]
Orion consists of a large rectangle of stars — including the first magnitude stars Betelgeuse and Rigel in opposite corners — with a striking string of three equally bright stars forming Orion's belt in the center. From Orion's belt hang three more stars, forming Orion's sword. [Top 10 Winter Sky Targets]
In the Southern Hemisphere, Orion appears inverted, and the belt and sword don't make much sense, so Southerners often call this group of stars "the Frying Pan."
Let Orion be your guide to the stars of winter (or summer, if you're south of the equator).
Face south on a northern winter night (or north on a southern summer night) and you'll readily spot Orion about halfway up the sky. Look first for the slightly lopsided rectangle with reddish Betelgeuse in one corner and bluish Rigel in the opposite corner. Halfway in between are the three stars of Orion's belt.
These three stars point toward reddish Aldebaran in the constellation Taurus and the Pleiades star cluster beyond in one direction, and bluish Sirius, the brightest star in the sky, in the constellation Canis Major in the opposite direction.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The line from Rigel to Betelgeuse leads you towards the constellation Gemini, with its twin bright stars Castor and Pollux. South of the Twins is the bright star Procyon. If you are blessed with dark unpolluted skies, you may spot some of Orion's dimmer companions. Monoceros, the unicorn, is home to some of the richest star clusters in the Milky Way. The constellation Eridanus ("the river") contains many faint galaxies as it winds southward toward Canopus, the second-brightest star in the sky.
Under a dark sky you can make out more of the figure of Orion. In one hand he holds a shield to protect himself from the angry bull Taurus. In the other he raises high a club to threaten his enemies.
Just south of Orion's belt hangs Orion's sword. Look closely with binoculars, and you’ll see that each star in the sword is actually a star cluster or multiple star, with the center star being the greatest jewel in the sky, the Orion Nebula. Looking slightly fuzzy to the naked eye, it looks fuzzier still in binoculars.
Even the smallest telescope reveals its true nature: It is a nebula, a cloud of gas and dust in which new stars are being formed. The Orion Nebula repays study with any telescope, with its glowing wisps of gas surrounding the brilliant multiple star, the Trapezium, at its core.
How many stars can you see in the Trapezium? Small telescopes will show four stars, but larger telescopes will reveal several more fainter stars, all enveloped in the glow of the nebula. If you have a nebula filter, try it on the Orion Nebula. Different magnifications will reveal different areas of interest within this nebula.
If you have a telescope with four inches aperture or more, take a close look at Rigel. It is a beautiful double star: Its brilliant primary star is accompanied by the tiny speck of a secondary star.

Space.com is the premier source of space exploration, innovation and astronomy news, chronicling (and celebrating) humanity's ongoing expansion across the final frontier. Originally founded in 1999, Space.com is, and always has been, the passion of writers and editors who are space fans and also trained journalists. Our current news team consists of Editor-in-Chief Tariq Malik; Editor Hanneke Weitering, Senior Space Writer Mike Wall; Senior Writer Meghan Bartels; Senior Writer Chelsea Gohd, Senior Writer Tereza Pultarova and Staff Writer Alexander Cox, focusing on e-commerce. Senior Producer Steve Spaleta oversees our space videos, with Diana Whitcroft as our Social Media Editor.
