NASA Beams Mona Lisa to Moon with Laser
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Call it the ultimate in high art: Using a well-timed laser, NASA scientists have beamed a picture of Leonardo da Vinci's masterpiece, the Mona Lisa, to a powerful spacecraft orbiting the moon, marking a first in laser communication.
The laser signal, fired from an installation in Maryland, beamed the Mona Lisa to the moon to be received 240,000 miles (384,400 km) away by NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been orbiting the moon since 2009. The Mona Lisa transmission, NASA scientists said, is a major advance in laser communication for interplanetary spacecraft.
"This is the first time anyone has achieved one-way laser communication at planetary distances," David Smith, a researcher working with the LRO's Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter — which received the Mona Lisa message — said in a statement. "In the near future, this type of simple laser communication might serve as a backup for the radio communication that satellites use. In the more distance future, it may allow communication at higher data rates than present radio links can provide."
Article continues belowThe LRO spacecraft was the prime choice to test out the novel communication method because the spacecraft was already equipped with a laser receiver. While most spacecraft exploring the solar system today are tracked using radio signals, NASA is tracking LRO via lasers as well.
But the timing had to be just right.
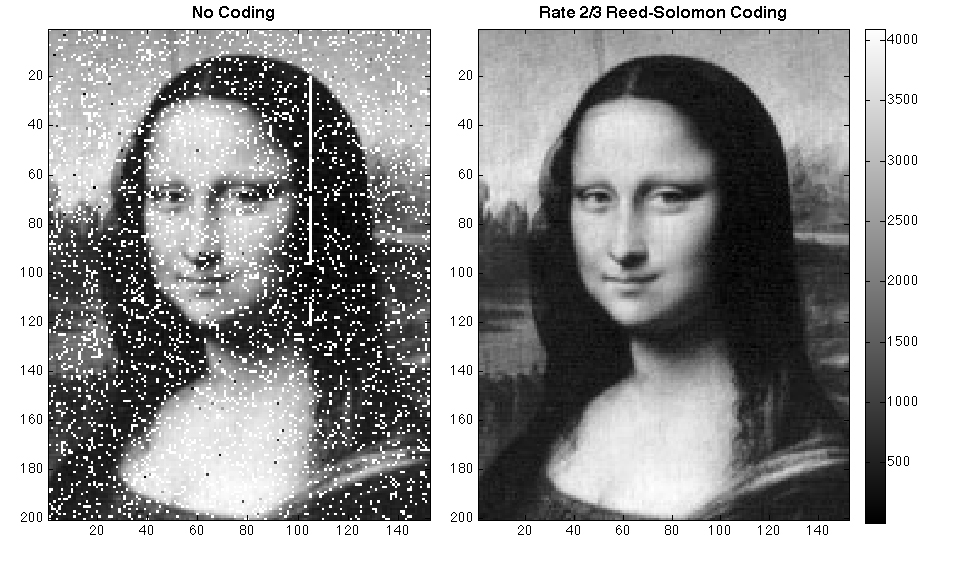
NASA used its Next Generation Satellite Laser Ranging station at the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., to send the Mona Lisa signal to LRO. The team divided the famous da Vinci painting into sections measuring 150 by 200 pixels and then transmitted them via the pulsing of the laser to the orbiter at a data rate of about 300 bits per second.
Once the lunar orbiter received the image, it reconstructed the photo, corrected for distortions created as the laser signal zipped through Earth's atmosphere, and then sent the image back to Earth using its normal form of communication: radio waves.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"This pathfinding achievement sets the stage for the Lunar Laser Communications Demonstration," Richard Vondrak, another researcher with the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter said, "a high data rate laser-communication-demonstrations that will be a central feature of NASA's next moon mission, the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust environment Explorer."
The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer is slated to launch toward the moon later this year and will focus on mapping the lunar atmosphere and environment.
Follow Miriam Kramer on Twitter @mirikramer or SPACE.com @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

Miriam Kramer joined Space.com as a Staff Writer in December 2012. Since then, she has floated in weightlessness on a zero-gravity flight, felt the pull of 4-Gs in a trainer aircraft and watched rockets soar into space from Florida and Virginia. She also served as Space.com's lead space entertainment reporter, and enjoys all aspects of space news, astronomy and commercial spaceflight. Miriam has also presented space stories during live interviews with Fox News and other TV and radio outlets. She originally hails from Knoxville, Tennessee where she and her family would take trips to dark spots on the outskirts of town to watch meteor showers every year. She loves to travel and one day hopes to see the northern lights in person. Miriam is currently a space reporter with Axios, writing the Axios Space newsletter. You can follow Miriam on Twitter.

