Perseid Meteor Shower Peaks August 12
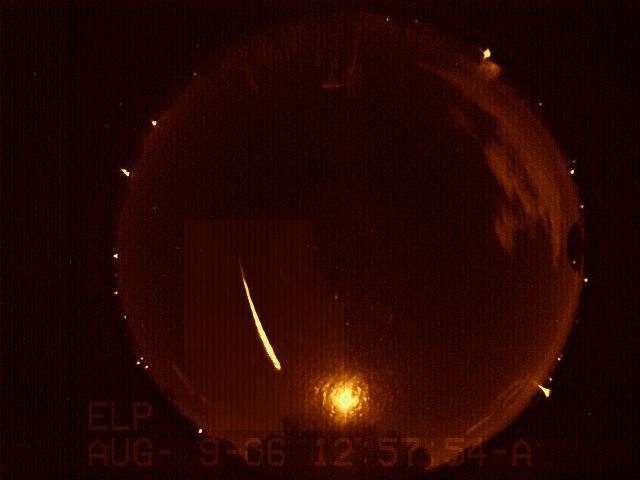
Every August, just when many people go vacationing in the country where skies are dark, the best-known meteor shower makes its appearance.
It is also the month of "The Tears of St. Lawrence," more commonly known as the Perseid Meteor Shower.
Laurentius, a Christian deacon, is said to have been martyred by the Romans in 258 AD on an iron outdoor stove. It was in the midst of this torture that Laurentius cried out:
"I am already roasted on one side and, if thou wouldst have me well cooked, it is time to turn me on the other."
The saint's death was commemorated on his feast day, Aug. 10. King Phillip II of Spain built his monastery place, the "Escorial," on the plan of the holy gridiron. And the abundance of shooting stars seen annually between approximately Aug. 8 and 14 have come to be known as St. Lawrence's "fiery tears."
Viewing prospects
In 2008, the Perseids are expected to reach their maximum on Aug. 12.
The exact time of maximum should be about 7:00 a.m. EDT (1100 GMT) Aug. 12, according to Margaret Campbell-Brown and Peter Brown in the 2008 Observer's Handbook of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. If so, the timing is very good for meteor watchers observing before dawn in North America, especially in the western states. And that morning, the waxing gibbous moon sets around 1:30 a.m. local daylight saving time, leaving a dark sky for the next 3 hours.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Take full advantage of that moonless period. Next year, a last quarter moon will illuminate the after-midnight sky with its light and will hinder observation of the Perseids.
Comet bits
We know today that these meteors are actually the dross of the Swift-Tuttle comet. Discovered back in 1862, this comet takes approximately 130 years to circle the sun. And in much the same way that the Tempel-Tuttle comet leaves a trail of debris along its orbit to produce the Leonid meteors of November, Comet Swift-Tuttle produces a similar debris trail along its orbit to cause the Perseids. Indeed, every year during mid-August, when the Earth passes close to the orbit of Swift-Tuttle, the material left behind by the comet from its previous visits rams into our atmosphere at approximately 37 miles (60 kilometers) per second and creates bright streaks of light in our midsummer night skies.
Comet Swift-Tuttle made its most recent appearance sixteen years ago, in December 1992. For several years before and after its 1992 return, the Perseids were a far more prolific shower, appearing to produce brief outbursts of as many as several hundred meteors per hour, many of which were dazzlingly bright and spectacular. The most likely reason was that the Perseids parent comet was itself passing through the inner solar system and that the streams of Perseid meteoroids in the comet's vicinity were larger and more thickly clumped together — hence the reason for the brighter meteors and much-higher-than-normal meteor rates.
But with the comet now far back out in space, Perseid activity has pretty much returned to normal.
Meteor clumps
A very good shower will produce about one meteor per minute for a given observer under a dark country sky. Any light pollution or moonlight considerably reduces the count. The August Perseids are among the strongest of the readily observed annual meteor showers, and at maximum activity nominally yield 50 or 60 meteors per hour. However, observers with a wide-open view of exceptionally dark skies often record even larger numbers on the order of 90 or even 100 per hour.
But while 60 meteors per hour correspond to one meteor sighting every minute, keep in mind that this is only a statistical average. In reality, what usually is seen is what some have called, "the clumping effect." Sometimes you'll see two or even three Perseids streak across the sky in quick succession, all within less than minute. This is usually followed by a lull of several minutes or more, before the sky suddenly bears fruit once again.
When and where to look
Typically during an overnight watch, the Perseids are capable of producing a number of bright, flaring and fragmenting meteors, which leave fine trains in their wake.
On the night of shower maximum, the Perseid radiant is not far from the famous "Double Star Cluster" of Perseus. Low in the northeast during the early evening, it rises higher in the sky until morning twilight ends observing. Shower members appearing close to the radiant have foreshortened tracks; those appearing farther away are often brighter, have longer tracks, and move faster across the sky. About five to 10 of the meteors seen in any given hour will not fit this geometric pattern, and may be classified as sporadic or as members of some other (minor) shower.
Watching for the Perseids consists of lying back, gazing up into the stars and waiting. Perseid activity increases sharply in the hours after midnight, so plan your observing times accordingly. We are then looking more nearly face-on into the direction of the Earth's motion as it orbits the Sun, and the radiant is also higher up. Making a meteor count is as simple as lying in a lawn chair or on the ground and marking on a clipboard whenever a "shooting star" is seen.
Counts should be made on several nights before and after the predicted maximum, so the behavior of the shower away from its peak can be determined. Usually, good numbers of meteors should be seen on the preceding and following nights as well. The shower is generally at one-quarter strength one or two nights before and after maximum.
A few Perseids can be seen as much as two weeks before and a week after the peak. The extreme limits, in fact, are said to extend from July 17 to Aug. 24, though an occasional one might be seen almost anytime during the month of August.
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for The New York Times and other publications, and he is also an on-camera meteorologist for News 12 Westchester, New York.

Joe Rao is Space.com's skywatching columnist, as well as a veteran meteorologist and eclipse chaser who also serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, Sky & Telescope and other publications. Joe is an 8-time Emmy-nominated meteorologist who served the Putnam Valley region of New York for over 21 years. You can find him on Twitter and YouTube tracking lunar and solar eclipses, meteor showers and more. To find out Joe's latest project, visit him on Twitter.
