The Spectacular Breakup of ATV: One Final Experiment
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
In earlyMarch 2008, the European Space Agency launched a new spacecraft called theAutomated Transfer Vehicle (ATV). ATV is a bigger version of the RussianProgress, a re-supply ship for the International Space Station (ISS). ATV had aperfect launch and docked to ISS as planned. After delivering supplies, thecraft was used as crew quarters, and at one point helped push ISS out of the wayof a dangerous piece of orbital debris. On September 5, 2008, it was finallytime to call an end to the mission and the ATV was undocked from the ISS, readyto enter Earth's atmosphere over the South Pacific Ocean. Lacking a heat shieldto save weight, the craft will break up on reentry in a spectacular fireball.
Our teamcame in the picture relatively late in the game. It turned out that we were notthe only ones who were fascinated by the fact that the 13-ton ATV would enterin a controlled manner with a speed of 4.7 miles (7.6 kilometers) per second.If we could use guidance from the ATV Control Center for latest trajectoryupdates, we thought it would be possible to position two research aircraftalongside the shallow entry trajectory and observe the breakup process indetail. There is no way to do this for natural fireballs, which appear atrandom in the sky and at unknown times. Fragmentation is the single mostimportant phenomenon that determines the physical conditions in naturalmeteors.
ESA wassupportive of our proposed mission. A documentation of the breakup processcould help validate the models built to study how that fragmentation evolves ina series of disruptions of major components. At reentry into the atmosphere,ATV would execute one final experiment before the missioncompletion. Our experience with meteor spectroscopy carried the promise ofperhaps being able to identify some of the fragments from their radiationsignatures. The ATV-1 "Jules Verne" Multi-Instrument AircraftCampaign was born.
A workshopwas organized at NASA Ames Research Center to discuss how best to observe theATV reentry, bringing observers and ATV mission managers together. It wasdecided to postpone the reentry by three weeks so that the reentry would happenat nighttime for best viewing conditions.
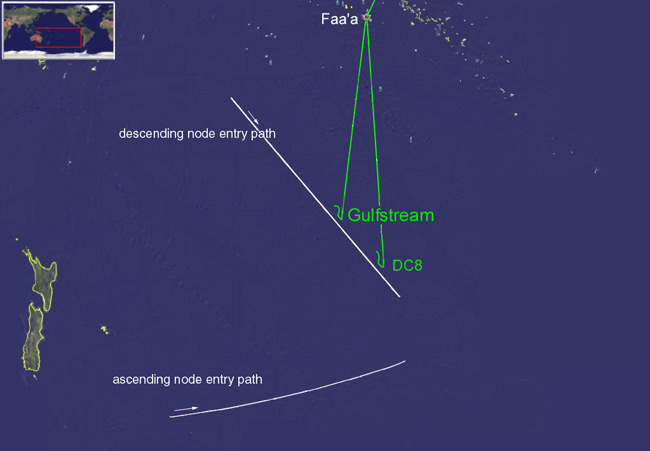
As inearlier multi-aircraft(MAC) missions, NASA Ames took the lead in organizing the effort. Twoaircraft will participate in this campaign. One is NASA's DC-8 AirborneLaboratory, operated by the University of North Dakota (NSERC) and NASA Dryden Flight Research Center from the Dryden Aircraft Operations Center in Palmdale. Theother aircraft is a privately owned Gulfstream V, operated by H211 LLC at NASA Ames Research Center. Together they make it possible to triangulate the importantfragmentation events and measure their altitude in the atmosphere.
A largeteam of researchers from ESA, NASA, universities and private organizations willjoin in the mission, including a team from NASA's Orbital Debris Office at NASAJohnson Space Flight Center. ESA project manager Dr. Jason Hatton has organizedthe ESA effort, while program manager Dave Jordan of NASA Ames Research Center has coordinated the NASA effort. The logistics for some 36 researchers arecoordinated by the SETI Institute. SETI Institute's meteor astronomer, Dr.Peter Jenniskens, is the mission scientist.
The reentryis expected in the early morning of September 29. The two aircraft will leavefrom NASA Ames and NASA Dryden in the evening of September 26 to a staging areaon the island of Tahiti in French Polynesia. From there, the team will departdeeper into the south Pacific on the early morning of September 29. If all goesto plan, the reentry will take only about 4 minutes, during which all data needto be collected.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Observingthe ATV reentry is challenging, requiring good planning and communications withthe spacecraft operators. Past observation attempts have often beenunsuccessful due to lack of good coordination or wrong instrument settings. Oneexample is the reentryof MIR, which was not observed from two chartered private aircraft back in2001. Instead, MIR was directed to enter closer to the staging area, and onlythose that stayed behind at the hotel in Fiji observed the MIR reentry.
Our effortsare supported by the ATV Control Center in Toulouse, France. We hope to receivelast-minute updates on the reentry process to be able to position ourselveswell along the reentry path. Predictions have been made of how bright ATV willbe, just prior to breakup, and we hope that this will enable us to have ourinstruments correctly configured. It is still a challenge and we hope you willbe rooting for us. This trip to Tahiti will be no honeymoon.
For moreinformation on the mission, please visit our mission website at: http://atv.seti.org.
Peter is a distinguished Dutch-American astronomer and senior research scientist at the Carl Sagan Center of the SETI Institute and at NASA Ames Research Center. He is a noted expert on meteor showers, meteor falls, and artificial meteors who also wrote the books "Meteor Showers and Their Parent Comets from 2006 and "Atlas of Earth's Meteor Showers from 2023. He's a graduate of Leiden University where he obtained his M.S. and Ph.D.
