EXCLUSIVE: Satellite Sleuth Closes in on Noah's Ark Mystery

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
High on Mt. Ararat in eastern Turkey, there is a baffling mountainside "anomaly," a feature that one researcher claims may be something of biblical proportions.
Images taken by aircraft, intelligence-gathering satellites and commercial remote-sensing spacecraft are fueling an intensive study of the intriguing oddity. But whether the anomaly is some geological quirk of nature, playful shadows, a human-made structure of some sort, or simply nothing at all-that remains to be seen.
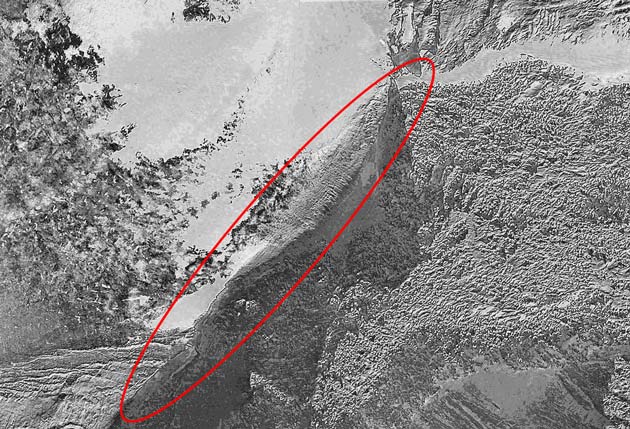
Whatever it is, the anomaly of interest rests at 15,300 feet (4,663 meters) on the northwest corner of Mt. Ararat, and is nearly submerged in glacial ice. It would be easy to call it merely a strange rock formation.
Article continues belowBut at least one man wonders if it could be the remains of Noah's Ark-a vessel said to have been built to save people and selected animals from the Great Flood, the 40 days and 40 nights of deluge as detailed in the Book of Genesis.
The Genesis blueprint of the Ark detailed the structure as 6:1 length to width ratio (300 cubits by 50 cubits). The anomaly, as viewed by satellite, is close to that 6:1 proportion.
Newfound optimism
Identifying the Ararat anomaly has been a 13-year-long quest of Porcher Taylor, an associate professor in paralegal studies at the University of Richmond's School of Continuing Studies in Virginia.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Taylor has been a national security analyst for more than 30 years, also serving as a senior associate for five years at the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) in Washington, D.C.
"I've got new found optimism ... as far as my continuing push to have the intelligence community declassify some of the more definitive-type imagery," Taylor told SPACE.com/LiveScience. He points to a "new and significant development," a high-resolution image taken by DigitalGlobe's impressive QuickBird satellite and shown here publicly for the first time [alternate version with no annotation].
"I'm calling this my satellite archeology project," Taylor said. It's an effort that has now included use of QuickBird, GeoEye's Ikonos spacecraft, Canada's Radarsat 1, as well as declassified aerial and satellite images taken by the various U.S. intelligence agencies.
Making the mountain transparent
Taylor said his goal is straightforward: Combining this imagery to make the Ararat anomaly transparent to the public, as well as to the discerning, dispassionate eyes of scientists, imagery analysts, and other experts.
"I had no preconceived notions or agendas when I began this in 1993 as to what I was looking for," Taylor said.
As for the saga of Noah's Ark, he is quick to note that there are those who say it is fable while some take it as truth.
Nevertheless, the anomaly may not be a ridge line of ice, snow and possibly rock, but an artificial ridge line, Taylor said. "I maintain that if it is the remains of something manmade and potentially nautical, then it's potentially something of biblical proportions."
While chiding the intelligence communities to release more of their closely guarded satellite imagery, Taylor said that soon-to-fly commercial remote sensing spacecraft are sure to help his archeological undertaking.
"We've got three new birds that are going up. I'm using all my clout, rapport and lobbying to, hopefully, have them at least fly calibration runs over Mt. Ararat," Taylor said. Those images would make the mountain even more transparent, he said.
Will it float?
Meanwhile, Taylor has an ever-expanding network of experts to help tease out the truth about the anomaly.
For example, satellite imagery analyst Rod Franz of SunTek Media Group/RiteImage, Inc., located in Henderson, Nevada, has taken a look at imagery provided by Taylor of the Ararat anomaly and carried out additional analysis of the area. As director of training for the firm, Franz sharpened his skills by serving nearly 25 years as a military intelligence imagery analyst.
For the anomaly assessment, the same software tools used for studying government and commercial remote sensing data were employed, Franz told SPACE.com/LiveScience. Ground distances and scales of the anomaly were determined. That software also has the ability to adjust brightness, haze, sharpness, contrast and other factors of the area of interest, he said.
"Along with many other image manipulation functions ... I also used the pseudo-color function trying to determine if I could detect anything under the ice and snow," Franz said.
The face of the anomaly measured 1,015 feet (309 meters) across, Franz said. "I also found the shape of the anomaly appears to fit on a circle. I am not sure what this means, if anything, but I find it curious."
Given that length, Taylor pointed out, the anomaly dwarfs the Titanic and Bismarck in size, and equals the size of the largest modern aircraft carrier. That analysis would seem to call into question whether the anomaly is a wooden ship and raises a key question: If a boat were truly that huge, would it float?
There are also experts in remote sensing who offer a skeptical view.
"Image interpretation is an art," said Farouk El-Baz, Director of the Boston University Center for Remote Sensing.
"One has to be familiar with Sun lighting effects on the shape of observed features," El-Baz said. "Very slight changes in slope modify shadow shapes that affect the interpretations. Up to this time, all the images I have seen can be interpreted as natural landforms. The feature that has been interpreted as the 'Ararat Anomaly' is to me a ledge of rock in partial shadow, with varied thickness of snow and ice cover.
Visual truth serum
Thanks to more satellite imagery in the offing, as well as other studies underway, Taylor said his remote archeological research is on the upswing.
There is an ultimate end-game. That is, on-the-spot ground truth ... and Taylor hopes his research findings will catalyze a top-notch expedition to the area. "It is whatever it is," he said.
But for now, satellite remote sensing to carry out archeological "digs" from space will fill in for an in-the-field expedition.
Just a few weeks ago, for example, NASA scientists utilizing space- and aircraft-based remote sensing hardware and techniques uncovered Maya ruins hidden in the rainforests of Central America for more than 1,000 years.
"For explorers, imagery from GeoEye's Ikonos satellite married with Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite data has become as indispensable as water and freeze dried food for any expedition. One does not want to leave home without it," said Mark Brender, GeoEye Vice President for communications and marketing, headquartered in Dulles, Virginia.
For researchers, imagery from space like those provided by GeoEye provides "the ultimate high shot" and a contextual view you could never get from observations on the ground or even from a plane, Brender told SPACE.com/LiveScience. "It's visual truth serum."
- Zoom in on Mt. Ararat
- 2002: Satellite Search Underway For Noah's Ark
- 2001: Satellites Search for Noah's Ark
- Claimed Discovery of Atlantis Called 'Completely Bogus'
- End of the World? Not Likely, Scientists Say
- The Truth Behind the Shroud of Turin

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years. Currently writing as Space.com's Space Insider Columnist among his other projects, Leonard has authored numerous books on space exploration, Mars missions and more, with his latest being "Moon Rush: The New Space Race" published in 2019 by National Geographic. He also wrote "Mars: Our Future on the Red Planet" released in 2016 by National Geographic. Leonard has served as a correspondent for SpaceNews, Scientific American and Aerospace America for the AIAA. He has received many awards, including the first Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History in 2015 at the AAS Wernher von Braun Memorial Symposium. You can find out Leonard's latest project at his website and on Twitter.