New Method Measures Astronomical Distances
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
A newmethod for measuring cosmic distances could pinpoint objects in the universe upto 300 million light-years away and beyond.
Thejust-realized technique was announced today at a meeting of the AmericanAstronomical Union in Pasadena, Calif., and could help astronomers in theirquest to track the universe's expansion rate.
Until now,astronomers have partly relied on giant stars called short-period cepheids thatbrighten and dim every few days to calculate distances to objects in theuniverse. This lightblinking directly relates to the star's true brightness, and astronomerscan compare the true and apparent luminosity (as seen from Earth) to determinethe distanceto that object. But beyond 100 million light-years from Earth, the stars'signals get lost among other bright stars.
(Alight-year is the distance lightwill travel in a year, which is about 6 trillion miles, or 10 trillion km.)
The newmethod involves so-called ultra long period cepheids (ULP cepheids), which aremuch brighter and so stand out at even farther distances.
KrzysztofStanek of Ohio State University and his colleagues searched the literature,finding records for 18 such ULP cepheids, ranging from 12 to 20 times the massof the sun and located in nearby galaxies. The distances to these nearbygalaxies are well known, so the astronomers used that knowledge to calibratethe distance to the ULP cepheids.
They foundthat they could use ULP cepheids to determine distance with a 10 to 20 percenterror, a rate typical of other methods used for measuring cosmic distances. Theresearchers hope to reduce that error as more ULP cepheids are recorded.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
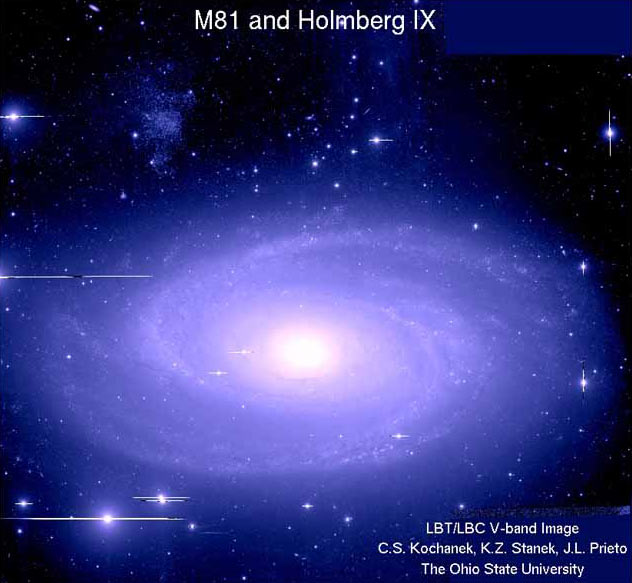
Now, theresearchers are using the Large Binocular Telescope in Tucson, Ariz., to look for more ULP cepheids. Stanek said they've found a few good candidates inthe galaxy M81, but those results have yet to be confirmed.
The research was funded by the NationalScience Foundation.
- Top 10 Star Mysteries
- How Massive Stars Form: Simple Solution Found
- Video ? When Stars Collide

Space.com is the premier source of space exploration, innovation and astronomy news, chronicling (and celebrating) humanity's ongoing expansion across the final frontier. Originally founded in 1999, Space.com is, and always has been, the passion of writers and editors who are space fans and also trained journalists. Our current news team consists of Editor-in-Chief Tariq Malik; Editor Hanneke Weitering, Senior Space Writer Mike Wall; Senior Writer Meghan Bartels; Senior Writer Chelsea Gohd, Senior Writer Tereza Pultarova and Staff Writer Alexander Cox, focusing on e-commerce. Senior Producer Steve Spaleta oversees our space videos, with Diana Whitcroft as our Social Media Editor.