Crash of Falling Russian Spacecraft Imminent, Experts Say

Russia's botched Mars probe mission Phobos-Grunt is fast-approaching a fiery death, with just one or two days remaining before it falls from space, experts and Russian space officials say.

"The European Space Agency's current re-entry prediction for Phobos-Grunt … points to the early evening (Central European Time) on Sunday, Jan.15, with an uncertainty of plus/minus five orbits," equal to plus or minus 7.5 hours, Heiner Klinkrad, head of the space debris office at ESA’s European Space Operations Center in Darmstadt, Germany, told SPACE.com today (Jan. 14) in an email.
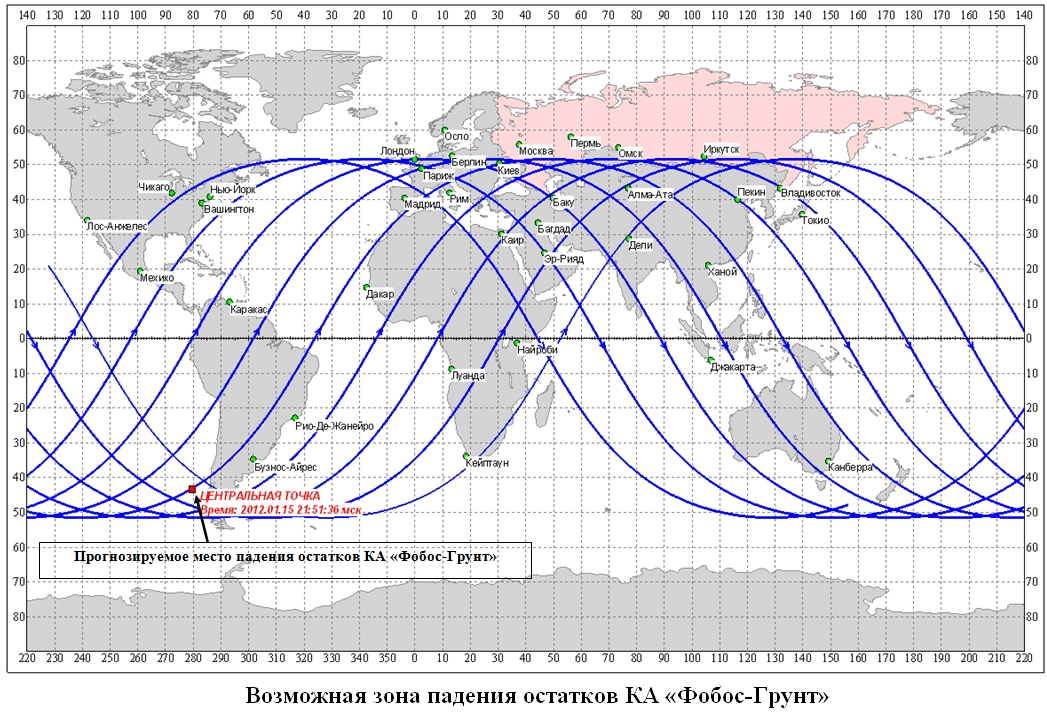
A statement today by Russia's Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) also pegged Sunday as the crash day for Phobos-Grunt, but went even farther. According to the statement, released in Russian, the 14-ton spacecraft filled with fuel is expected to fall on Jan. 15 and may crash in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of Chile.
The translation of the statement and map released by Russian space officials depict the potential crash time as occurring at about 2151 GMT (4:51 p.m. EST), although major uncertainties still remain. There is a chance the spacecraft could fall earlier in the day, or later on Monday, Jan. 16.
Falling Russian Mars probe
ESA, among a host of other space agencies and organizations, has been closely monitoring the decay of the doomed Russian spacecraft. [Infographic: The Fall of Russia's Doomed Phobos-Grunt]
Russian space agency officials have reported that they expect that, at most, about 20 to 30 fragments of Phobos-Grunt may survive the fiery re-entry and reach Earth's surface.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
But given that most of the Earth's surface is covered with water, the odds that these leftovers — a predicted total mass of less than 440 pounds (200 kilograms) — would fall onto dry land is very small, scientists have said.
Russia launched the Phobos-Grunt mission into space on Nov. 8 (Nov. 9 Moscow time). The spacecraft was designed to fly to Phobos, one of two moons circling Mars.
Once at Phobos, the space probe was expected to collect samples from the Martian moon and then return them to Earth in 2014. However, shortly after launch, the spacecraft failed to boost itself out of Earth orbit to begin the trip to Mars.
Packed with toxic fuel
One unique aspect of the Phobos-Grunt re-entry is its large cache of onboard fuel.
While the dry mass of the wayward satellite is just 2.5 tons, the probe totes about 11 tons of toxic propellant, unused when the craft became marooned in Earth orbit and not outbound to Mars. [Photos of the Phobos-Grunt Mars Mission]
Orbital debris experts suggest that Phobos-Grunt's fuel tanks, reportedly made of aluminum that contains the unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH), will explode high above the Earth. Those heat-succumbing tanks would therefore release the load of propellant to burn up in Earth's atmosphere.
"The 'it just burns up' issue remains invisible frankly," said Martin Ross, Director of The Aerospace Corporation's Center for Launch Emissions and Atmospheric Research in El Segundo, Calif.
"What is needed is a full accounting of the material that gets vaporized and re-condenses into small particles that may remain in the upper atmosphere for many years," Ross told SPACE.com. "Some of these particles may influence chemistry, since the vaporized materials are exotic in some cases, in that region of the atmosphere in subtle ways. It remains a question mark," he said.
Flying in space is hard
Phobos-Grunt is also outfitted with a nose-cone shaped descent vehicle wrapped in a thermal protection system. It was meant to haul back to Earth samples collected at Phobos. That hardware was designed to sky dive through Earth’s atmosphere and hard land without parachute into the Sary Shagan missile test range in Kazakhstan — if the Mars mission achieved success.
Nestled inside that re-entry sample capsule is the Planetary Society's tiny Living Interplanetary Flight Experiment (LIFE) biomodule that carries a select set of microorganisms.
"Trackers won't be able to predict where debris may fall until just a few hours before the event, so it’s impossible to say whether the biomodule will be recovered," Planetary Society officials explained in a statement on Jan. 13.
“What we’ve seen is heartbreaking reinforcement of an oft-repeated maxim. Space is hard! We are disappointed that our remarkable test of the hardiness of living organisms will not get the 34 months in deep space we had hoped for," said the Planetary Society's Chief Executive Officer Bill Nye, also known as Bill Nye the Science Guy.
"We also offer our condolences to the China National Space Administration; it's their first Mars mission and a disappointment," Nye added.
Like LIFE, China's Yinghuo-1 orbiter hoped to catch a ride to Mars on Phobos-Grunt in order to study the Red Planet.
Russia's satellite crash past
The former Soviet Union (USSR), and now Russia, has a bit of history regarding satellites falling from space and tumbling onto land.
Due to a propulsion system failure, the Cosmos 954 spacecraft — a Soviet nuclear-powered Radar Ocean Reconnaissance Satellite — fell into Canada's Northwest Territories in January 1978. It had only been in space for four months.
Large amounts of radioactive material from the satellite's fall was scattered from Great Slave Lake into northern Saskatchewan and Alberta.
Subsequently, a joint U.S.-Canadian clean-up operation picked up roughly 0.1 percent of Cosmos 954's power source. The spacecraft's nuclear reactor worked on uranium, enriched with isotope of uranium-235.

Liability for damage
Canadian authorities determined that all but two of the Cosmos 954 fragments recovered were radioactive. Some fragments located proved to be of lethal radioactivity.
The spacecraft's plummet into Canada also marked the first time that the adjudicative process built into the United Nation's Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects was put to the test.
Canada claims from the USSR added up to more than $6 million. In the end, in 1981, the Soviet Union coughed up $3 million to settle the Canadian claim of reimbursement.
Unlike the Cosmos satellite, Russia's Phobos-Grunt is a solar-powered spacecraft. One instrument on the probe does carry a small amount of the radioactive element cobalt-57.
However, Lev Zelenyi, director of the Space Research Institute in Moscow and chairman of the Russian Academy of Sciences’ Solar System Exploration Board, has stated that the amount contained in that instrument is less than 10 micrograms and no significant problems are anticipated.

Standby alert
Meanwhile, as Phobos-Grunt draws closer and closer to its fiery finale, a worldwide team of skywatchers is on standby alert in the hopes of spotting the fall.
"Experienced observers know that the probability of seeing any given satellite re-entry is very small, so they maintain very low expectations," said Toronto, Canada-based Ted Molczan, a leader in the citizen network of observers.
"Those who are keen to observe one [a re-entry of space hardware] will monitor the trend in the decay estimates," Molczan told SPACE.com.
"If it appears that re-entry will occur at about the time Earth’s rotation drags their location through the plane of the orbit, then they may go out and have a look, still fully expecting to see nothing, but knowing they have maximized their personal odds," Molczan said.
Leonard David has been reporting on the space industry for more than five decades. He is a winner of last year's National Space Club Press Award and a past editor-in-chief of the National Space Society's Ad Astra and Space World magazines. He has written for SPACE.com since 1999.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years. Currently writing as Space.com's Space Insider Columnist among his other projects, Leonard has authored numerous books on space exploration, Mars missions and more, with his latest being "Moon Rush: The New Space Race" published in 2019 by National Geographic. He also wrote "Mars: Our Future on the Red Planet" released in 2016 by National Geographic. Leonard has served as a correspondent for SpaceNews, Scientific American and Aerospace America for the AIAA. He has received many awards, including the first Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History in 2015 at the AAS Wernher von Braun Memorial Symposium. You can find out Leonard's latest project at his website and on Twitter.
