Voyager: 15 incredible images of our solar system captured by the twin probes (gallery)
The twin probes have captured some remarkable images of our cosmic neighborhood.

NASA's twin probes Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have captured some truly remarkable images of our solar system and are currently roaming through interstellar space.
Despite its name Voyager 2 launched before Voyager 1, when it lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a Titan IIIE-Centaur on Aug. 20, 1977. Voyager 1 followed suit about two weeks later on Sept. 5.
While Voyager 1 primarily focused on Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 2 visited both gas giants and then ventured on to Uranus and Neptune. But the duo didn't stop there. Voyager 1 officially entered interstellar space on Aug. 25, 2012, while Voyager 2 entered on Nov. 5, 2018. The pair continue to journey through the cosmos and have enough power and fuel to keep scientific instruments running until at least 2025, according to NASA.
Here we celebrate the achievements of both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 with some incredible images captured by the pair.
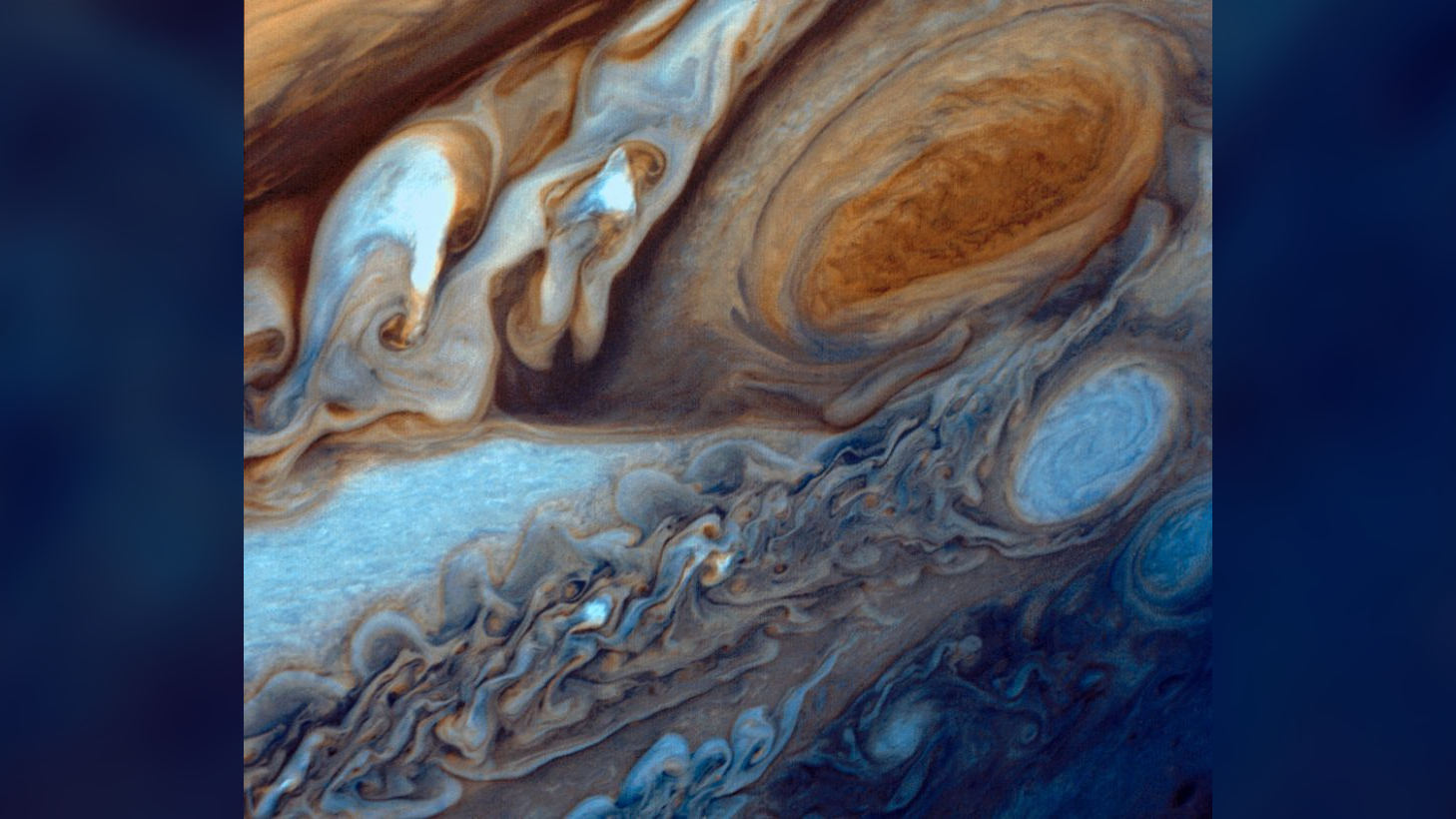
This image was taken when NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft zoomed toward Jupiter in January and February 1979, capturing hundreds of images during its approach, including this close-up of swirling clouds around Jupiter's Great Red Spot.
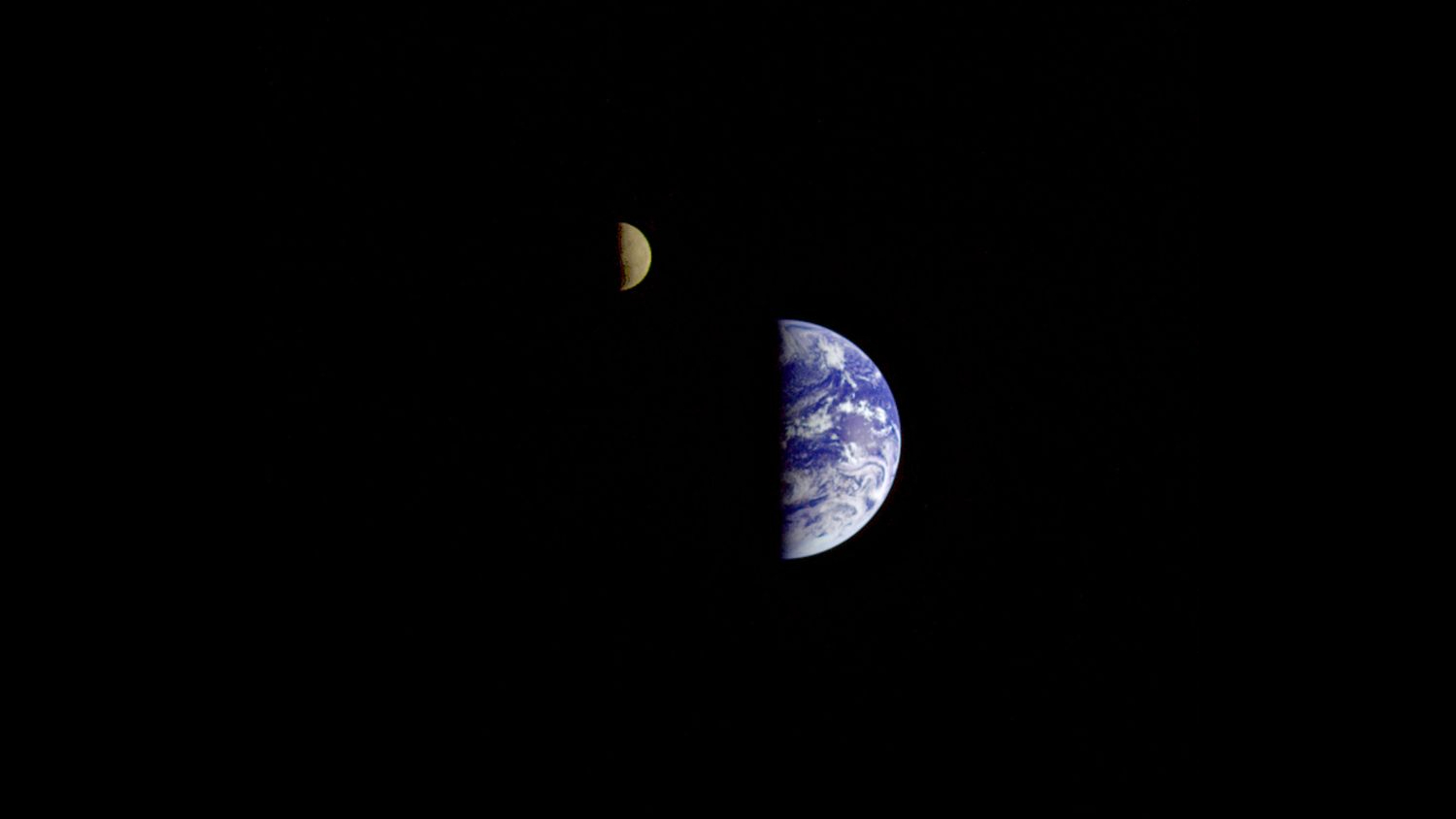

This image of the Earth and moon are in a single frame. Voyager was the first spacecraft to achieve this and captured the iconic image on Sept. 18, 1977, by Voyager 1 when it was 7.25 million miles from Earth. The moon is at the top of the picture and beyond the Earth as viewed by Voyager.
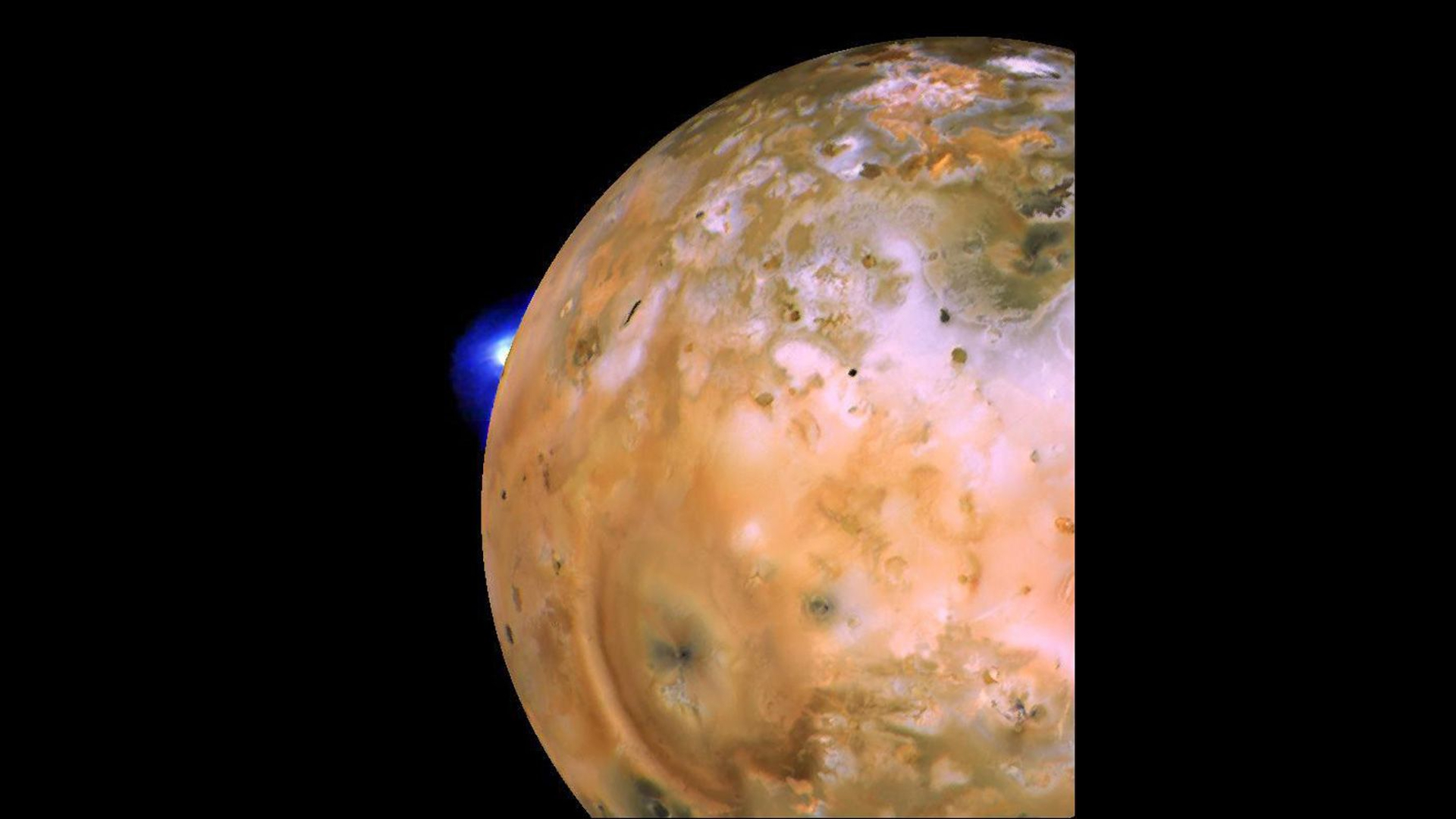
A Voyager 1 image of Jupiter's moon Io showing the active plume of the volcano Loki. The heart-shaped feature southeast of Loki consists of fallout deposits from the active plume Pele. The images that make up this mosaic were taken from an average distance of approximately 340,000 miles (490,000 kilometers) from the moon.
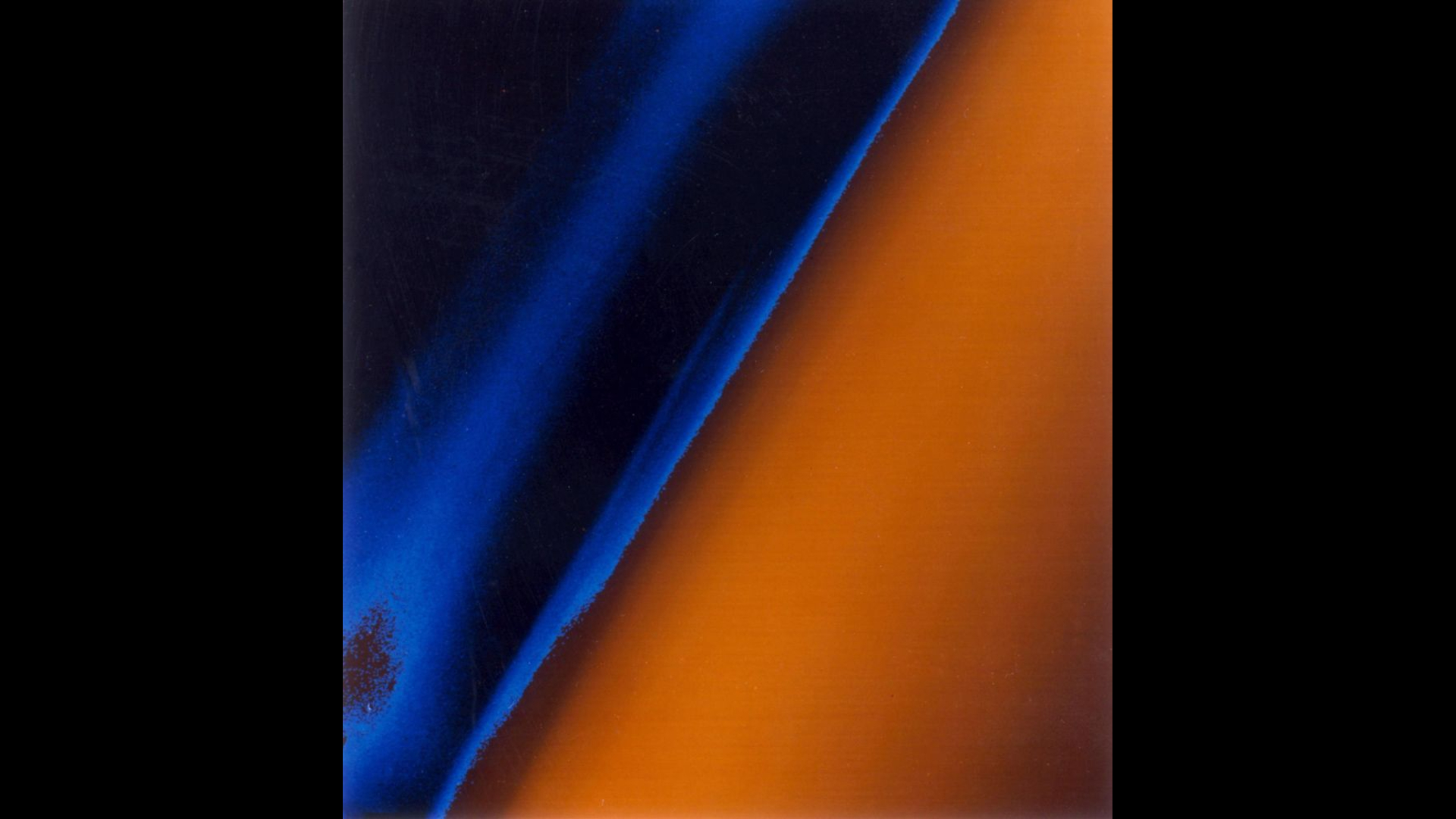

Layers of haze covering Saturn's moon Titan are seen in this image taken by Voyager 1 on Nov. 12, 1980, at a range of 13,700 miles (22,000 km). This false-color image shows the details of the haze that covers Titan. The upper level of the thick aerosol above the moon's limb appears orange.
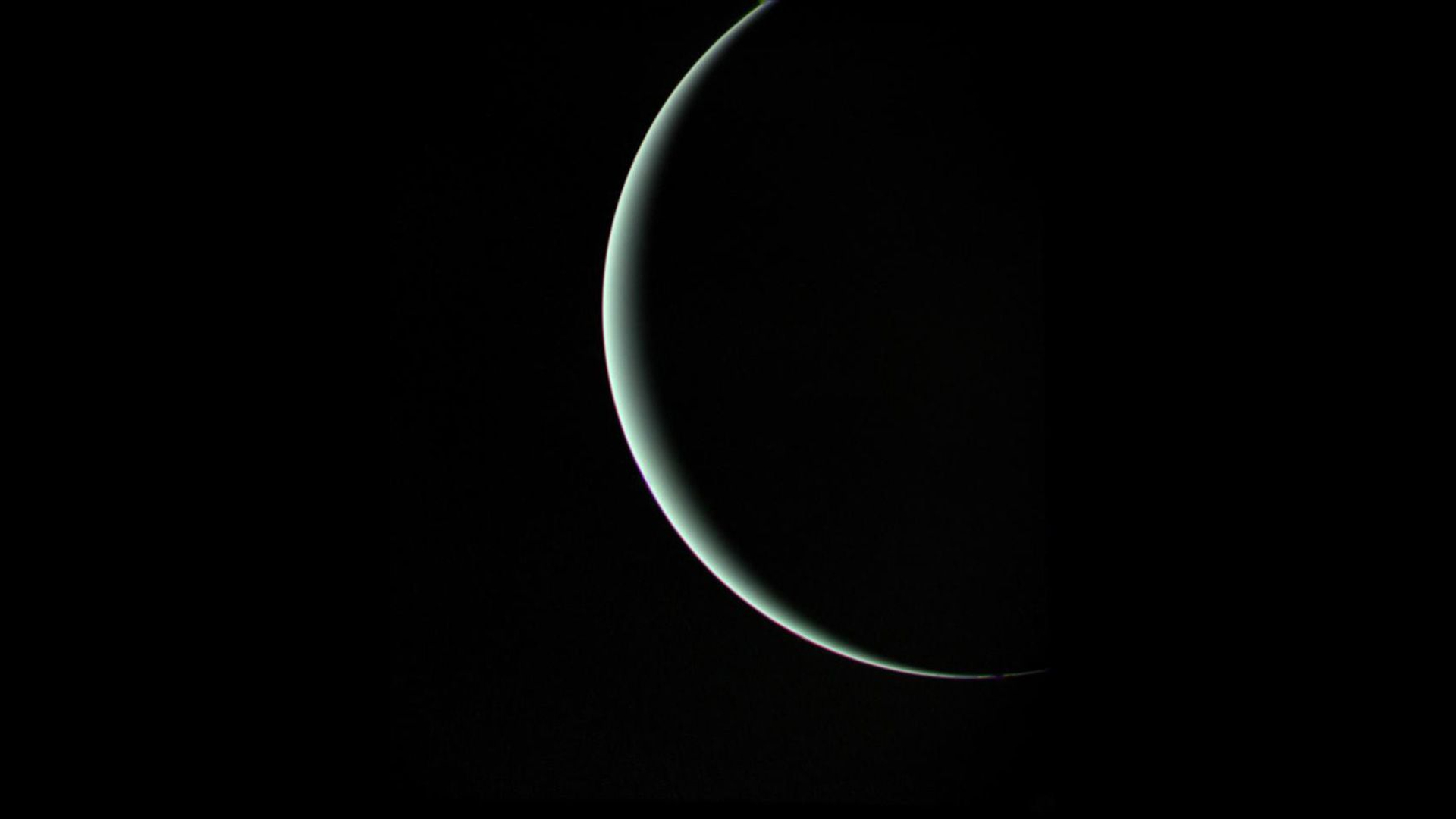

This view of Uranus was recorded by Voyager 2 on Jan. 25, 1986, as the spacecraft left the planet behind and set forth on the cruise to Neptune. Even at this extreme angle, Uranus retains the pale blue-green color seen by ground-based astronomers and recorded by Voyager during the historic encounter.
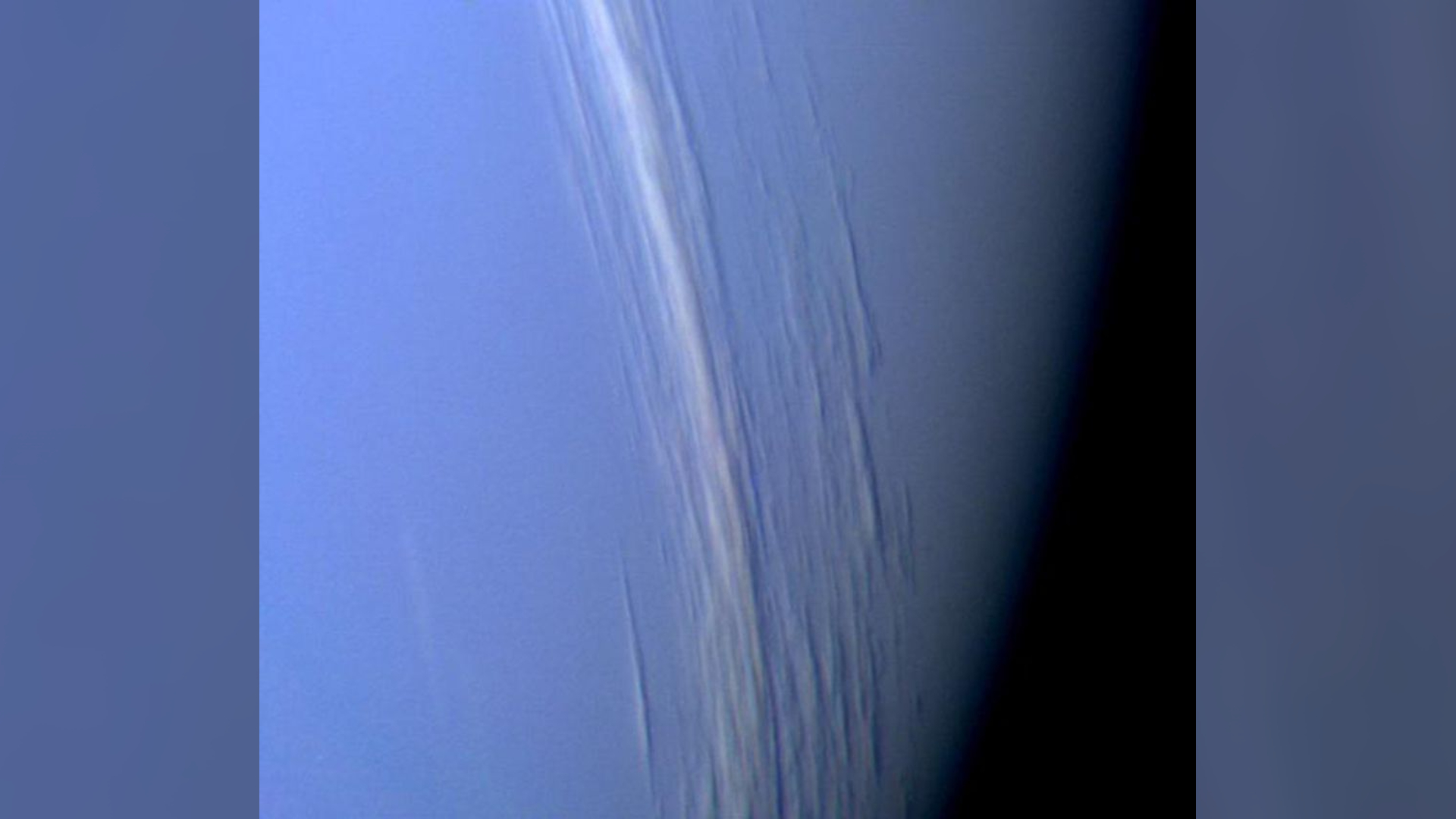

This Voyager 2 high-resolution color image provides obvious evidence of vertical relief in Neptune's bright cloud streaks. These clouds were observed at a latitude of 29 degrees north near Neptune's east terminator, the "line" on a planet where daylight meets darkness.
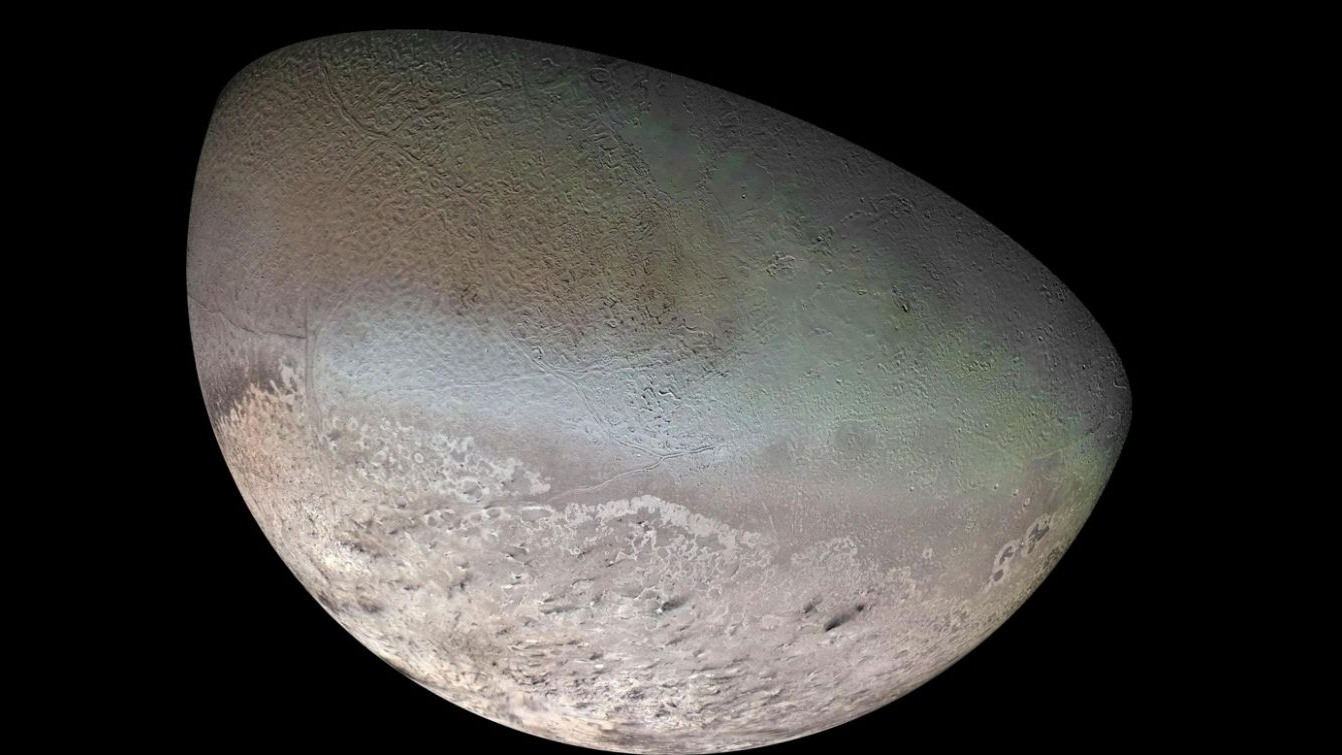
Global color mosaic of Triton, taken in 1989 by Voyager 2 during its flyby of the Neptune system. The color was synthesized by combining high-resolution images taken through orange, violet and ultraviolet filters; these images were displayed as red, green and blue images and combined to create this color version.
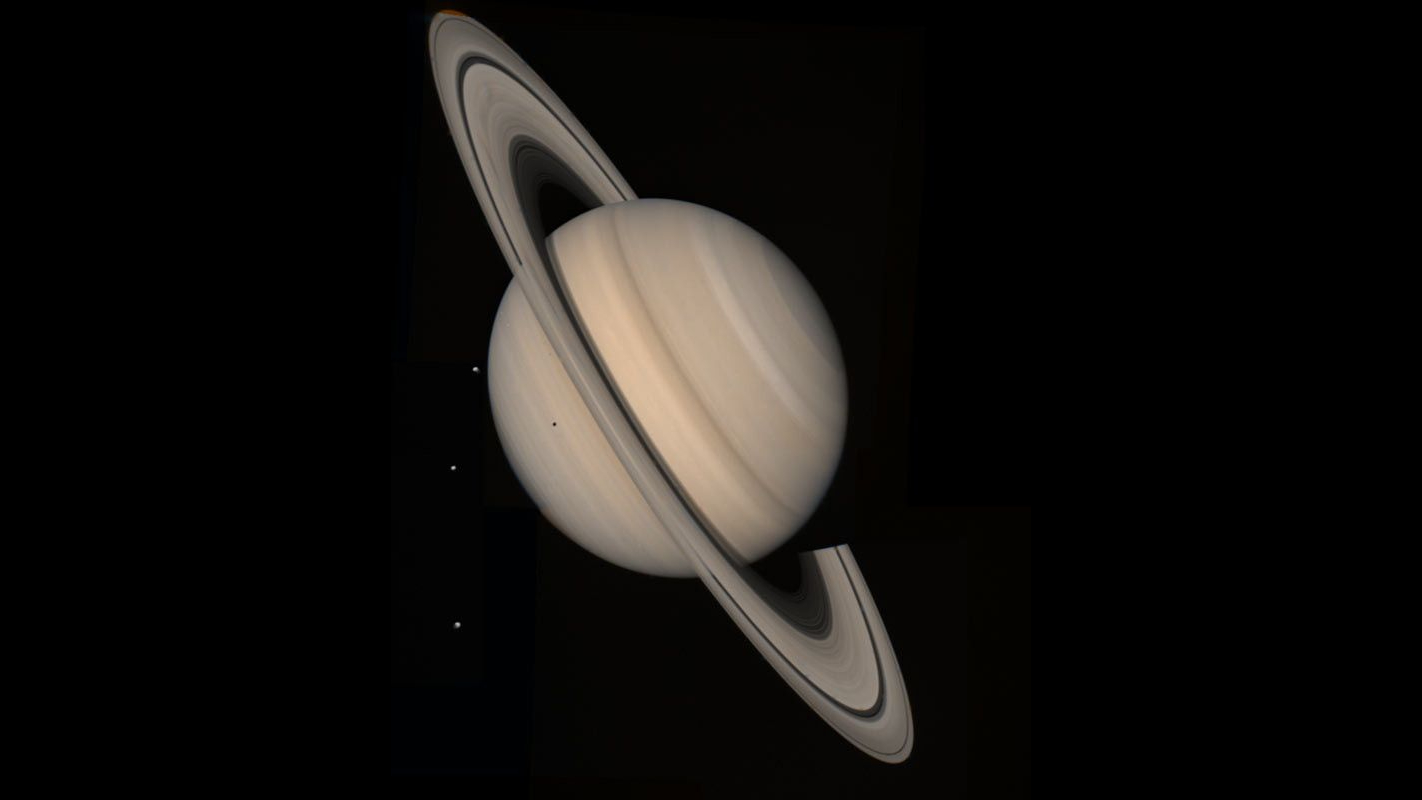

Saturn and three of its moons, Tethys, Dione and Rhea, seen by a Voyager spacecraft on Aug. 4, 1982, from a distance of 13 million miles (21 million km).

This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed the "Pale Blue Dot," is a part of the first ever 'portrait' of the solar system taken by Voyager 1. The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles (6 billion km) from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic, which is the plane that contains most of the planets of the solar system.

Enhanced color view of Saturn's ring system captured by Voyager 2 on Aug. 17, 1981, at a distance of 5.5 million miles (8.9 million km). The color variations between the rings possibly indicate variations in chemical composition from one part of Saturn's ring system to another.
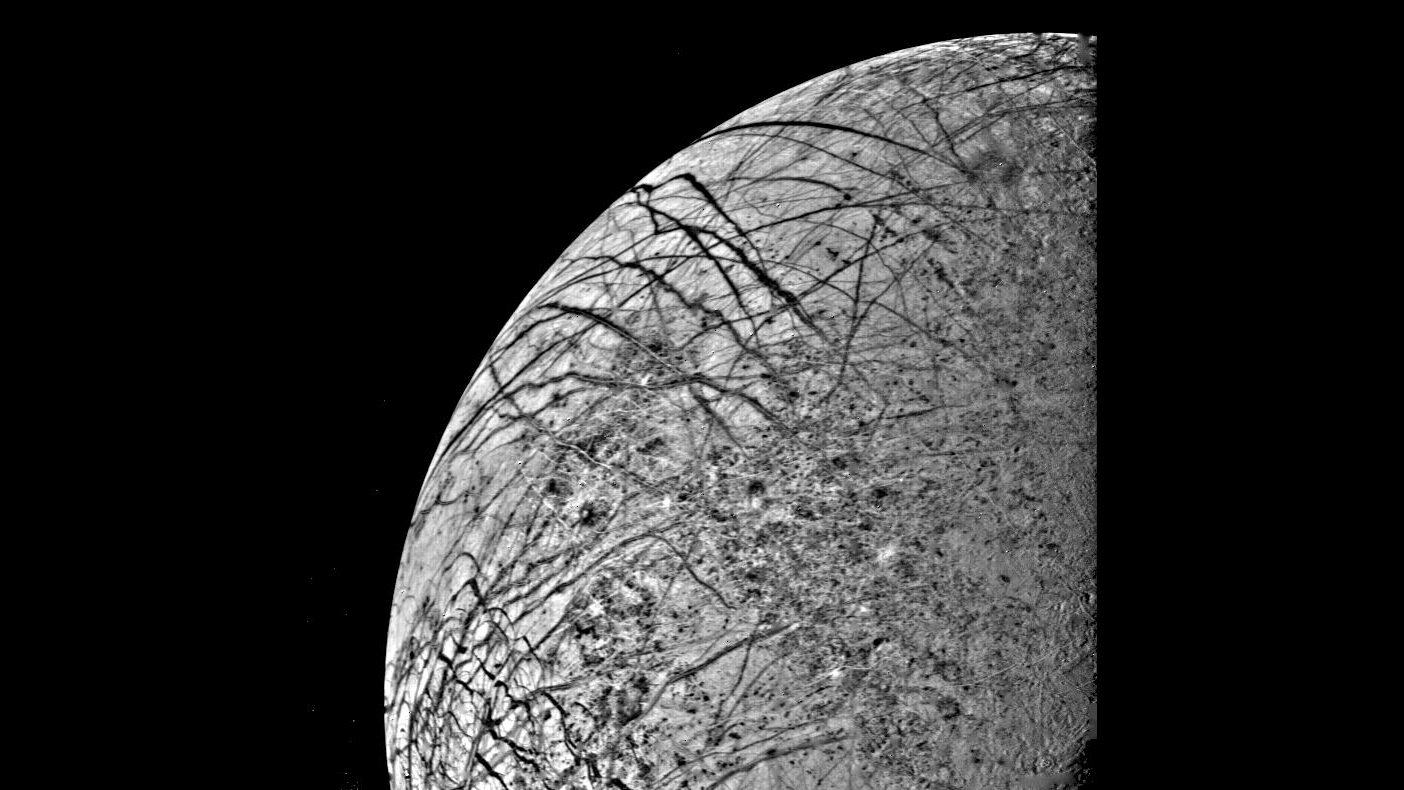
Close-up of the surface of Jupiter's moon Europa captured by Voyager 2 at a distance of 152,000 miles (246,000 km).

Voyager 2 captured this image of Neptune's rings on Aug. 26, 1989, from a distance of 175,000 miles (280,000 km).
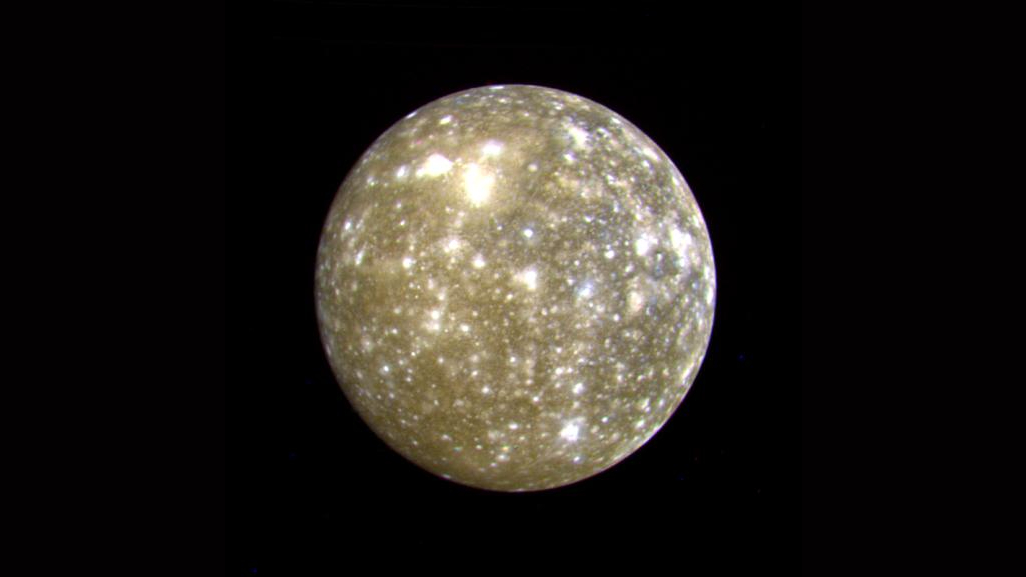

A false-color image of Callisto captured on July 7, 1979, by Voyager 2 at a distance of about 677,000 miles (1.09 million km). Callisto is the second largest moon of Jupiter and is the most heavily cratered of the Galilean satellites.

Daisy Dobrijevic joined Space.com in February 2022 having previously worked for our sister publication All About Space magazine as a staff writer. Before joining us, Daisy completed an editorial internship with the BBC Sky at Night Magazine and worked at the National Space Centre in Leicester, U.K., where she enjoyed communicating space science to the public. In 2021, Daisy completed a PhD in plant physiology and also holds a Master's in Environmental Science, she is currently based in Nottingham, U.K. Daisy is passionate about all things space, with a penchant for solar activity and space weather. She has a strong interest in astrotourism and loves nothing more than a good northern lights chase!
- Mike WallSenior Space Writer


