What's in a 'Space Hamburger'? Ingredients for Life, It Seems
A young protostar that bears a striking resemblance to a giant "space hamburger" contains the molecular building blocks of life, researchers discovered.
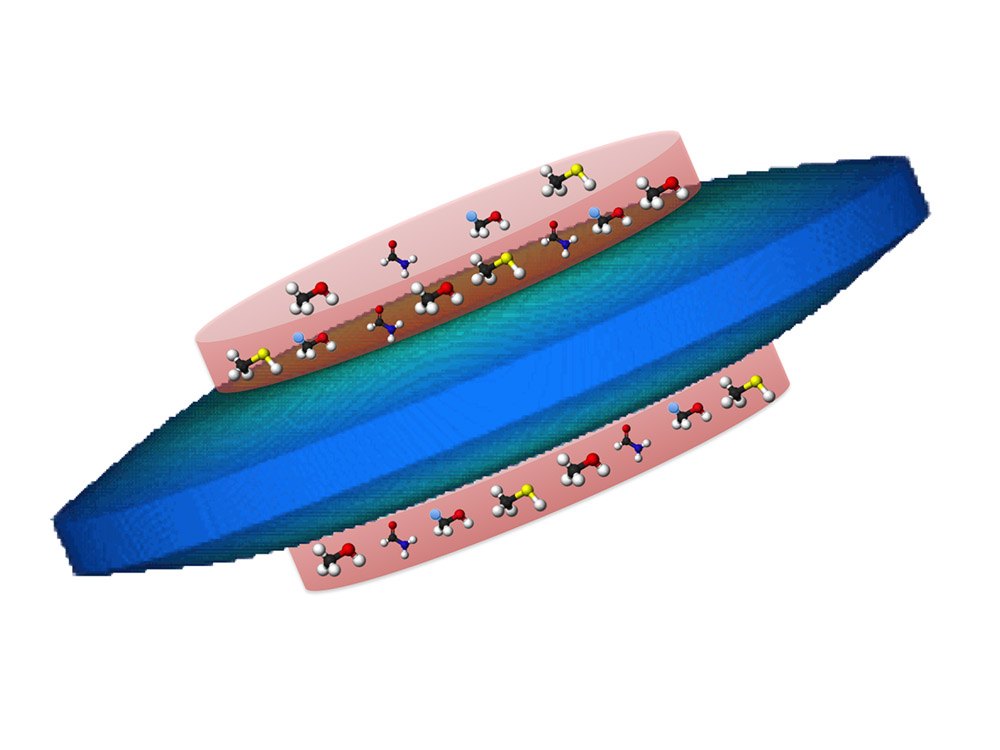
What astronomers call the "space hamburger" is actually a cloud of gas and dust that is collapsing to form a baby star. That baby star will eventually be surrounded by planets, much like Earth's own solar system. The hamburger is called Herbig-Haro object 212, or HH 212.
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, astronomers have identified complex organic molecules in the atmosphere around the protostar's accretion disk — the space hamburger's giant bun and patty, if you will. The types of molecules discovered in the protostar likely played a key role in the development of life on Earth, the researchers said. This finding suggests that the building blocks for life begin to form in the earliest phases of star formation, long before planets have the chance to form around their central star. [Meet ALMA: Amazing Photos from Giant Radio Telescope]
The atmosphere around the space hamburger contains methanol (CH3OH), deuterated methanol (CH2DOH), methanethiol (CH3SH) and formamide (NH2CHO), which "have been proposed to be the precursors for producing biomolecules such as amino acids and sugars," the researchers said in a statement.
"It is so exciting to discover complex organic molecules on an accretion disk around a baby star," Chin-Fei Lee, a researcher at the Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics in Taiwan, who led the study, said in the statement.
"When such molecules were first found in the protoplanetary disk around a star in a later phase of star formation, we wondered if they could have formed earlier. Now, using ALMA's unprecedented combination of spatial resolution and sensitivity, we [can] not only detect them on a younger accretion disk, but also determine their location," Lee said. "These molecules are the building blocks of life, and they are already there in the disk atmosphere around the baby star in the earliest phase of star formation."
Scientists estimate that the space hamburger is only 40,000 years old, which pales in comparison to Earth's 4.5 billion-year-old sun. The space hamburger's radius is about 60 astronomical units, or 60 times the average distance between the Earth and the sun.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
HH 212 lies about 1,300 light-years away from Earth, so if life does eventually form there, even intelligent life, Earthlings will have nothing to worry about. The space hamburger would still be much too far away for any aliens (or humans) to travel between the two solar systems. Humanity would just have to sit back and watch life flourish from afar.
Email Hanneke Weitering at hweitering@space.com or follow her @hannekescience. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.

Hanneke Weitering is a multimedia journalist in the Pacific Northwest reporting on the future of aviation at FutureFlight.aero and Aviation International News and was previously the Editor for Spaceflight and Astronomy news here at Space.com. As an editor with over 10 years of experience in science journalism she has previously written for Scholastic Classroom Magazines, MedPage Today and The Joint Institute for Computational Sciences at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. After studying physics at the University of Tennessee in her hometown of Knoxville, she earned her graduate degree in Science, Health and Environmental Reporting (SHERP) from New York University. Hanneke joined the Space.com team in 2016 as a staff writer and producer, covering topics including spaceflight and astronomy. She currently lives in Seattle, home of the Space Needle, with her cat and two snakes. In her spare time, Hanneke enjoys exploring the Rocky Mountains, basking in nature and looking for dark skies to gaze at the cosmos.