International Space Station Will Get a Commercial Airlock in 2019

Update: The launch of NanoRacks' airlock to the International Space Station has been delayed to Oct. 30, 2020, when it will launch with SpaceX's Dragon CRS-21 cargo resupply mission.
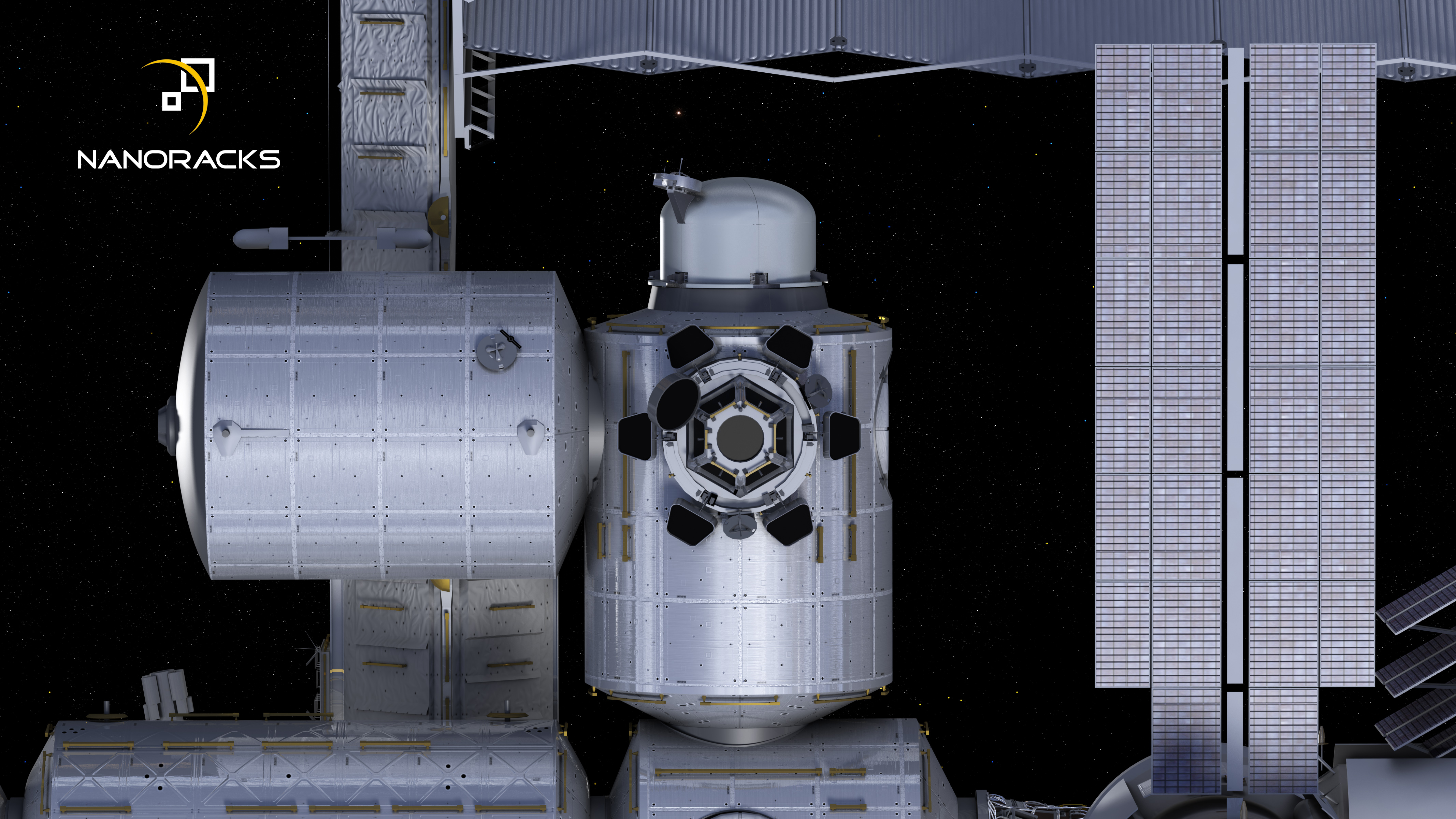
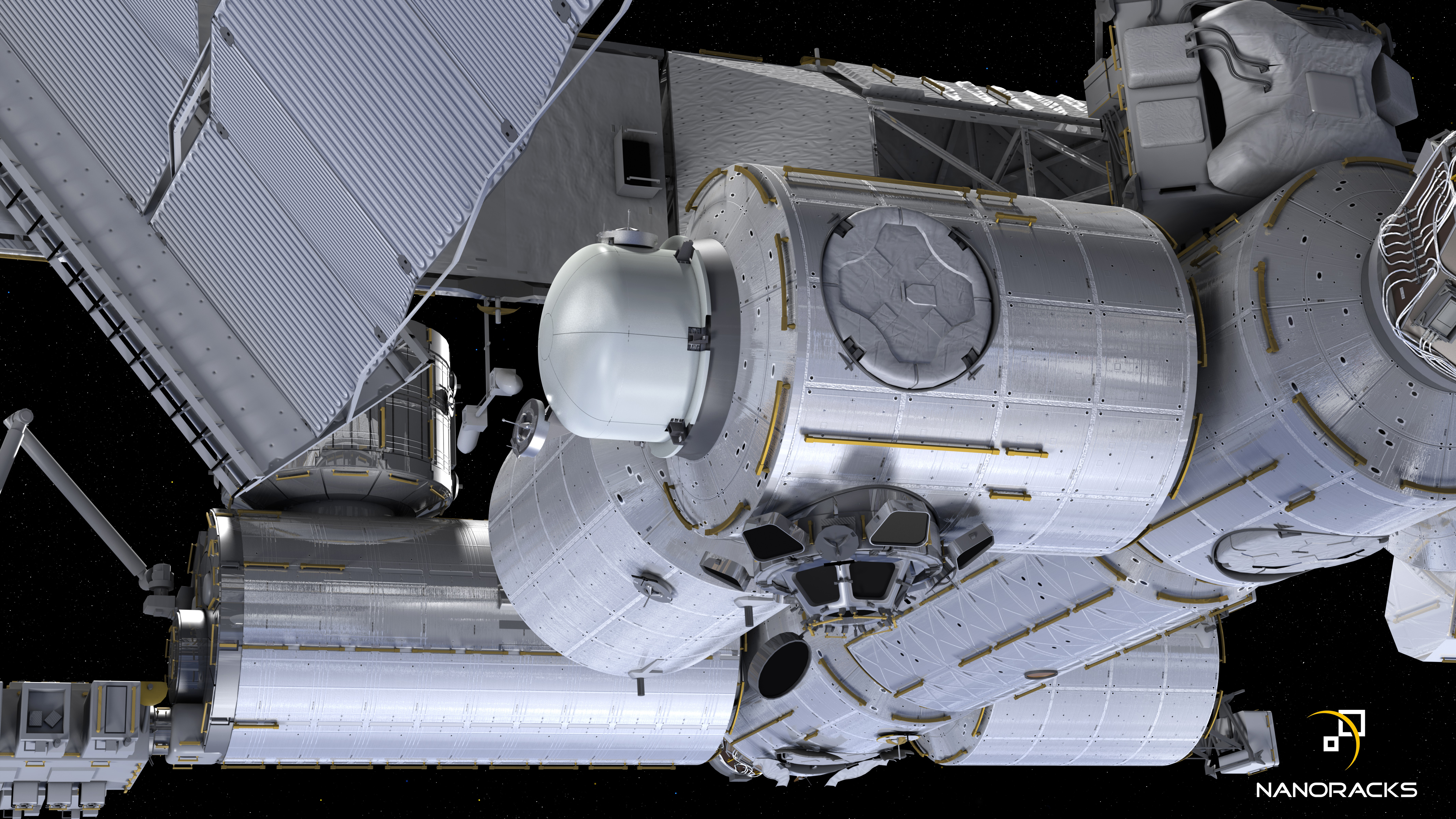
The International Space Station (ISS) will soon feature its first commercially funded airlock, which NASA officials said will allow more small satellites to be deployed from the orbiting lab.
NASA has agreed to let the Houston-based company NanoRacks develop the airlock, which is expected to launch in 2019.
"We want to utilize the space station to expose the commercial sector to new and novel uses of space, ultimately creating a new economy in low-Earth orbit for scientific research, technology development and human and cargo transportation," Sam Scimemi, director of NASA's ISS division, said in a statement. "We hope this new airlock will allow a diverse community to experiment and develop opportunities in space for the commercial sector."
NanoRacks — which has already deployed numerous tiny cubesats from the station's Japanese Kibo module — signed an independent partnership with aerospace giant Boeing on Monday (Feb. 6) to develop the new airlock.
Payloads deployed into space via the new airlock will be coordinated and vetted through the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), which manages the U.S. national laboratory on the space station.NASA officials said the new airlock will be installed on a port on ISS' Tranquility module. Another Tranquility port currently hosts the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), a prototype designed to test how inflatable habitats perform in space.
Besides its current work with NanoRacks, CASIS and Bigelow Aerospace (which built BEAM), NASA issued a request for information last fall asking private enterprises how they can use resources on the space station, such as docking ports.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"As private sector partners play a greater role in this new economy, NASA is able to focus on its deep-space exploration goals, including sending humans beyond the moon and eventually, to Mars," agency officials said in the same statement.
Follow Elizabeth Howell @howellspace, or Space.com @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebookand Google+. Original article on Space.com.

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., was a staff writer in the spaceflight channel between 2022 and 2024 specializing in Canadian space news. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years from 2012 to 2024. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House, leading world coverage about a lost-and-found space tomato on the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?" (ECW Press, 2022) is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams.