In Photos: Universe's Expansion Revealed by Quasars & Cosmic Lenses
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
The Expanding Universe Revealed
On Jan. 26, 2017, astronomers announced that the universe is expanding faster than previously thought. See photos of the quasars seen by the Hubble Space Telescope that made the discovery possible.
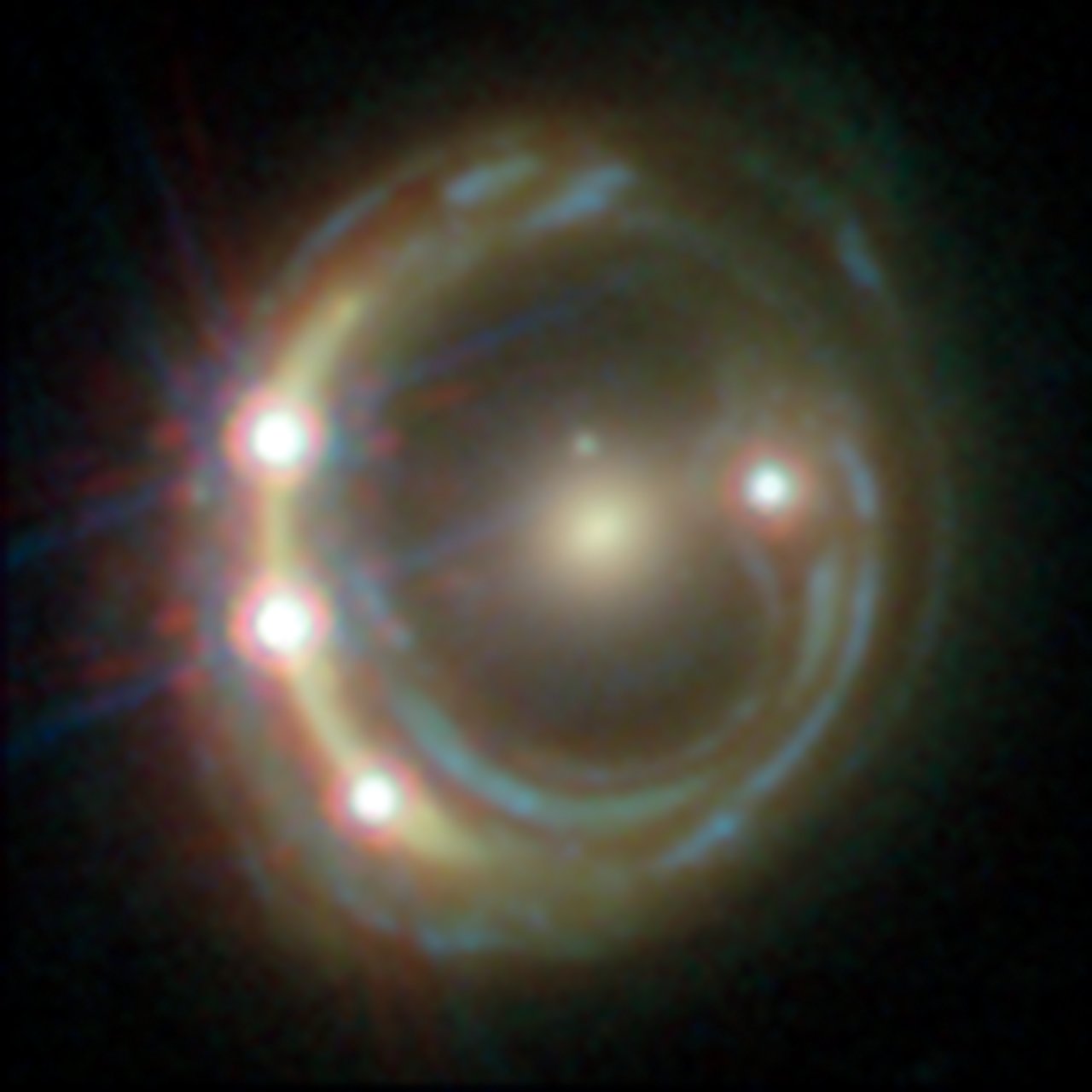
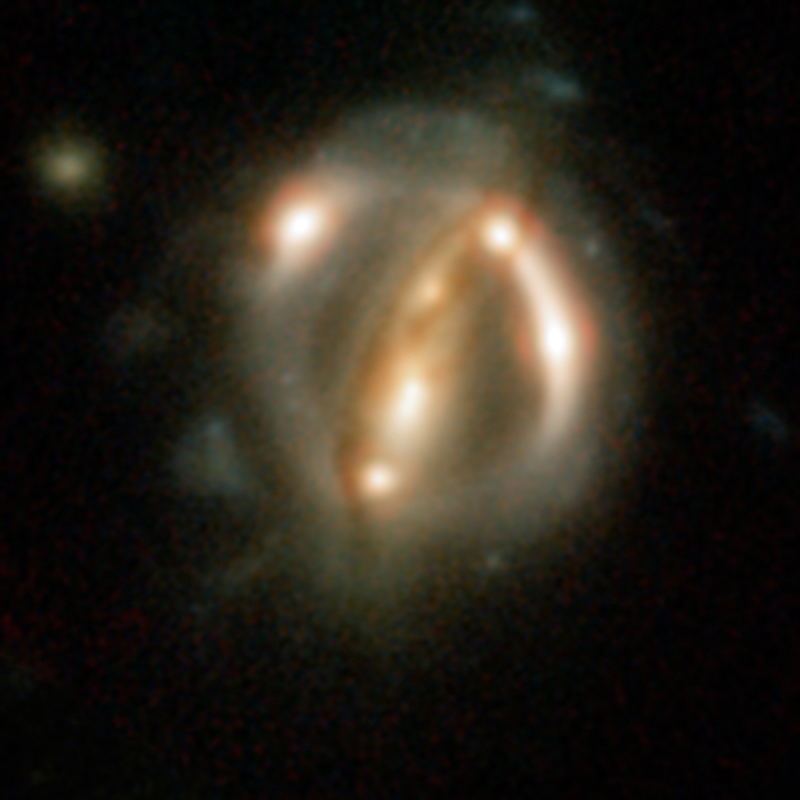
Shown Here: Hubble Space Telescope view of the distant quasar RXJ1131-1231. A foreground galaxy smears the image of the background quasar into a bright arc (left) and creates a total of four images — a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing. Such lensed views allowed scientists to come up with a new estimate for how fast the universe is expanding. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
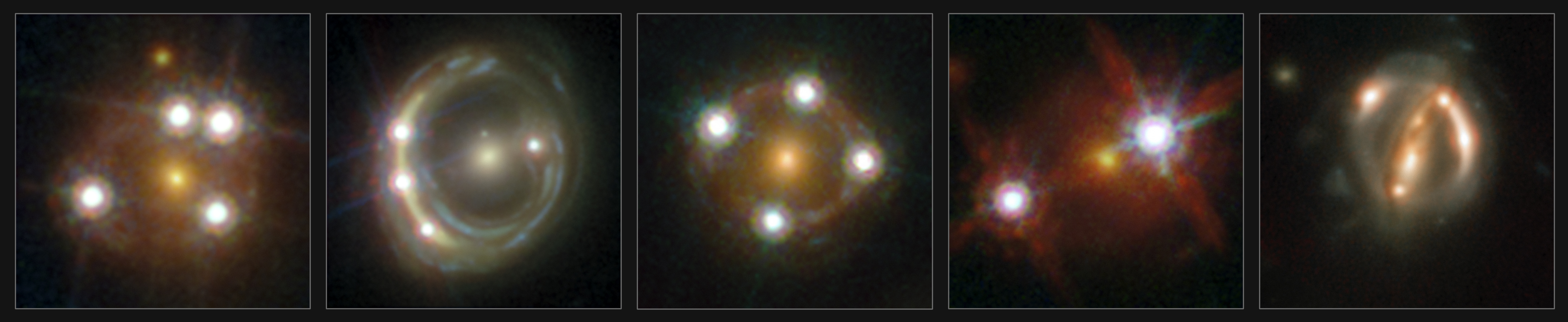
The Cosmic Five!
This montage rounds up five of the best lensed quasars (as well as their foreground galaxies) as seen by astronomers with the HOLICOW collaboration. The observations of these quasars allowed scientists to independently measure the Hubble constant and determine one and for all that the universe is actually expanding faster than expected. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
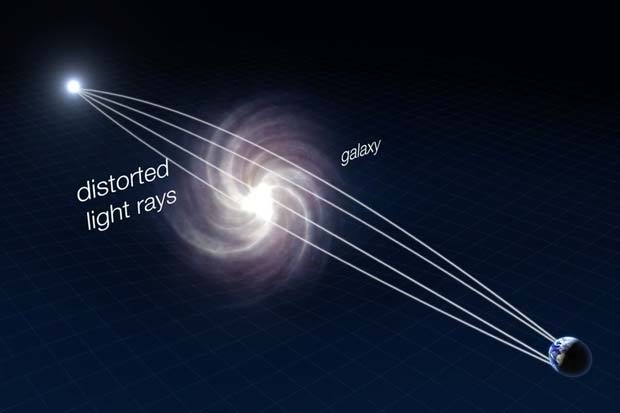
Article continues belowHow a Gravitational Lens Works
Gravitational lenses occur when the light from a more distant galaxy or quasar is warped by the gravity of a nearer object in the line of sight from Earth, as shown in this diagram. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
Meet Edwin Hubble
The Hubble constant is named in honor of famed astronomer Edwin Hubble, who first proposed the concept to explain his observations of distant galaxies. The Hubble Space Telescope is named in Hubble's honor, too.
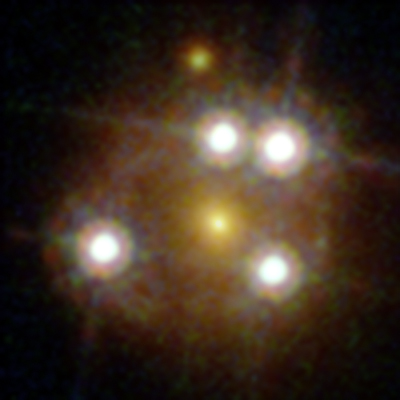
Quasar HE0435-1223 (Wide-View)
The quasar HE0435-1223, which is one of the five best lensed qusars ever found, is seen in the center of this wide-field view from the Hubble Space Telescope. The central galaxy is actually in the foreground, and a gravitational lens effect creates the four images of the more distant quasar around it. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
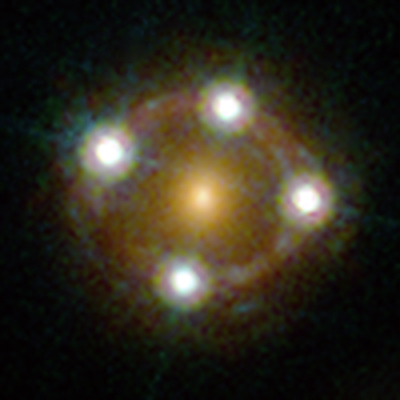
Quasar HE0435-1223 Close Up
You saw the wide view, now here is the close-up. The quasar HE0435-1223 is seen here by the Hubble Space Telescope. It is one of the five best lensed quasars ever seen and appears as four nearly evenly spaced objects around a central galaxy that is actually in the foreground. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Off-Kilter Quasar WFI2033-4723
This Hubble Space Telescope view shows a close-up of the distant quasar WFI2033-4723, which is one of the five best lensed quasars ever seen. The quasar appears as four bright objects in a cosmic lens around a central galaxy that is actually in the foreground. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
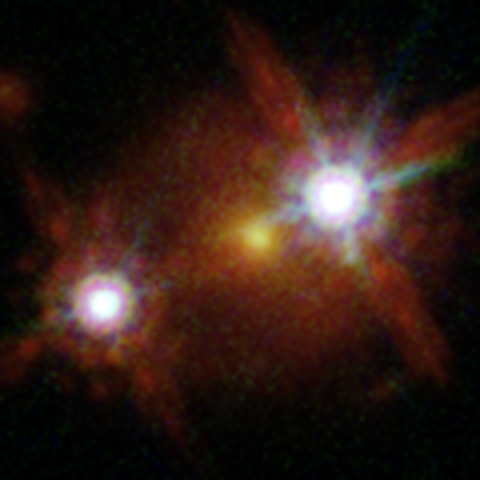
The Double Quasar HE1104-1805
Here, the quasar HE1104-1805 appears as only two distinct objects in a cosmic lens around a foreground galaxy, rather than the four objects created by other gravitaitonal lenses. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.
Quasar B1608+656 in View
What may look like a cosmic ornament is actually the distant quasar B1608+656, which is smeared into bright arcs by two closer galaxies in the foreground. Read the Full Story | Watch the Video.

Tariq is the award-winning Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001. He covers human spaceflight, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He's a recipient of the 2022 Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting and the 2025 Space Pioneer Award from the National Space Society. He is an Eagle Scout and Space Camp alum with journalism degrees from the USC and NYU. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast on the TWiT network. To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik.