Glittering Star Cluster May Help Solve Stellar Mystery (Video, Photos)
Stunning new photos taken by a telescope in Chile show an incredible grouping of stars that may help scientists solve a stellar conundrum.
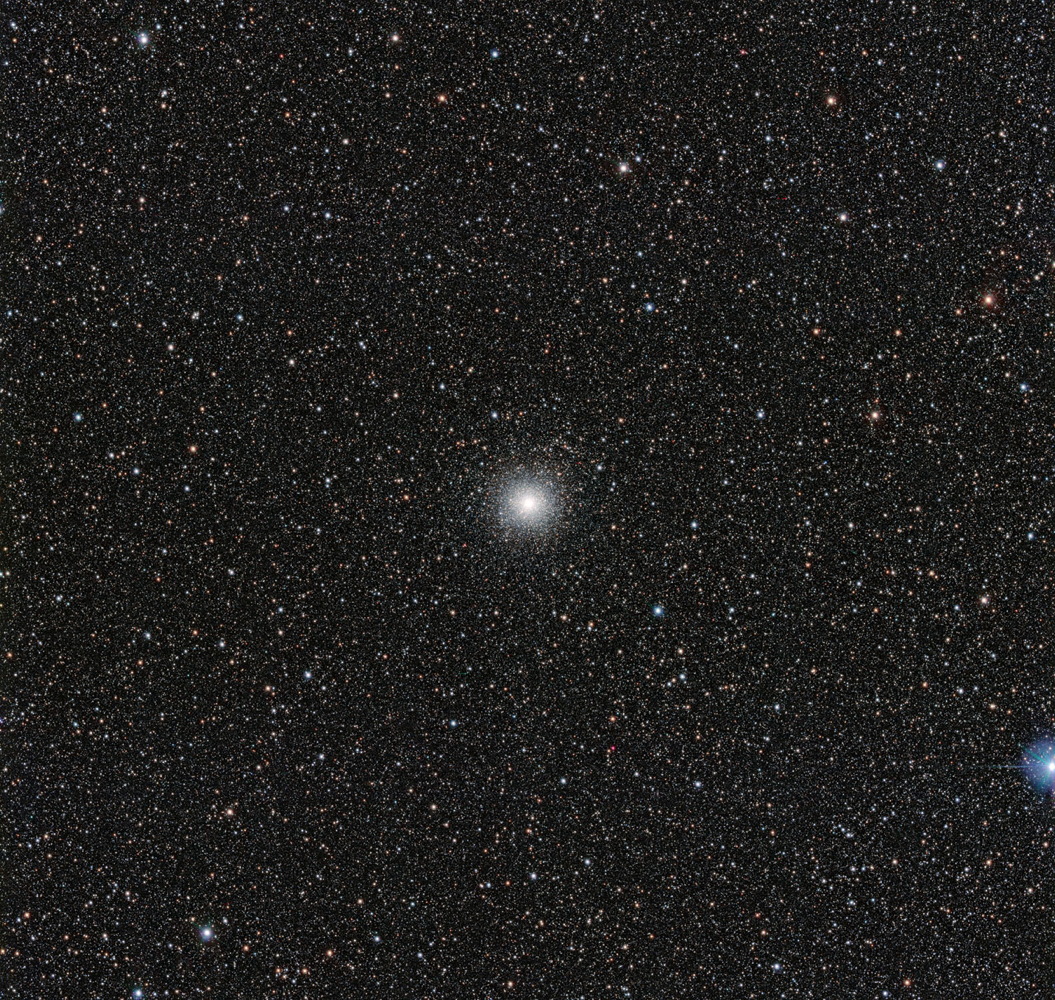
The image, released today by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), shows a distant cluster of bright stars outside of the Milky Way. A related video of the globular cluster Messier 54 shows it glowing in a small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way called the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy about 90,0000 light-years away, according to ESO.
Messier 54's location gives scientists a unique opportunity to study the stars of the cluster and make comparisons to those housed within the Milky Way. About 150 globular star clusters — groupings of stars that date back to the early days of the galaxy — orbit the Earth's galaxy, ESO representatives said. [Gallery: 65 All-Time Great Galaxy Hits (Photos)]
Astronomers have found that the old stars in globular clusters of the Milky Way actually have less of the element lithium than expected.
"Most of the light chemical-element lithium now present in the universe was produced during the Big Bang, along with hydrogen and helium, but in much smaller quantities," ESO representatives said in a statement. "Astronomers can calculate quite accurately how much lithium they expect to find in the early universe, and from this, work out how much they should see in old stars. But the numbers don't match. There is about three times less lithium in stars than expected."
Until now, researchers haven't been able to measure lithium in globular clusters outside of the Milky Way for comparison, but now, with the new data collected by ESO's VLT Survey Telescope, scientists have found that a sampling of stars in Messier 54 is also missing some lithium, according to ESO.
A group of scientists led by Alessio Mucciarelli of the University of Bologna, Italy, used the new information to find that the lithium puzzle doesn't just affect the Milky Way. Because Messier 54 is missing a similar amount of lithium, scientists have extrapolated that the element is missing from other galaxies, as well.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Astronomers have come up with a few explanations for the strange lithium mystery.
"The first is that the calculations of the amounts of lithium produced in the Big Bang are wrong, but very recent tests suggest that this is not the case," ESO representatives said. "The second is that the lithium was somehow destroyed in the earliest stars, before the formation of the Milky Way. The third is that some process in the stars has gradually destroyed lithium during their lives."
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.

Miriam Kramer joined Space.com as a Staff Writer in December 2012. Since then, she has floated in weightlessness on a zero-gravity flight, felt the pull of 4-Gs in a trainer aircraft and watched rockets soar into space from Florida and Virginia. She also served as Space.com's lead space entertainment reporter, and enjoys all aspects of space news, astronomy and commercial spaceflight. Miriam has also presented space stories during live interviews with Fox News and other TV and radio outlets. She originally hails from Knoxville, Tennessee where she and her family would take trips to dark spots on the outskirts of town to watch meteor showers every year. She loves to travel and one day hopes to see the northern lights in person. Miriam is currently a space reporter with Axios, writing the Axios Space newsletter. You can follow Miriam on Twitter.