See Saturn's Stunning Auroras Glow Over Time in These Hubble Photos
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
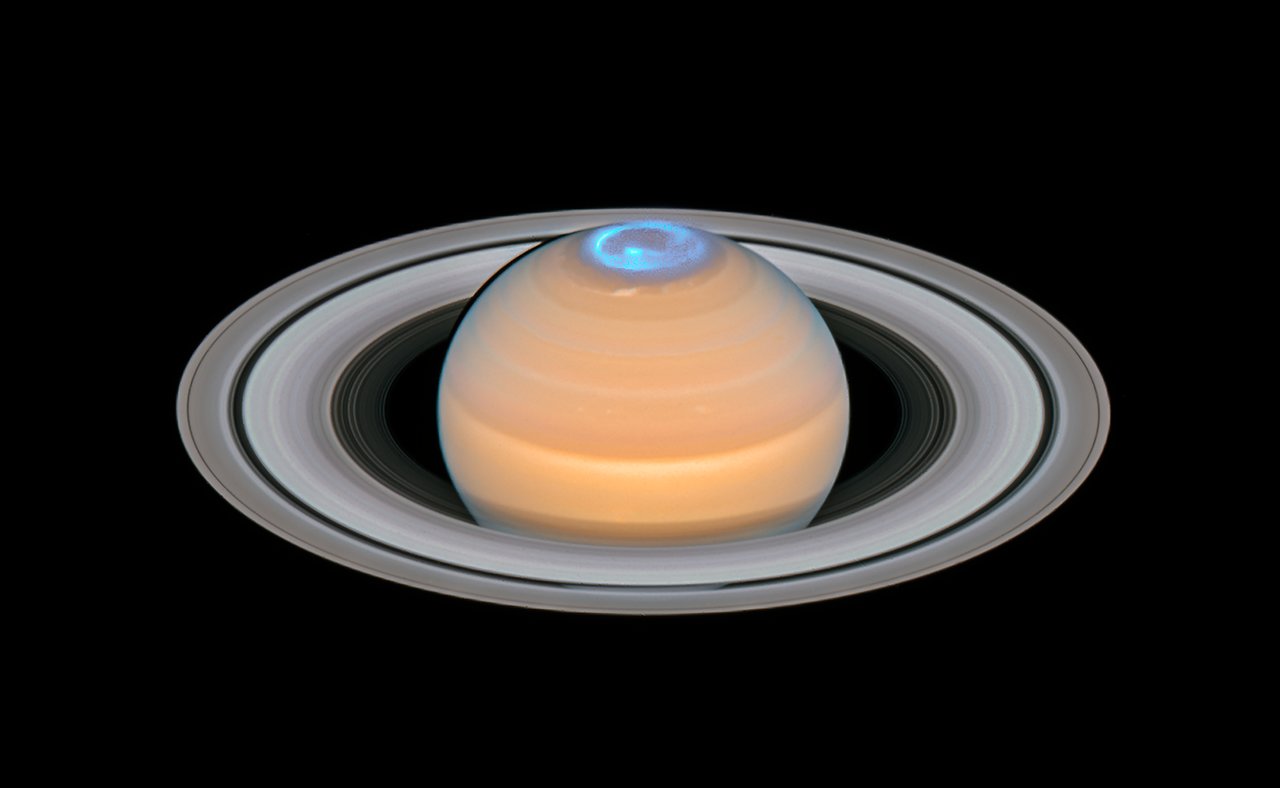
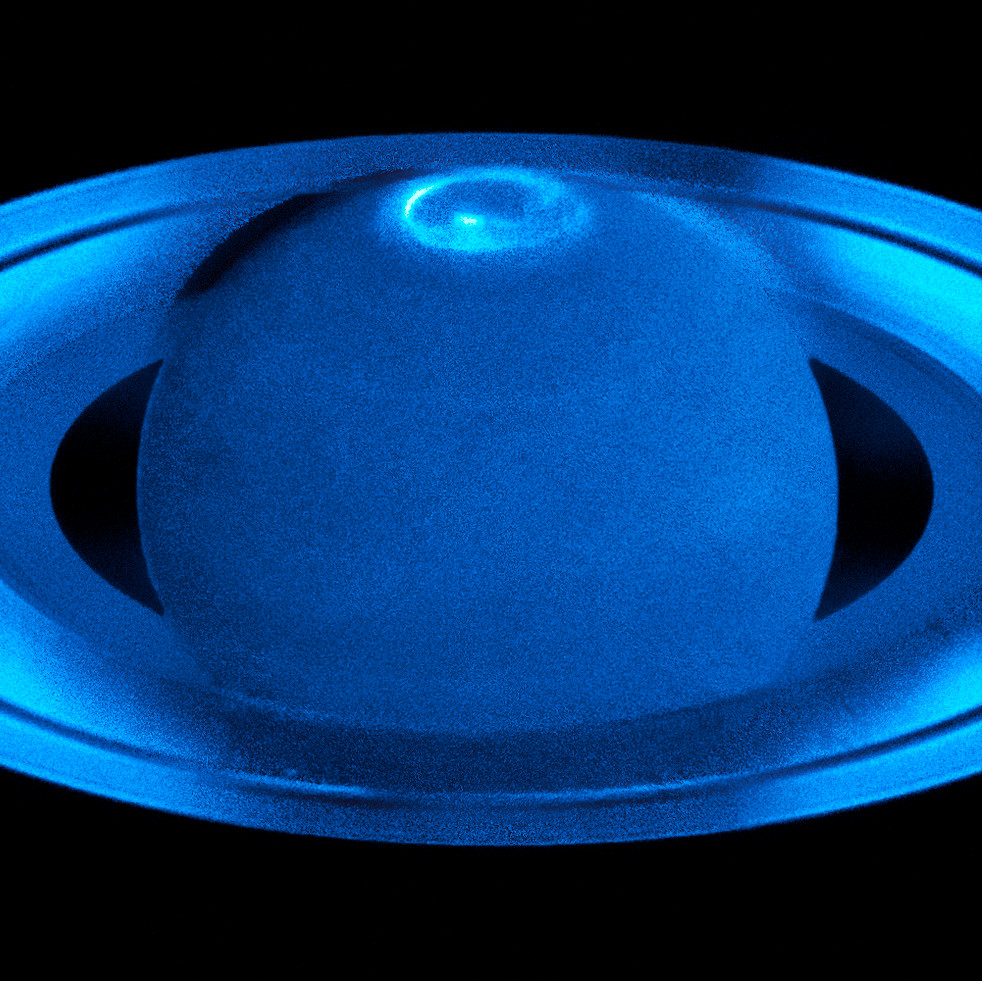
New images from the Hubble Space Telescope show Saturn's ultraviolet auroras swirling at the planet's north pole in the months before and after the northern summer solstice.
Scientists imaged Saturn's auroras using the spectrograph on Hubble during the solstice because it's the best time to view the planet's north pole, and to coincide with observations by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, which finished its mission in September with a dramatic dive. By doing so, they got their most detailed look ever at how the auroras behave over time, Hubble scientists said in a statement.
Earth's northern and southern auroras happen when the planet's magnetic field interacts with the solar wind, the stream of charged particles streaming from the sun. When those particles become trapped at the planet's poles, they interact with the oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere to produce a dazzling light show. The auroras of Saturn and other outer planets form in a similar way, but because their atmospheres are mostly hydrogen, the light produced is in the ultraviolet range.
The human eye can't pick up that ultraviolet light, and most of it would be absorbed by Earth's atmosphere anyway. But luckily, there are other, more powerful eyes on the sky — in this case, the spectrograph tool on Hubble, which orbits Earth.
Hubble's observations revealed an ever-changing aurora on Saturn's north pole that varies as the solar wind ebbs and flows and as the planet rotates. (A full Saturn rotation takes just 11 hours.) The aurora peaked in brightness at the planet's dawn and just before midnight, researchers said in the statement — but that midnight peak, never seen before, might have something to do with the way the solar wind hits the planet around solstice, in particular.
Hubble has studied Saturn's auroras before, and this type of analysis lets researchers learn more about the planet's powerful magnetic field from afar.
Email Sarah Lewin at slewin@space.com or follow her @SarahExplains. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Sarah Lewin started writing for Space.com in June of 2015 as a Staff Writer and became Associate Editor in 2019 . Her work has been featured by Scientific American, IEEE Spectrum, Quanta Magazine, Wired, The Scientist, Science Friday and WGBH's Inside NOVA. Sarah has an MA from NYU's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program and an AB in mathematics from Brown University. When not writing, reading or thinking about space, Sarah enjoys musical theatre and mathematical papercraft. She is currently Assistant News Editor at Scientific American. You can follow her on Twitter @SarahExplains.