Solar Storm Forecasts Improve as Sun’s Fury Increases
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
If this week's raging solar storm was any indication, the sun is ramping up its activity — and scientists will be ready for it. By meticulously studying our planet's star, they are able to predict these potentially dangerous space weather events better than ever before.
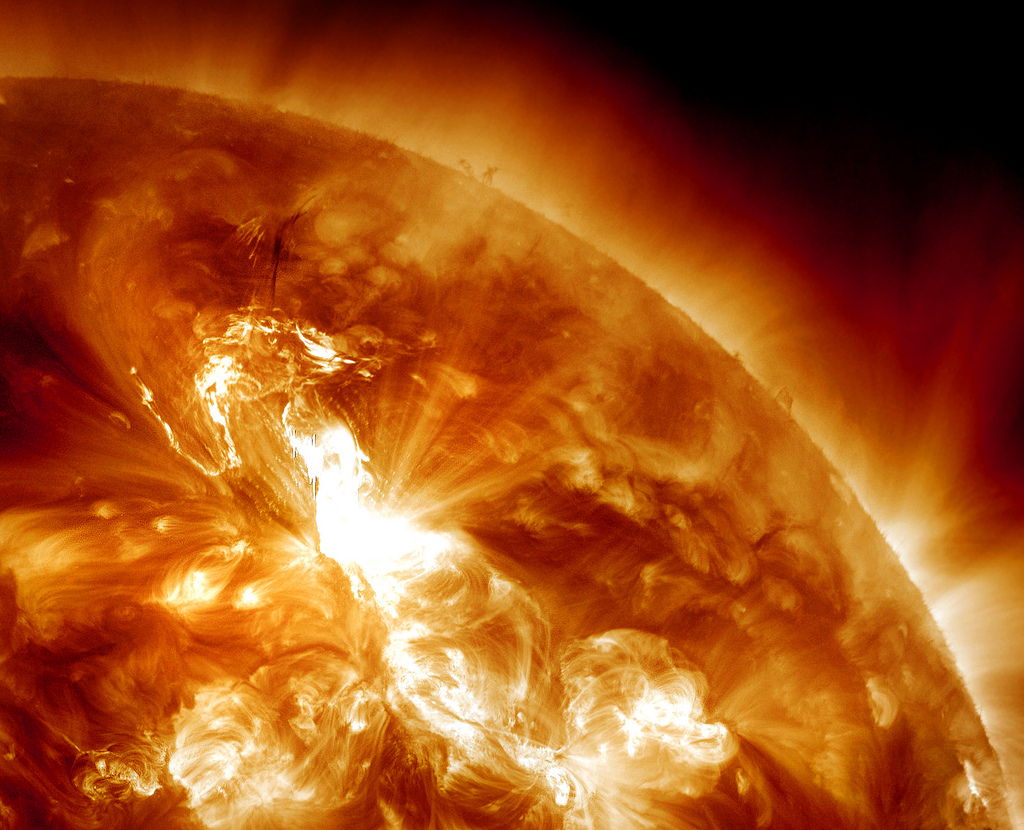
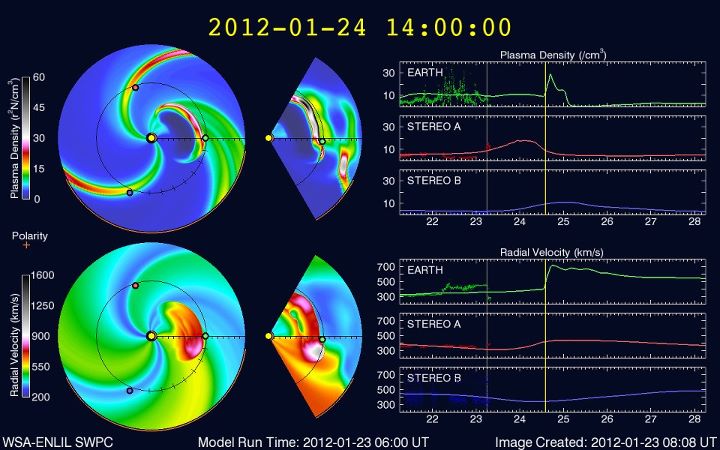
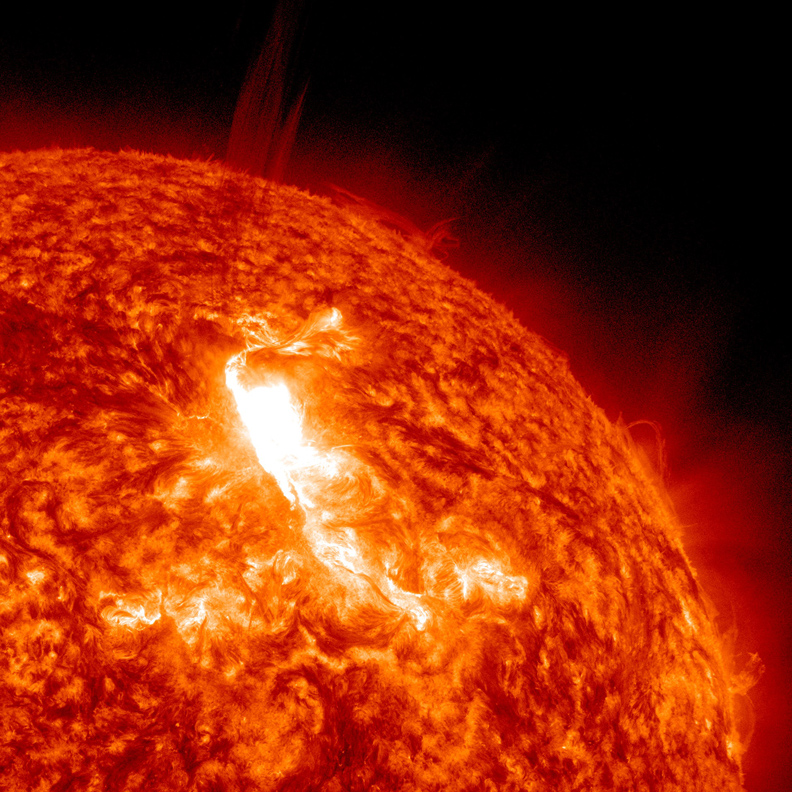
A huge solar flare erupted Jan. 23, triggering the strongest radiation storm in nearly a decade. A wave of charged particles, called a coronal mass ejection (CME), bombarded Earth yesterday (Jan. 24). The bombardment is over now, but some minor disruptions to spacecraft and power grids were reported.
Scientists' forecast for the arrival of the disruptive wave was off by only 13 minutes, far more accurate than in the past. And with much of the world's networks interconnected and populations increasingly reliant on technology, the ability to predict and track potentially harmful space weather events will become ever more crucial. [Photos: Huge Solar Flare Sparks Major Radiation Storm]
Article continues belowSolar flares and CMEs are expected to increase in frequency as the sun emerges from the dormant phase of its 11-year activity cycle.
When a CME hits Earth, the resulting geomagnetic storm interacts with the planet's magnetic field lines. This not only amps up Earth's auroras (the northern and southern lights), but, in the case of a strong CME aimed directly at Earth, can disrupt the operations of satellites in orbit and power grids and other communications infrastructures on the ground.
"There was a major event back in 1989 that led to a major power failure in Quebec that had broad implications for the province," Harlan Spence, an astrophysicist at the University of New Hampshire, told SPACE.com. "Because the world has highly connected power grids, the effects of that particular geomagnetic storm were also felt through many parts of the continental U.S."
Yesterday's CME hit Earth at an angle, so the electromagnetic burst was largely shielded by the planet's magnetic field. Still, some commercial airlines implemented safety precautions by rerouting flights over the Earth's polar regions.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Space Weather Prediction Center also recorded some minor disruptions in space and on the ground.
"This is typical with space weather, but what I have heard is some science instruments and spacecraft saw increases in single-event upsets," Doug Biesecker, a physicist at NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center, told SPACE.com. "Some instruments were returning bad data, but this is the sort of thing they can handle. Some power grids did hear reports on fluctuations, but I don't have specifics on which grids and where they were."
Biesecker noted that these types of interferences are not unusual during intense solar storms, and the rate of reported disruptions has been relatively low. Furthermore, new observations show that things appear to be returning to normal.
"After the arrival of a CME yesterday and the subsequent activity which ensued, conditions are now beginning to trend back towards a return to quiet," NOAA officials wrote in an update on the Space Weather Prediction website.
Scientists rely on several spacecraft, including the Solar Dynamics Observatory, the Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and the Stereo spacecraft, to constantly monitor the sun's activity. Scientists use data from these satellites to make models and predictions of solar flares and CMEs.
"By incorporating the information from multiple points of view, we can determine to a very good degree the CME properties, such as its speed and direction," said Yihua Zheng, a lead researcher for the Space Weather Center at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "We put all that into the model and we get a prediction."
Once scientists understand the strength and path of a CME, forecasts can be made about how the ejection might affect things in space and on the ground. As these predictions become more refined, they can act as an early warning system for space weather, much like how meteorologists track storms and weather patterns.
"A CME is kind of like a space hurricane," Zheng told SPACE.com. "You have to predict how it will form and evolve. From the models, we can see which spacecraft will be in its path and what will be impacted."
For yesterday's CME, Zheng and her colleagues at the Space Weather Center succeeded in making the most accurate predictions to date on when it would arrive at Earth.
"We predicted it would arrive at 9:18 a.m., and in reality it arrived at 9:31 a.m., so ours has a 13-minute error," Zheng said. "Usually for this kind of model, the average error is seven hours, so this is the best case."
These types of advances indicate how far the field of space weather prediction has come, she added.
The sun's activity ebbs and flows in its 11-year cycle. Currently the sun is coming out of a dormant phase of Solar Cycle 24, and the star is expected to become more active, with more solar flares and CMEs, as it heads into the so-called solar maximum in 2013.
"If you look back to the last time that the sun was entering into this state, our physical understanding was much less mature," Spence said. "In the intervening decade we have developed improved knowledge, improved techniques, faster computers, faster algorithms, and better real-time capability to get data to the scientists and customers who worry about space weather. Certainly 20 years ago, you'd be sitting more or less blind, waiting for data to come down and be processed."
You can follow SPACE.com staff writer Denise Chow on Twitter @denisechow. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.

Denise Chow is a former Space.com staff writer who then worked as assistant managing editor at Live Science before moving to NBC News as a science reporter, where she focuses on general science and climate change. She spent two years with Space.com, writing about rocket launches and covering NASA's final three space shuttle missions, before joining the Live Science team in 2013. A Canadian transplant, Denise has a bachelor's degree from the University of Toronto, and a master's degree in journalism from New York University. At NBC News, Denise covers general science and climate change.