In Photos: India’s Most Powerful Rocket Launches on Debut Flight
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
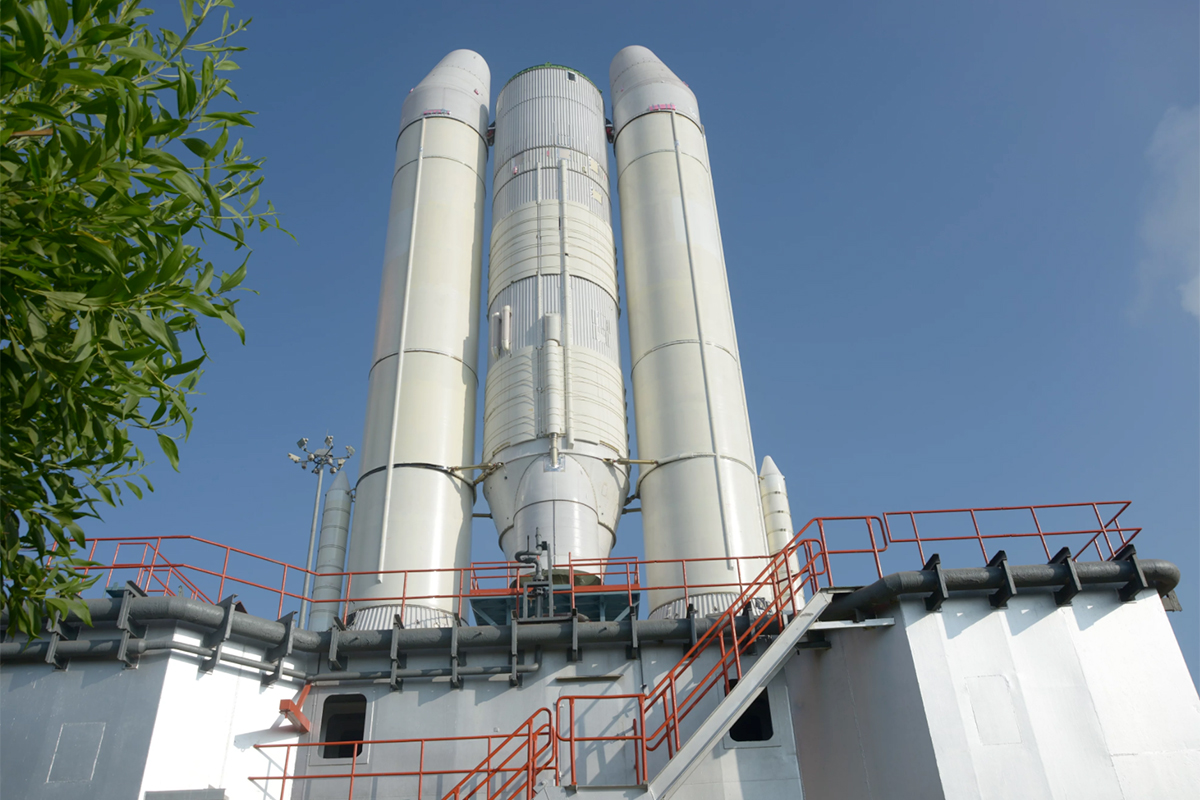
Headless Rocket?
Looking bit like a Headless Horseman, but for space, India's first orbital GSLV Mark III rocket stands half-built on its pedestal. Here the twin S200 solid rocket stages have been attached to the core stage, but the upper stage still waits to be attached.
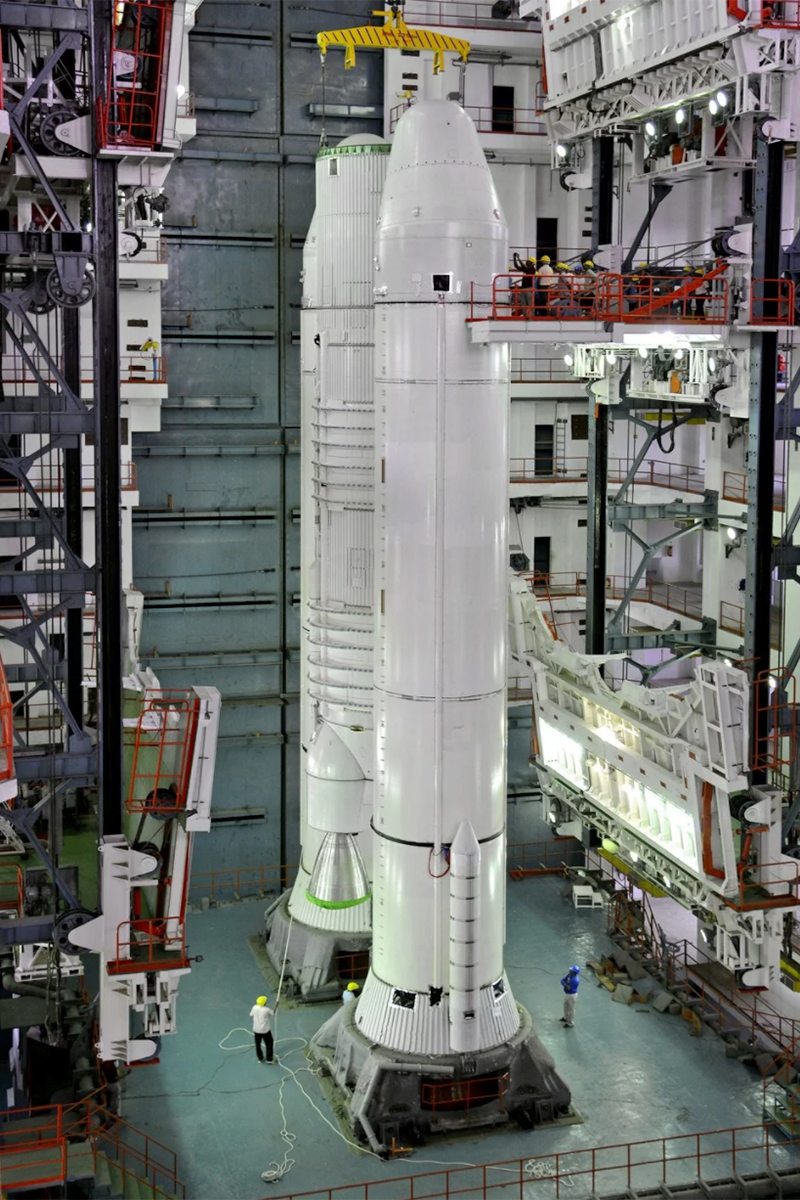
Stacking Things Up
Inside India's Vehicle Assembly Building, the twin solid rocket boosters and core liquid-fueled stage of ISRO's GSLV Mark III rocket are mated together.
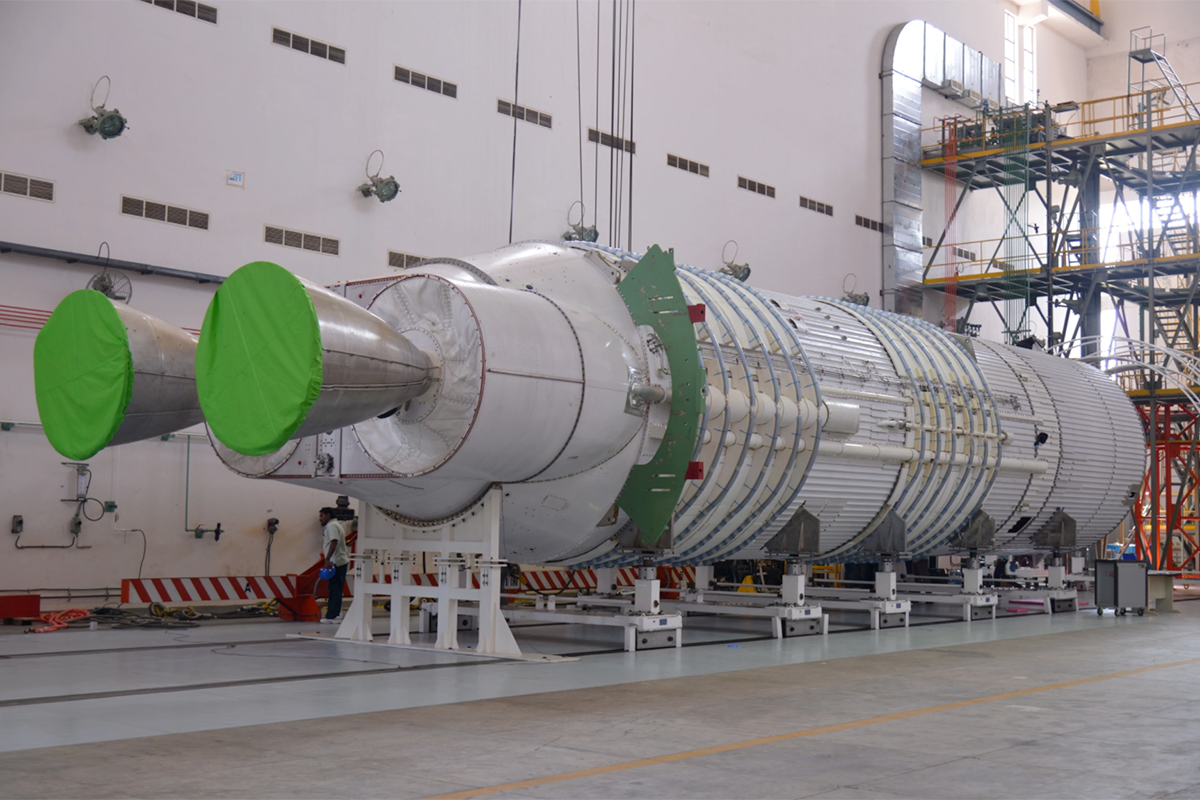
The Rocket's Core
Powered by two of India's Vika rocket engines, the core stage of the GSLV Mark III is seen during the rocket process. The core stage stands about 69 feet tall (21 meters) and is 13 feet (4 m) wide.
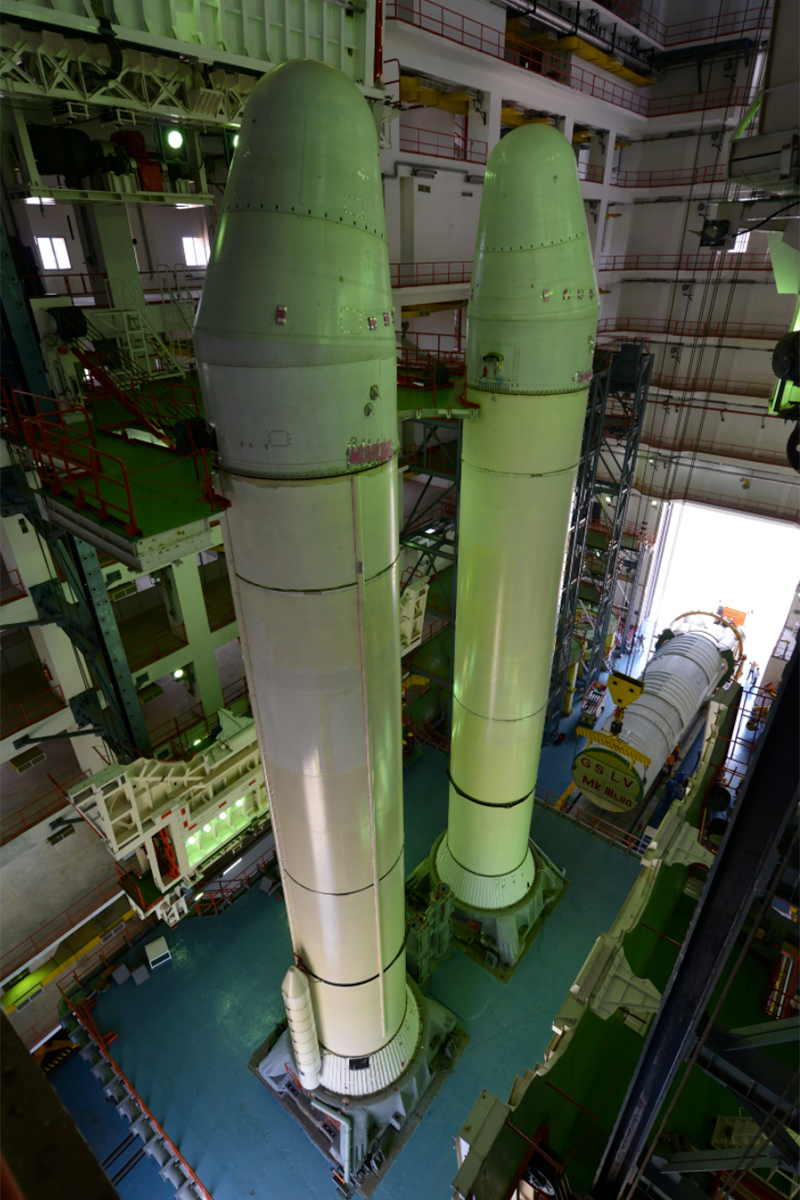
Twin Boosters
The two S200 strap-on solid rocket boosters for the GSLV Mark III rocket stand like lonely sentinels as they await their core stage. Each of the boosters is 82 feet packed with 205 metric tons of solid HTPB (hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene) propellant.
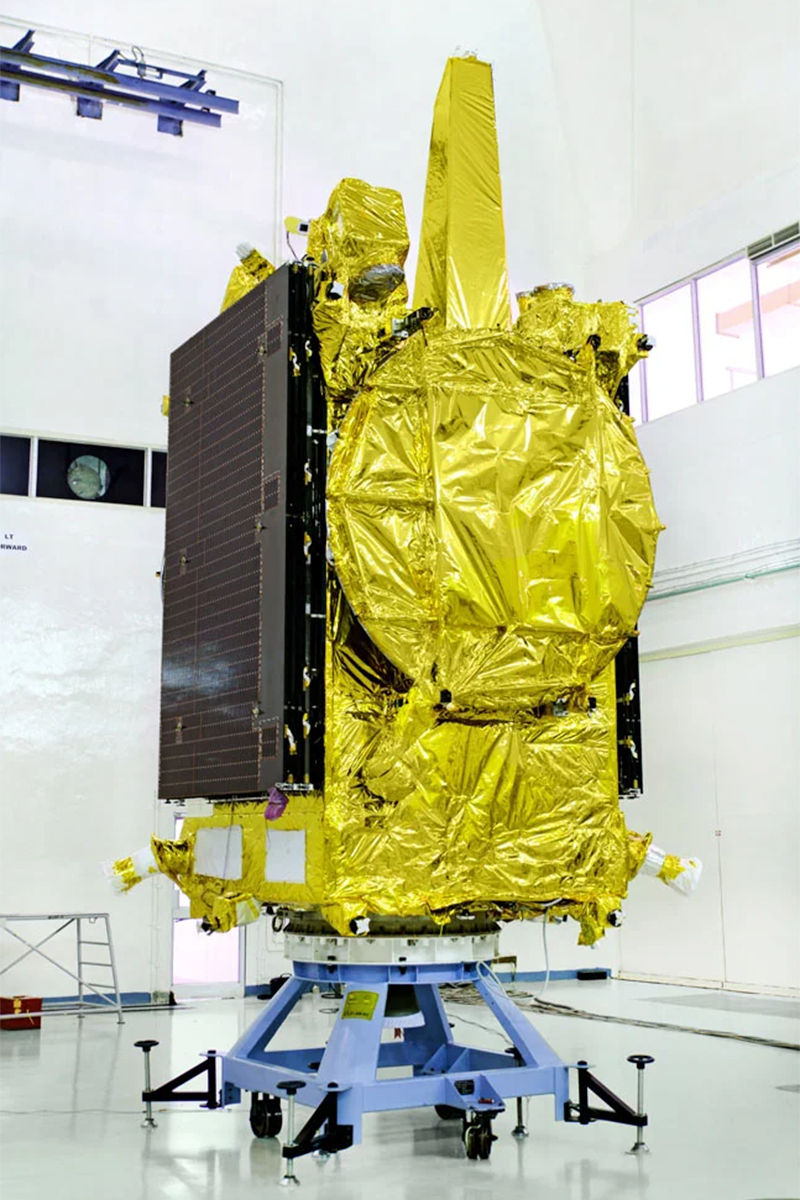
Packing for Flight
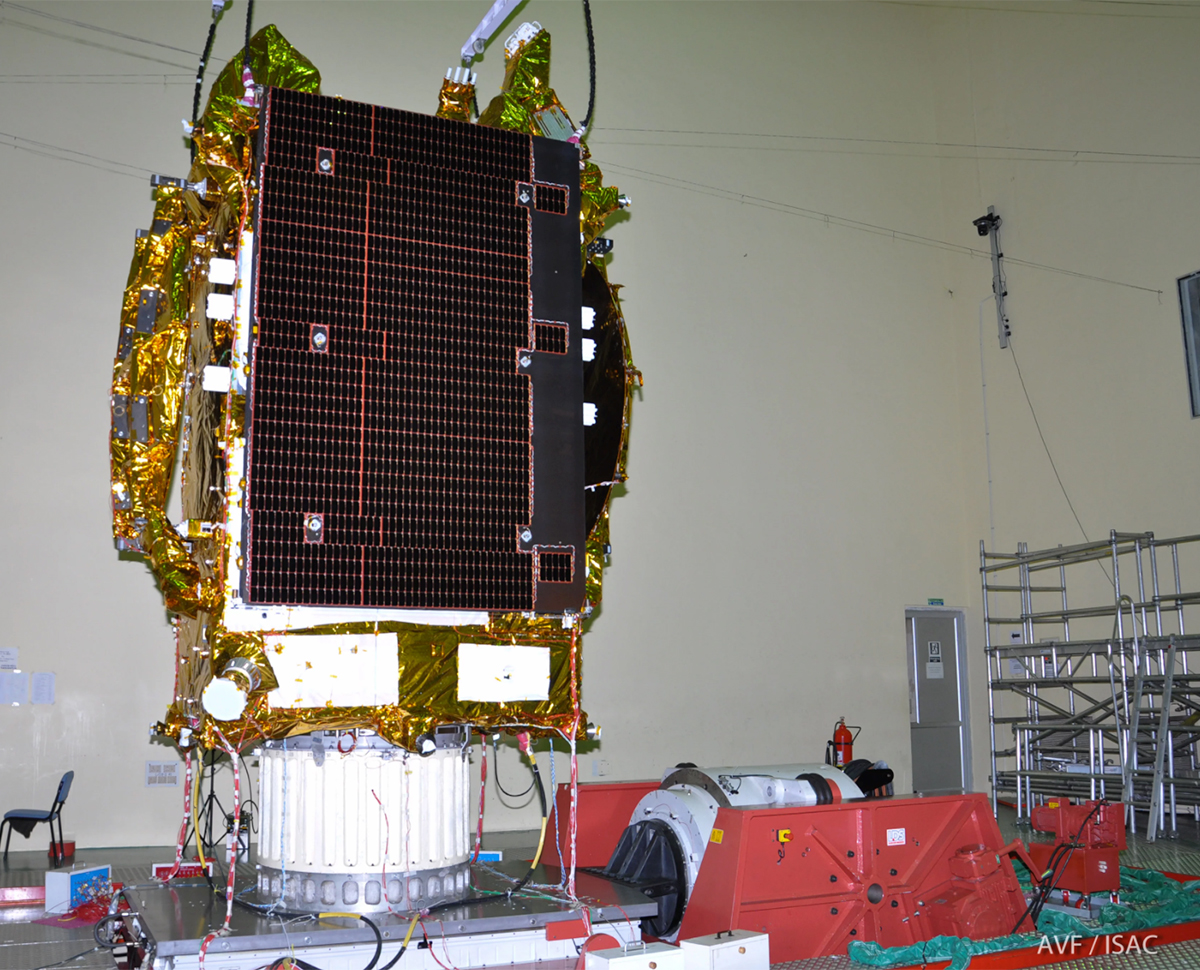
India's GSAT-19 communications satellite is seen in the clean room at the ISRO's Satish Dhawan Space Centre. Clean rooms offer sterile environments that allow engineers to work on satellites like GSAT-19 without fear of contamination to the spacecraft.
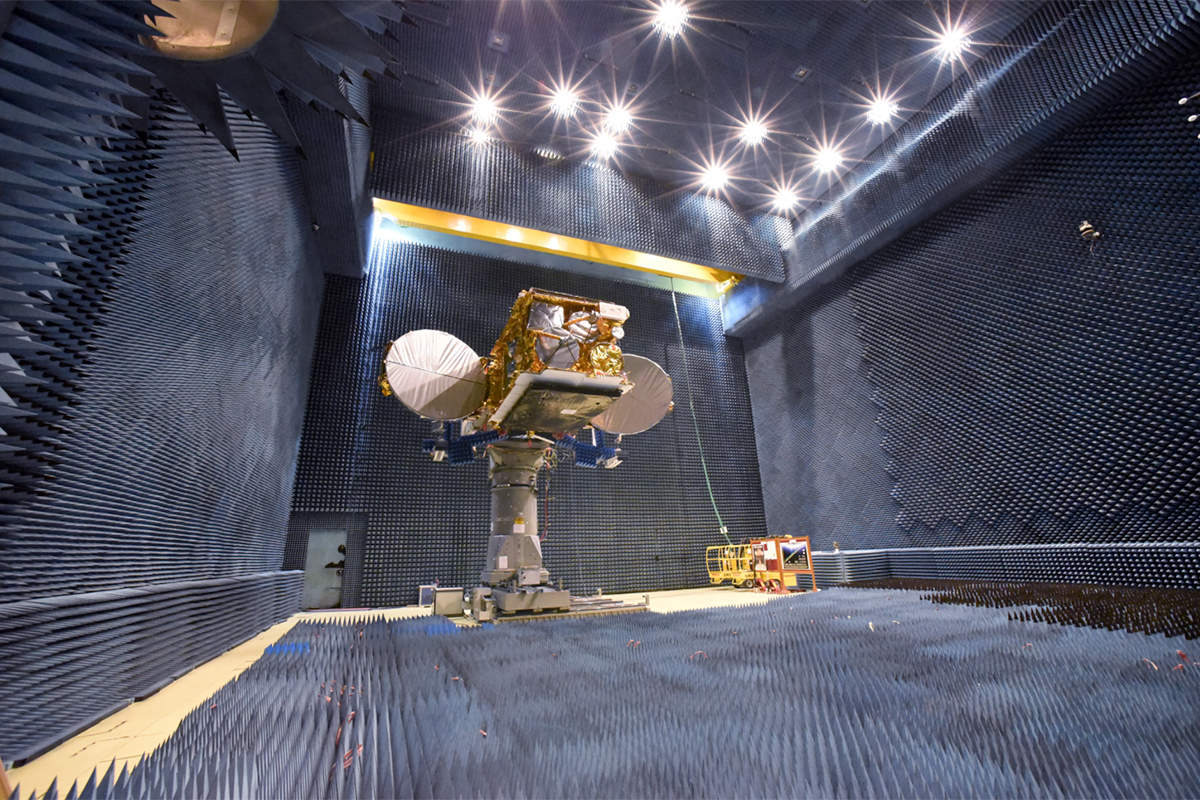
Passing the Test
ISRO Engineers test the GSAT-19 communication satellite's antennas during a preflight check. The massive 6,913-pound (3,136-kilogram) satellite is designed to provide television broadcasts, data and broadband services for customers across India.
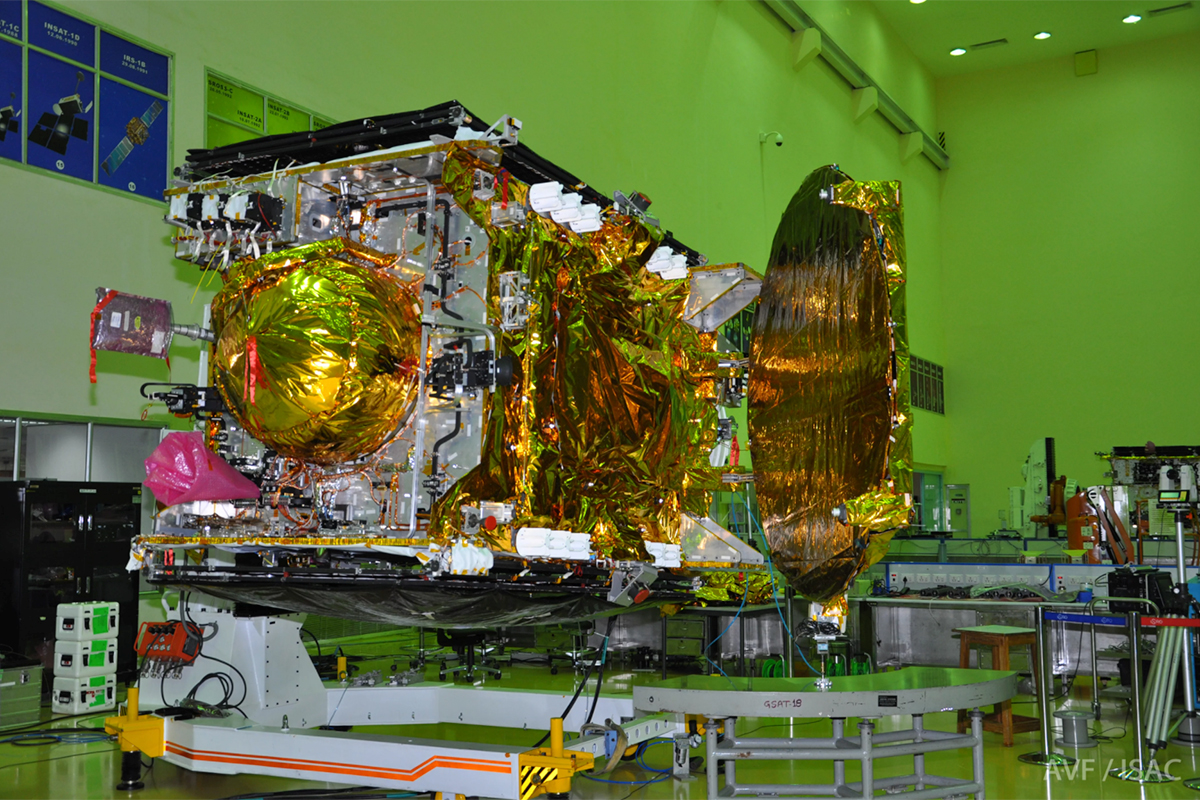
Inspecting GSAST-19
ISRO Engineers look over the GSAT-19 satellite to ensure it will be ready for its launch on the first orbital GSLV Mark III rocket.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
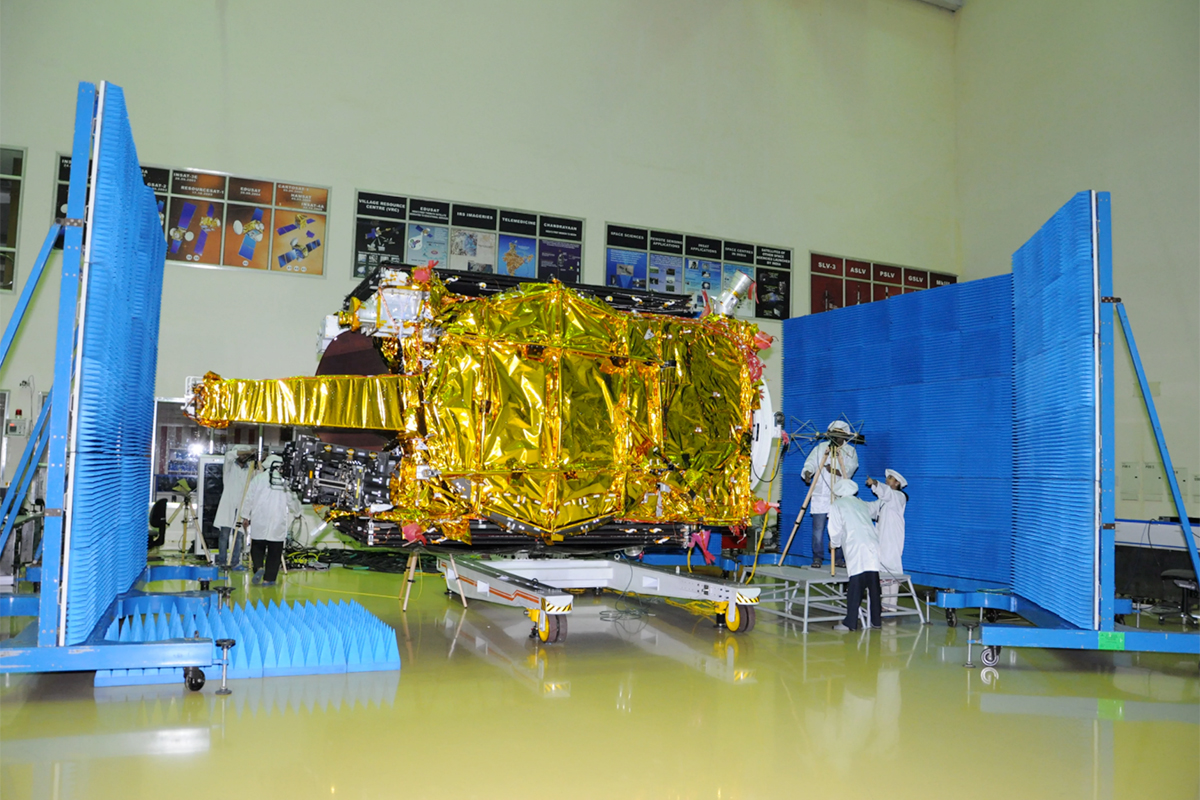
A Close Inspection
Much of the testing work on GSAT-19 was conducted at the ISRO Satellite Centre, which is home to the space agency's ISRO Satellite Integration and Test Establishment, or ISITE. Here, the satellite is seen during one of its many tests to make sure it is fit for flight.
Shake and Rattle
The GSAT-19 communications satellite undergoes a vibration test to make sure it can withstand the launch into orbit.
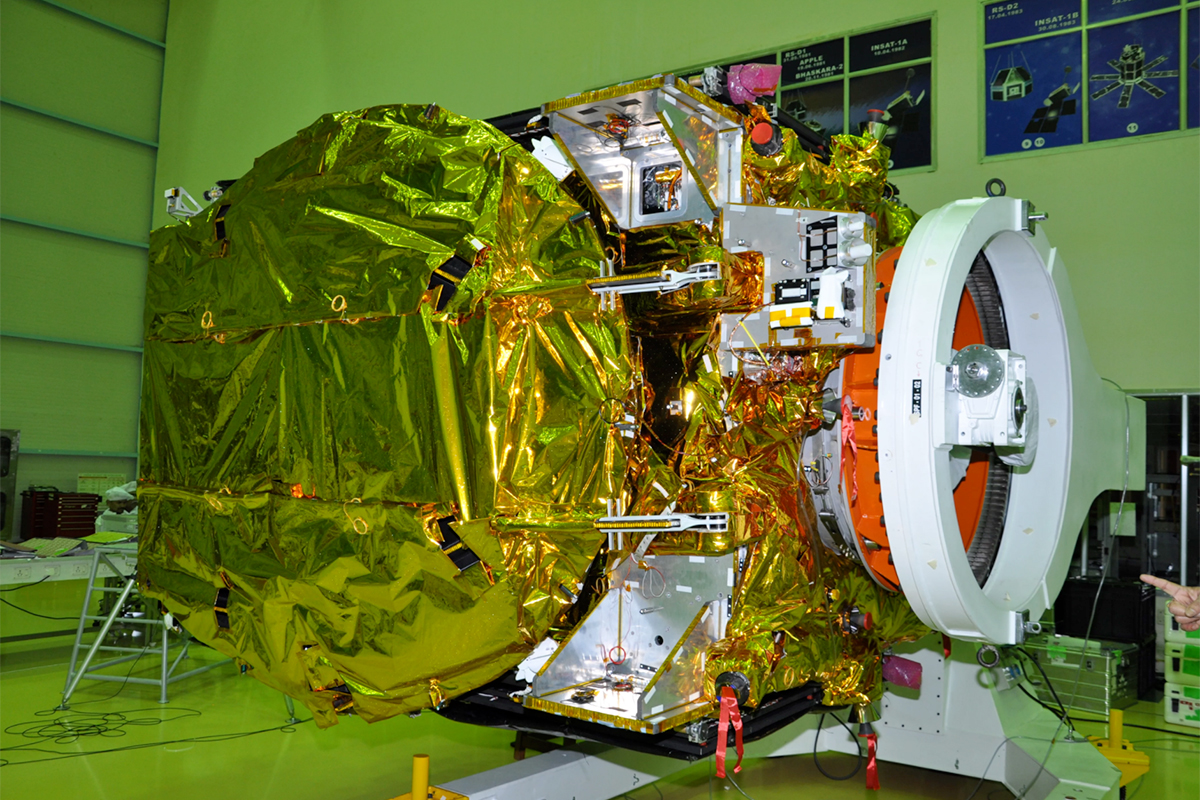
Reflections
India's GSAT-19 undergoes a reflector deployment test to make sure the communications satellite's systems will perform as expected in orbit.

Tariq is the award-winning Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001. He covers human spaceflight, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He's a recipient of the 2022 Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting and the 2025 Space Pioneer Award from the National Space Society. He is an Eagle Scout and Space Camp alum with journalism degrees from the USC and NYU. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast on the TWiT network. To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik.