Inside the Curiosity Rover's Mars Methane Discovery (Infographic)
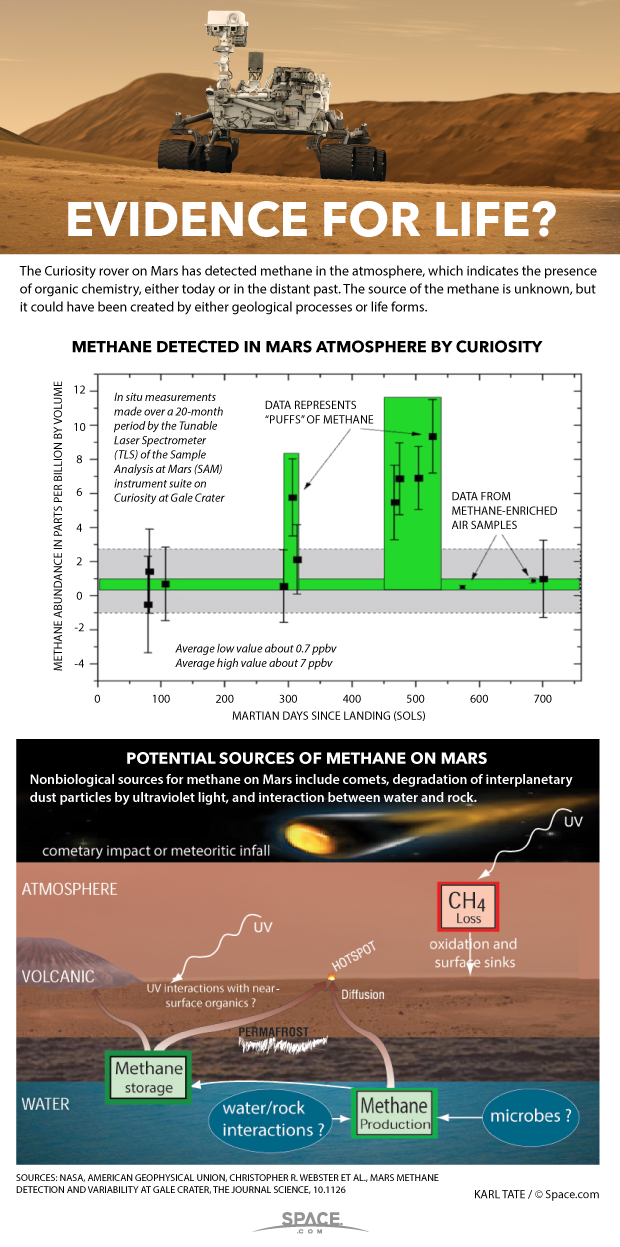
NASA's Curiosity rover on Mars has detected methane in the atmosphere, which indicates the presence of organic chemistry, either today or in the distant past. The source of the methane is unknown, but it could have been created by either geological processes or, potentially, by microbes.
Full Story: Curiosity Rover Finds Methane on Mars: What It Could Mean for Life
Nonbiological sources for methane on Mars include comets, degradation of interplanetary dust particles by ultraviolet light, and interaction between water and rock.
Curiosity's methane discovery is significant because the rover, which landed in Gale Crater on Mars in August 2012, initially did not find any trace of methane in the region. The research was presented at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco on Dec. 16, 2014.
Curiosity Sniffs Mars' Methane - Where's It Coming From? | Video
Curiosity detected a spike in methane levels in the Martian atmosphere over a 60-day (or Martian sol) period. During that time, the levels of methane in the planet's atmosphere rose from a background level of 0.7 parts per billion up to 7 parts per billion, a substantial increase that quickly faded to background levels.
The relatively swift rise and fall of methane levels detected by Curiosity is perplexing because scientists expect methane on Mars to last about 300 years.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Paul Mahaffy, study co-author at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland: "Right now, it's too much of a single-point measurement for us really to jump to any conclusions. So all we can really do is lay out the possibilities. And we certainly should have an open mind. Maybe there are microbes on Mars cranking out methane, but we sure can't say that with any certainty. It's just speculation at this point."
- The Search for Life on Mars (A Photo Timeline)
- Mars Rover Curiosity's 7 Biggest Discoveries (So Far)
- 7 Biggest Mars Mysteries Ever
- Mars Myths & Misconceptions: Quiz
Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+.

Karl's association with Space.com goes back to 2000, when he was hired to produce interactive Flash graphics. From 2010 to 2016, Karl worked as an infographics specialist across all editorial properties of Purch (formerly known as TechMediaNetwork). Before joining Space.com, Karl spent 11 years at the New York headquarters of The Associated Press, creating news graphics for use around the world in newspapers and on the web. He has a degree in graphic design from Louisiana State University and now works as a freelance graphic designer in New York City.
