Private Antares Rocket & Cygnus Spacecraft Explained (Infographic)
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
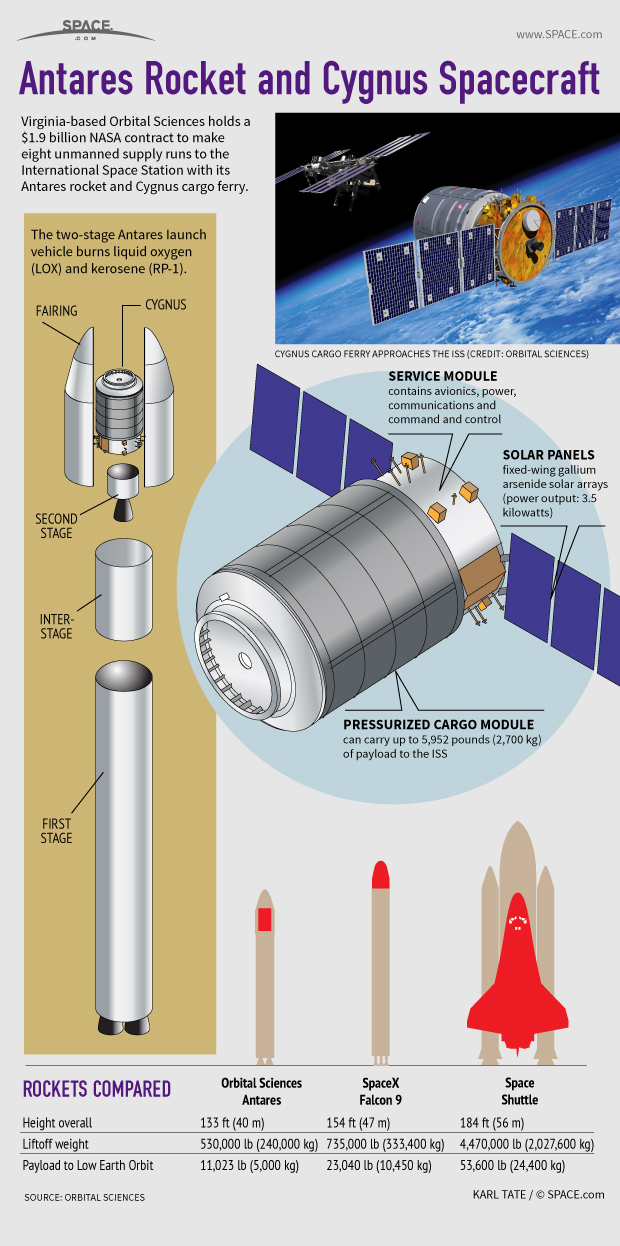
Virginia-based Orbital Sciences holds a $1.9 billion NASA contract to make eight unmanned supply runs to the International Space Station with its Antares rocket and Cygnus cargo ferry. They launch from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on Wallops Island, Va.
The two-stage Antares launch vehicle burns liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1). The rocket's height overall is 131 feet (40 meters). Its liftoff weight is 530,000 pounds (240,000 kilograms). The Antares rocket was originally called Taurus 2. [Photos: Orbital's Antares Rocket and Cygnus Capsule]
The Cygnus pressurized cargo module can carry up to 5,952 pounds (2,700 kg) of payload to the International Space Station.
At the rear of Cygnus is a service module containing avionics, power, communications and command and control hardware. On the outside of the service module are twin fixed-wing gallium arsenide solar arrays capable of putting out 3.5 kilowatts of electricity.
Future Cygnus spacecraft will be enhanced with a larger pressurized cargo module and lightweight solar panels.
The first Antares rocket launched on a successful test flight on April 21, 2013. The smooth flight set the stage for the first Cygnus test flight to the International Space Station in September 2013. [See photos from Orbital's 1st Cygnus spacecraft flight]
Article continues belowThe first Cygnus spacecraft launched on Sept. 18, 2013 and arrived on Sept. 29 after a one-week delay. Full Story: Private Cygnus Spacecraft Makes Historic 1st Rendezvous with Space Station
- Now Boarding: The Top 10 Private Spaceships
- Pushing Freight To Space Station - Antares Rocket Animation
- Special Report: The Private Space Taxi Race
Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Karl's association with Space.com goes back to 2000, when he was hired to produce interactive Flash graphics. From 2010 to 2016, Karl worked as an infographics specialist across all editorial properties of Purch (formerly known as TechMediaNetwork). Before joining Space.com, Karl spent 11 years at the New York headquarters of The Associated Press, creating news graphics for use around the world in newspapers and on the web. He has a degree in graphic design from Louisiana State University and now works as a freelance graphic designer in New York City.
