Giant Sun Eruption Captured in NASA Video
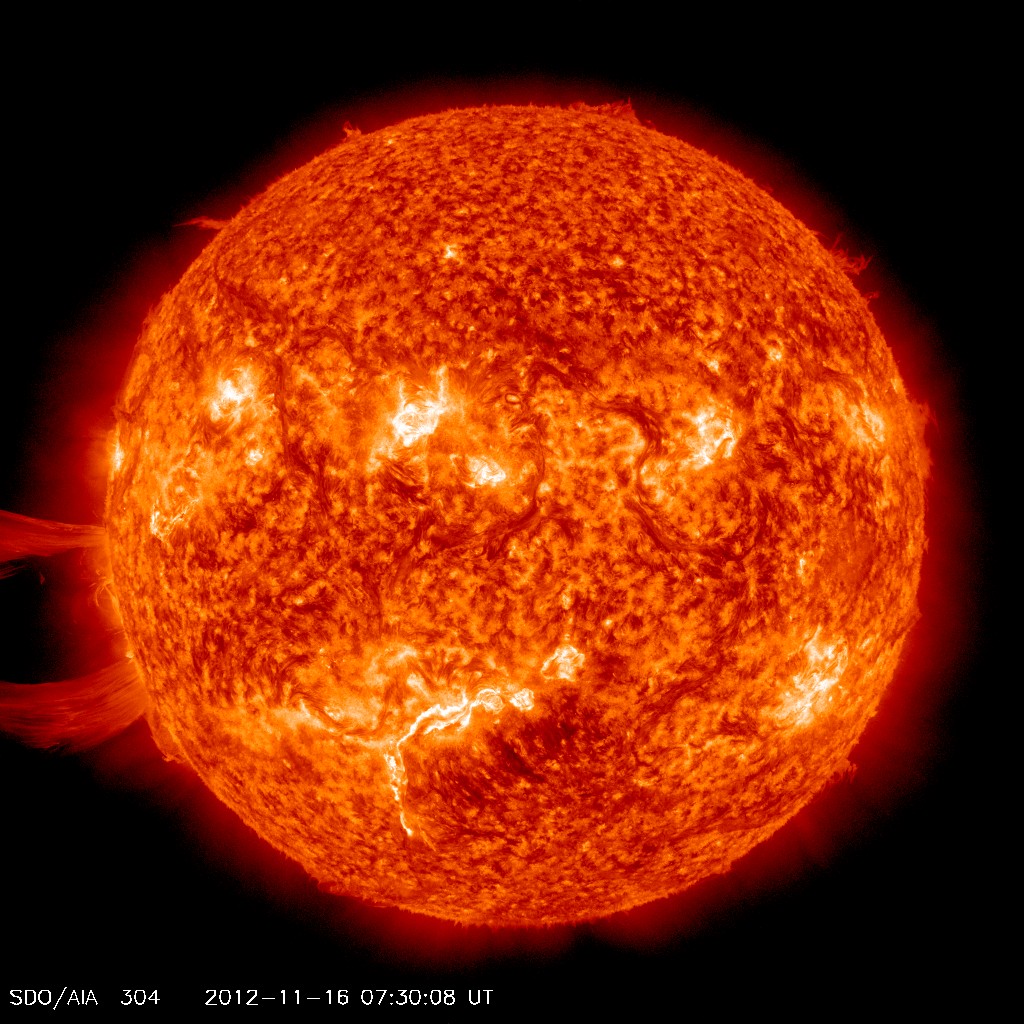
The sun unleashed a monster eruption of super-hot plasma Friday (Nov. 16) in back-to-back solar storms captured on camera by a NASA spacecraft.
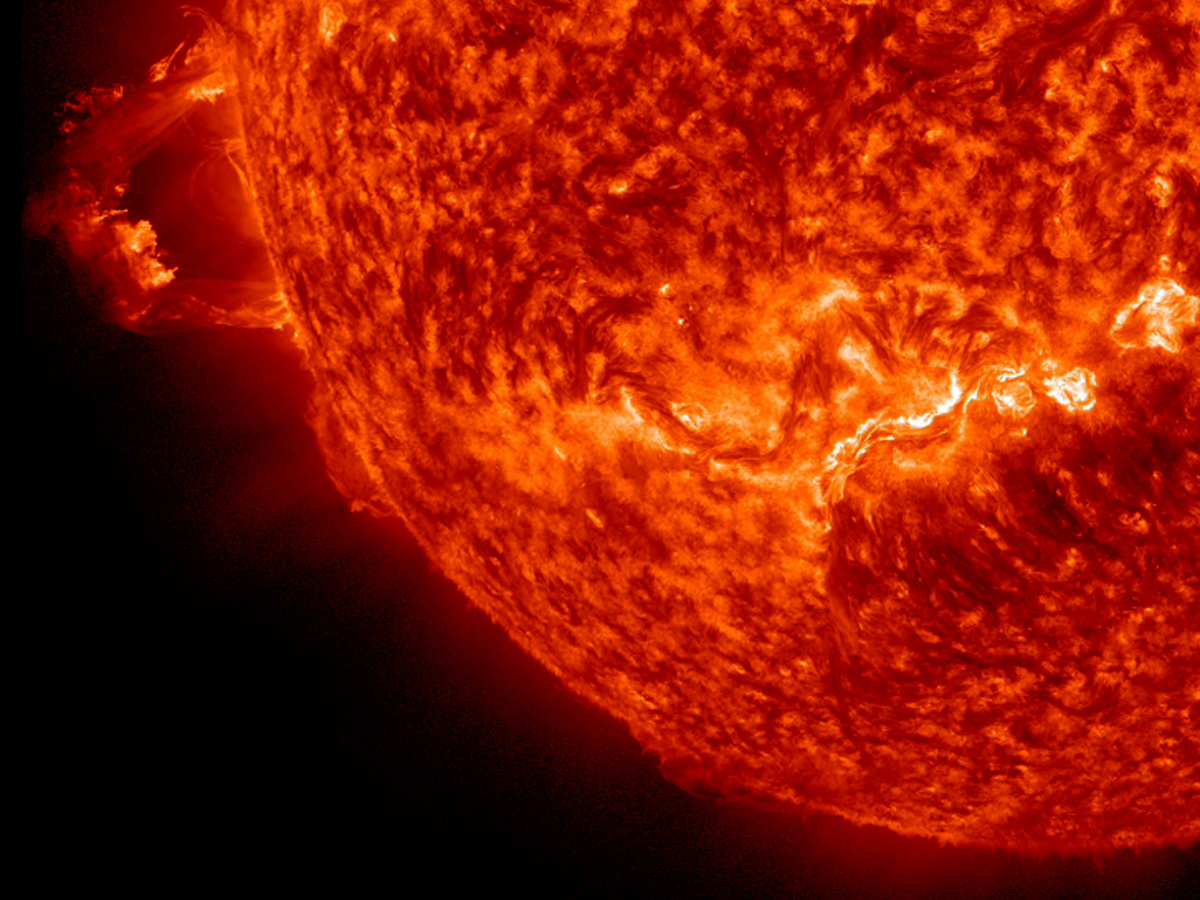
The giant sun eruption, called a solar prominence, occurred at 1 a.m. EST (0600 GMT), with another event flaring up four hours later. The prominences was so large, it expanded beyond the camera view of NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), which captured high-definition video of the solar eruption.
In the video, a colossal loop of glowing red plasma erupts from the lower left of the sun, arcing up and out of frame as it blasts away from the star.
"The red-glowing looped material is plasma, a hot gas made of electrically charged hydrogen and helium," officials with NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, which oversees the SDO mission, explained in a description. "The prominence plasma flows along a tangled and twisted structure of magnetic fields generated by the sun’s internal dynamo. An erupting prominence occurs when such a structure becomes unstable and bursts outward, releasing the plasma."
Friday's solar eruption does not appear to be aimed at Earth, so will likely have little effect on our planet. But that was not the case earlier this week when a powerful solar flare erupted on Monday (Nov. 12). That flare registered as an M6-class eruption, a moderate but still intense solar event.
On Tuesday and Wednesday (Nov. 13 and 14), space weather conditions sparked a geomagnetic storm that supercharged the Earth's auroras, creating spectacular northern lights displays for observers at high latitudes.
When aimed directly at Earth, the most powerful solar flares and eruptions can pose a threat to satellites and astronauts in orbit, and also interfere with communication, navigation and power systems on the ground.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The sun is currently in the middle of an active phase of its 11-year solar weather cycle. The current cycle is called Solar Cycle 24 and is expected to peak in 2013.
Editor's note: If you snap an amazing photo of the northern lights created by recent sun flares, or any other sky object, and you'd like to share it for a possible story or image gallery, send images, comments and location information to managing editor Tariq Malik at tmalik@space.com.
You can follow SPACE.com Managing Editor Tariq Malik on Twitter @tariqjmalik and SPACE.com on Twitter @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

Tariq is the award-winning Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001. He covers human spaceflight, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He's a recipient of the 2022 Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting and the 2025 Space Pioneer Award from the National Space Society. He is an Eagle Scout and Space Camp alum with journalism degrees from the USC and NYU. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast on the TWiT network. To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik.