U.S. government awards NOAA millions for wildfire response research
The Biden-Harris administration has granted millions of dollars in funding to assist NOAA's continued wildfire monitoring and prediction efforts.

Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
It doesn’t matter what time of year it is or where you are — wildfires are a threat to everyone. With just the right climate conditions, these disasters can spark and spread within seconds. Of course, there are certain times of year and certain locations associated with increased chances a wildfire begins blazing — for instance, dryness is directly correlated with such fires — but regardless, wildfire prevention, prediction and monitoring remain high priorities everywhere, and for everyone.
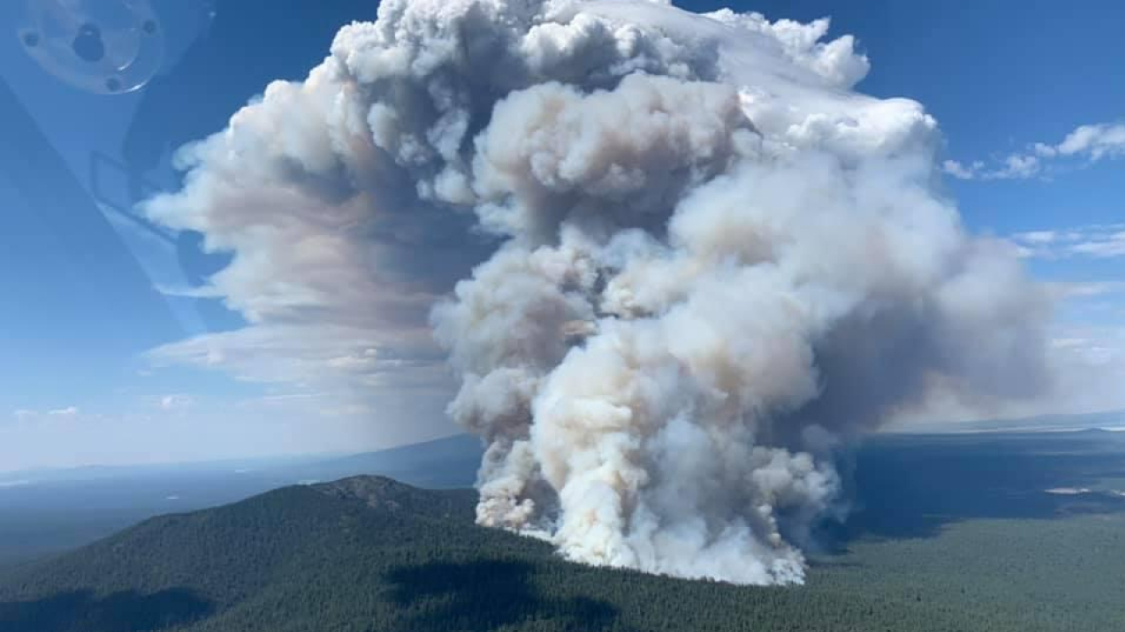
In August 2023, a wildfire that began on the Hawaiian island of Maui ended up as the deadliest wildfire in the U.S. in more than a hundred years, serving as a reminder of the importance of efforts to focus on continued improvement in early detection and monitoring of both these fires and the smoke they diffuse.
Related: Satellites watched wildfires burn a staggering 30% of Brazil's Pantanal wetlands
Just last week, it was announced that the Biden-Harris Administration awarded the NOAA as well as the Department of Commerce more than a combined $34 million in funding to aid in wildfire preparedness and response efforts. Over the next five years, some of this money will go toward six research universities that are all part of NOAA's Cooperative Institute system. The goal is to improve how scientists study and forecast wildfire behavior as well as provide enhanced warnings and early detection of such disasters.
"Americans are increasingly at risk from the threat of wildfires," Gina Raimondo, U.S. Secretary of Commerce said in the NOAA statement. "NOAA's observations, models, outlooks, and forecasts are essential for supporting wildfire response across America."
This funding is part of President Joe BIden's Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which addresses the human-driven climate crisis the world continues to face. The support will allow NOAA to have additional resources to continue to improve in areas such as weather forecasting, and work on providing increased warning times for those threatened by natural disasters.
“As part of President Biden's 'Investing in America' agenda, this funding will help increase lead times for fire weather warnings, speed detection of fire starts, and provide more real-time actionable information to prevent wildfires, support firefighting crews and keep communities safe," Raimondo said.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
This funding will also support critical satellite programs such as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES-R) and Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) series. Both of these endeavors aid in wildfire research through imagery as well as fire detection and monitoring systems. A few examples of how these satellites are assisting forecasters, emergency managers and firefighters include early wildfire detection, fire behavior and characteristics, smoke location and movement prediction, and providing data that assists in developing models that can forecast the spread or expansion of fires.
"Rising temperatures, declining snowpack and frequent droughts are all leading to a dramatic surge in wildfire frequency and severity across the United States," Dr. Rick Spinrad, NOAA Administrator, added in the statement. "These investments will help NOAA scientists develop new tools, technologies and systems to improve the accuracy of outlooks and forecasts for our land management and wildfire response partners, assist local officials' decision-making and communicate vital public safety information to more people more quickly."
Since 2016, tools such as the Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM), equipped on the GOES-R satellites, have already spurred a significant improvement when it comes to observing lightning. This has helped pinpoint where there is a concern for wildfires that could be triggered from thunderstorms. For example, during a drought when there are ample amounts of dry brush, and a thunderstorm develops with little rain but lots of lightning, the likelihood of a strike starting a wildfire significantly increases.
Other satellite instruments provide information that track carbon emissions and smoke from wildfires, both of which can contribute to poor air quality on a local, regional and national scale. In 2023 for example, a report by Climate Central shared that this was the worst year for Americans since 2006 in terms of breathing in wildfire smoke.
Breathing such smoke can create health consequences ranging from minor irritations, such as increased coughing, to more dangerous effects that risk leading to respiratory or cardiovascular illnesses. One of the immediate goals to come from this funding will be to improve in early fire detection, which will assist in helping to prevent wildfires from expanding or rapidly intensifying.
Further, climate change directly increases the chances of a wildfire forming — but our climate is not heating up because of Mother Nature, or the natural cycle alone. For instance a great article from The Wilderness Society highlights a few of the growing global warming issues and suggests where we, as a nation, can do better to help the environment. One highlight was with regard to the continued overuse of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, that contributes to increased amounts of greenhouse gases in the air. In short, this increases the warming of our planet. More specifically related to wildfires, the more we cut into forests and remote locations to develop infrastructure, the more we decrease the amount of areas that can provide a natural spot for wildfires to burn out on their own.
To learn more about this funding and future plans, you can visit NOAA’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act websites.

Meredith is a regional Murrow award-winning Certified Broadcast Meteorologist and science/space correspondent. She most recently was a Freelance Meteorologist for NY 1 in New York City & the 19 First Alert Weather Team in Cleveland. A self-described "Rocket Girl," Meredith's personal and professional work has drawn recognition over the last decade, including the inaugural Valparaiso University Alumni Association First Decade Achievement Award, two special reports in News 12's Climate Special "Saving Our Shores" that won a Regional Edward R. Murrow Award, multiple Fair Media Council Folio & Press Club of Long Island awards for meteorology & reporting, and a Long Island Business News & NYC TV Week "40 Under 40" Award.