Giant exoplanet found, imaged directly thanks to star-mapping data (photos)
The approach could lead to many more exoplanets being directly detected and imaged.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
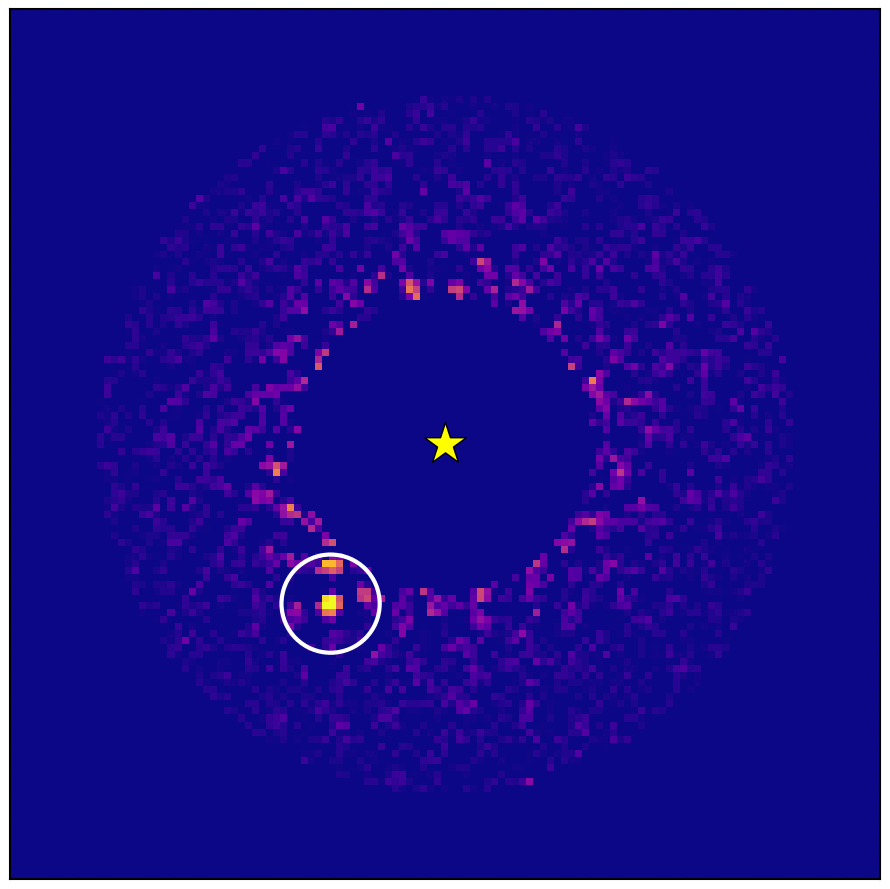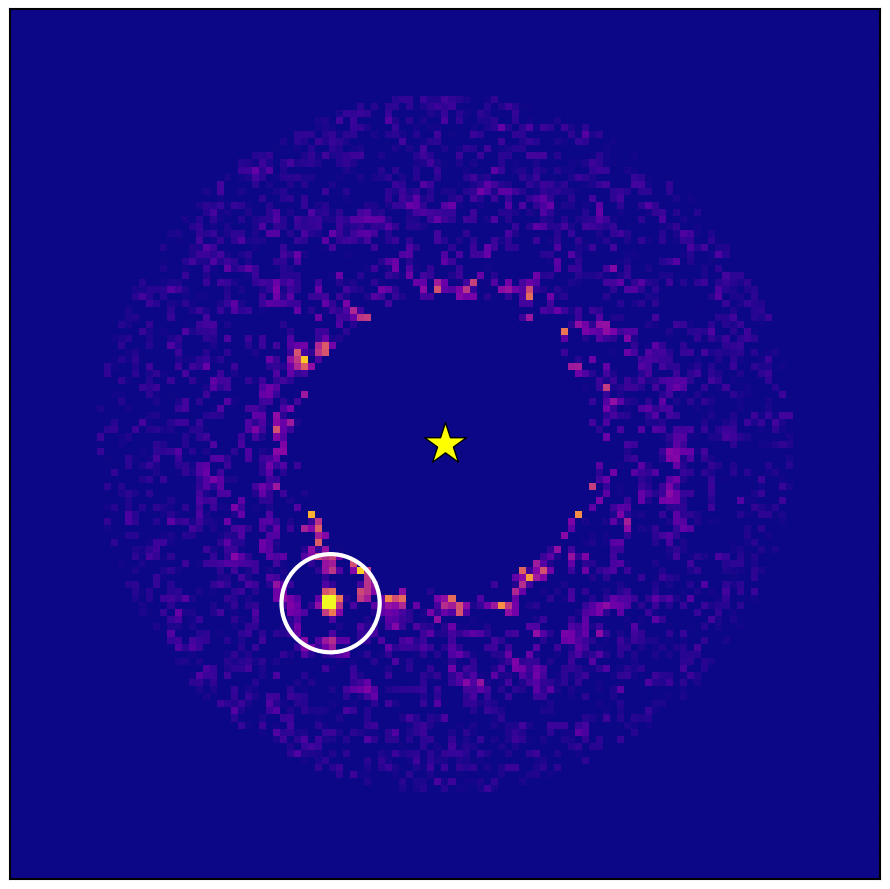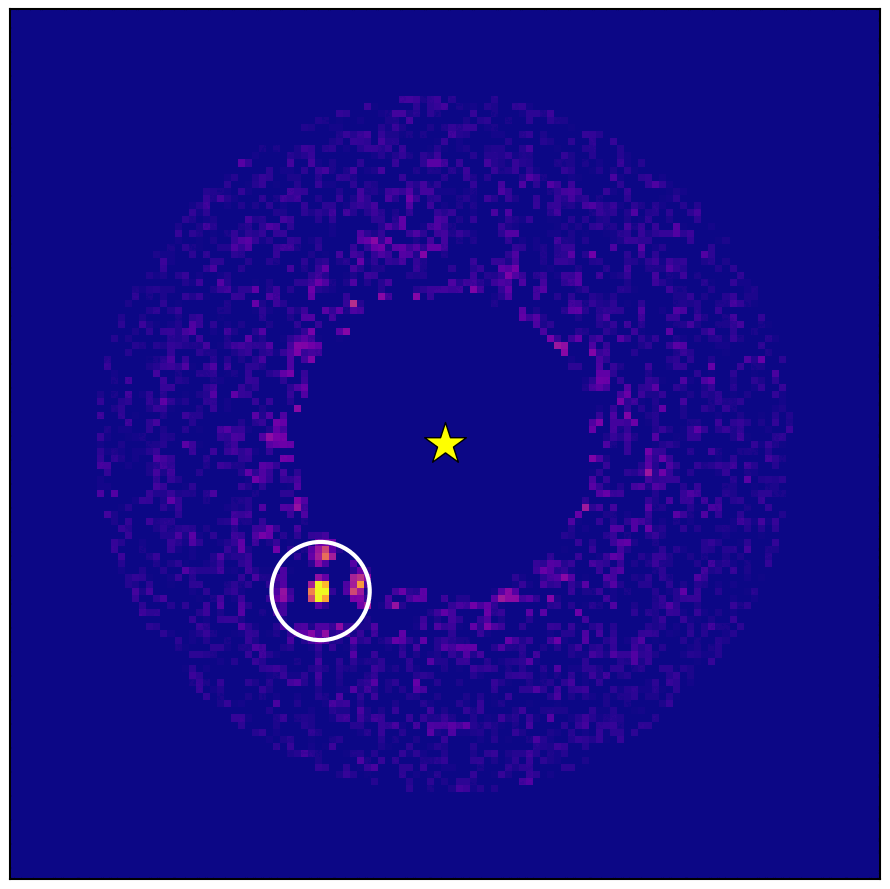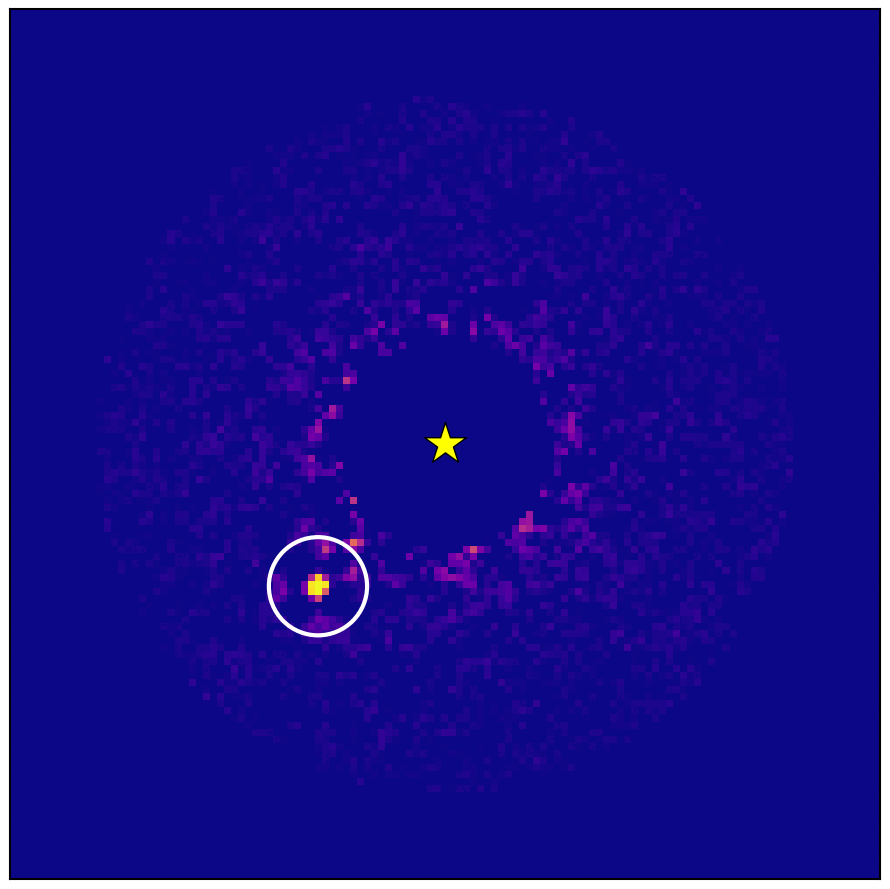
Astronomers have directly detected and imaged a gas giant orbiting another star by combining different techniques for hunting exoplanets.
Researchers first looked at a catalog of star-mapping data combined from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Gaia and older Hipparcos missions to identify stars that, based on their apparent movements or wobbles, are likely to be orbited by giant — and thus potentially visible — planets.
The international team of scientists then used the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan’s Subaru Telescope on Mauna Kea, Hawaii. Observations using the telescope’s coronagraphic adaptive optics and spectrograph instruments in July and September 2020 and May and October 2021 led to the discovery of the exoplanet HIP 99770B, a new study reports.
Related: Exoplanets: Worlds beyond our solar system
HIP 99770B is a gas giant planet about 15 times the mass of Jupiter orbiting the star HIP 99770, which is around twice as massive as our sun.
Direct imaging provides information such as the composition of atmospheres around planets and their temperatures. But actually finding planets in this fashion is very difficult, accounting for only a handful of exoplanet discoveries.
However, using star-mapping data means astronomers know exactly where to look with follow-up telescope observations. This approach could bring further discoveries of exoplanets by direct imaging, potentially including Earth-like planets, scientists said.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"This is sort of a test run for the kind of strategy we need to be able to image an Earth," study lead author Thayne Currie, who's based at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan in Hilo, Hawaii and the University of Texas-San Antonio, said in an ESA statement.
"It demonstrates that an indirect method sensitive to a planet’s gravitational pull can tell you where to look and exactly when to look for direct imaging," Currie said. "So I think that's really exciting."
The paper was published in the journal Science on April 13.
Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or on Facebook.

Andrew is a freelance space journalist with a focus on reporting on China's rapidly growing space sector. He began writing for Space.com in 2019 and writes for SpaceNews, IEEE Spectrum, National Geographic, Sky & Telescope, New Scientist and others. Andrew first caught the space bug when, as a youngster, he saw Voyager images of other worlds in our solar system for the first time. Away from space, Andrew enjoys trail running in the forests of Finland. You can follow him on Twitter @AJ_FI.