Space History Photo: Baikonur Soyuz Launch During Cold War
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Daily Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!

Twice a month
Strange New Words
Space.com's Sci-Fi Reader's Club. Read a sci-fi short story every month and join a virtual community of fellow science fiction fans!
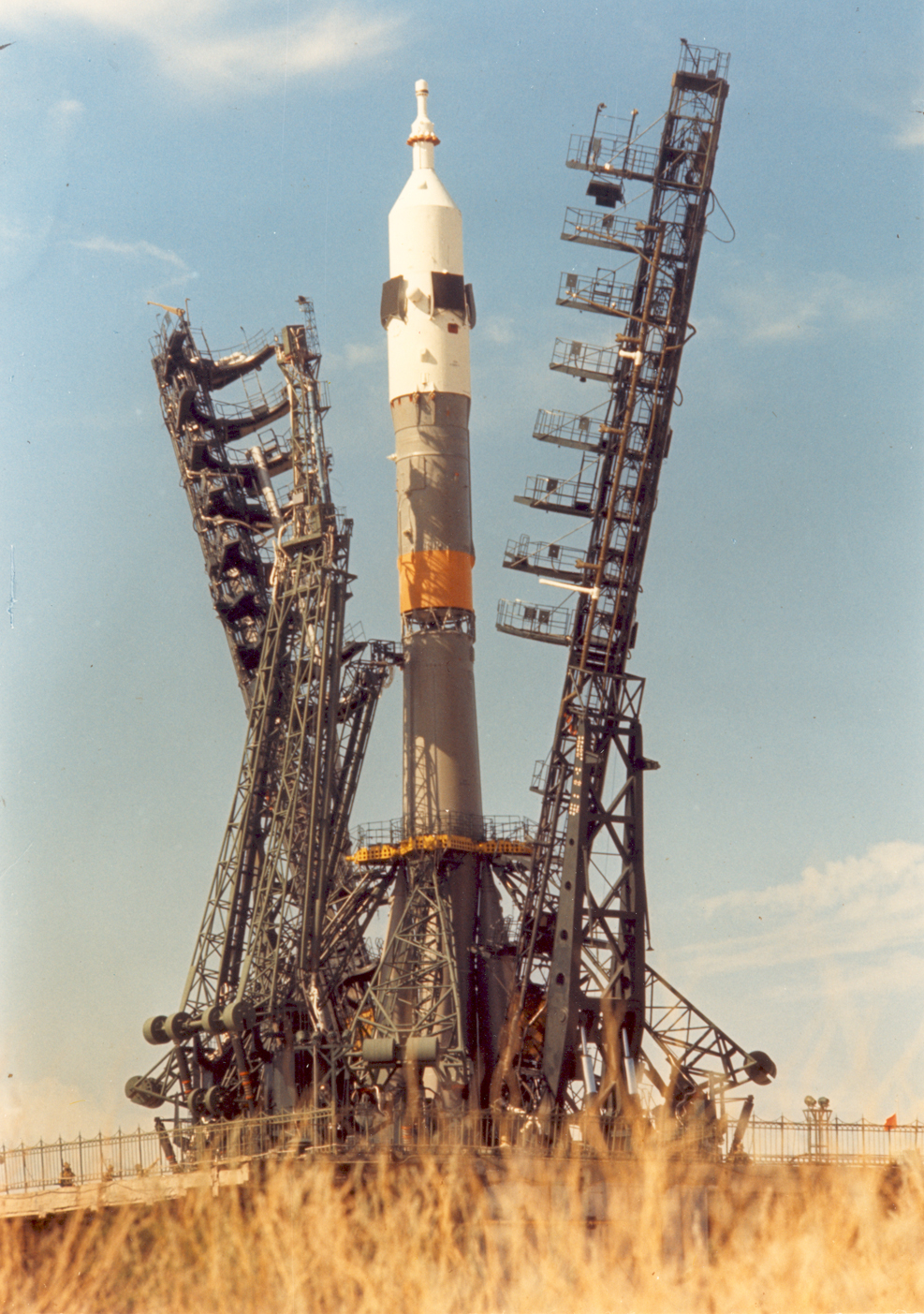
The Baikonur complex in Kazakhstan is the world's largest space center. In this historical photo from the U.S. space agency, the Soyuz spacecraft and launch vehicle are installed on the launch pad at Baikonur in 1975.
The launch was part of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP), a cooperation between NASA and the Soviets. The goals of ASTP were to test the ability of U.S. and USSR spacecraft to rendezvous and dock in space and to open the doors to possible international rescue missions and future collaboration on manned spaceflights. Given the high level of cooperation between Russia and America today, it’s easy to forget that during the Cold War, such cooperation was remarkable. Crews also performed in-flight intervehicular crew transfers and various scientific experiments. ASTP proved to be significant step toward improving international cooperation in space during the Cold War, according to NASA’s account of the mission.
The Soyuz and Apollo crafts launched from Baikonur and the Kennedy Space Center respectively, on July 15, 1975. The two spacecraft completed the rendezvous and docking on July 17. While the Soyuz craft returned to Earth on July 21, the Apollo craft stayed in space three more days, dropping into the Pacific Ocean July 24.
Each weekday, SPACE.com looks back at the history of spaceflight through photos (archive).
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is the U.S. government agency in charge of the civilian space program as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Founded in 1958, NASA is a civilian space agency aimed at exploring the universe with space telescopes, satellites, robotic spacecraft, astronauts and more. The space agency has 10 major centers based across the U.S. and launches robotic and crewed missions from the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral Florida. Its astronaut corps is based at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. To follow NASA's latest mission, follow the space agency on Twitter or any other social channel, visit: nasa.gov.
