Space History Photo: Launch Preparation
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
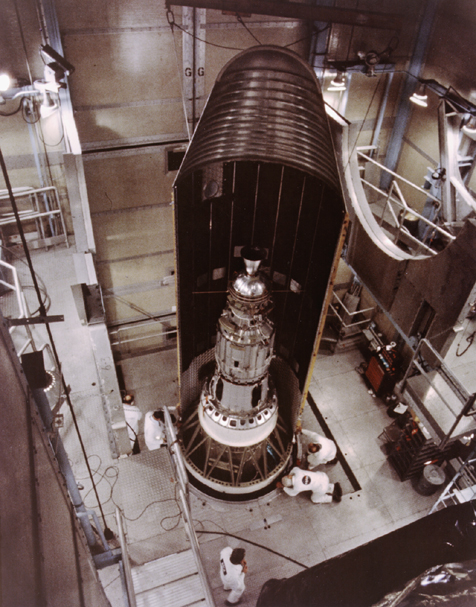
In this historical photo from the U.S. space agency, Goddard's geophysics research satellite, a 906-lb. (411-kg) satellite that looked more like a dimpled cosmic golf ball, is inside the nose cone of this Delta rocket.
The spacecraft, which NASA launched from the Western Test Range in California in 1976, provided a stable point in the sky to reflect pulses of laser light. By timing the return of the laser beam to an accuracy of about one ten-billionth of a second, scientists expected to measure the relative location of participating ground stations within one inch or a few centimeters. These measurements allowed scientists to track and analyze tectonic plate movement and continental drift.
The spacecraft, called the LAser GEOdynamics Satellite (LAGEOS), was the precursor to the current-day Global Positioning System (GPS) system operated by the Defense Department.
Article continues belowEach weekday, SPACE.com looks back at the history of spaceflight through photos (archive).
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is the U.S. government agency in charge of the civilian space program as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Founded in 1958, NASA is a civilian space agency aimed at exploring the universe with space telescopes, satellites, robotic spacecraft, astronauts and more. The space agency has 10 major centers based across the U.S. and launches robotic and crewed missions from the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral Florida. Its astronaut corps is based at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. To follow NASA's latest mission, follow the space agency on Twitter or any other social channel, visit: nasa.gov.
