Robert Goddard: American Father of Rocketry
Robert H. Goddard, the American father of modern rocketry, built and tested the world's first liquid-fuel rocket in 1926. His achievement is considered as significant as the Wright Brothers' first flight. Over the course of his career, Goddard not only developed the theoretical calculations for rocket flight but also made practical advances in rocket design and construction.
Early life
Robert Hutchings Goddard was born on Oct. 5, 1882, in Worcester, Mass., the only surviving child of Fannie Louise Hoyt and Nahum Danford Goddard. Interested in science as a child, Goddard became intrigued by space after reading H. G. Wells' science fiction novel, "The War of the Worlds."
Goddard enrolled as a student at Worcester Polytechnic Institute, where he attracted attention in 1907 when he tried to fire a powder rocket from the basement of the physics building. He received his Bachelor of Science in 1908, and went on to attain his master's and doctorate in physics from Clark University.
In 1912, he joined Palmer Physical Laboratory at Princeton University. Later, he served as a part-time instructor at Clark University. In 1924, he married Esther Christine Kisk.
Rocket science
Goddard's initial study of rockets was undertaken at his own expense. He began by experimenting with gunpowder, and launched his first powder rocket at Clark University in 1915, this time outside of the building. But powdered rockets were inefficient; only 2 percent of the available energy was being converted into motion.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Goddard turned his attention to the components of his rockets. A Swedish engineer, Gustav De Laval, had designed a turbine for a steam engine that implemented a new kind of nozzle to blow jets of steam onto the wheel. The nozzle first narrowed, then expanded, allowing the steam to reach the speed of sound and creating an efficient conversion of heat to motion.
By replacing his existing nozzle with the De Laval nozzle, Goddard's rockets were able to increase their efficiency to up to 63 percent.
In 1917, Goddard received a $5,000 grant from the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C., to support his development of a rocket to probe the upper atmosphere. Clark University also contributed financially, and Goddard had permission to use their lab and the lab at Worcester Polytechnic Institute for experimentation.
In 1919, the Smithsonian published Goddard's research. Though the papers focused on Goddard's search for methods to send weather-recording instruments to new heights, and his development of mathematical theories of rocket propulsion, he also discussed the possibility of escaping the Earth's gravity completely. According to his calculations, a rocket could one day travel to the moon and explode a load of flash powder to mark its arrival.
The press immediately seized hold of the idea. Many people shot down the idea that a thrust was possible in the vacuum of space. Goddard found himself receiving a great deal of attention, much of it negative. The New York Times published an editorial scoffing at the idea; in 1969, after the launch of Apollo 11, the newspaper published a correction.
Military applications
Throughout his life, Goddard attempted to catch the interest of the military. For much of the time, they saw little practical application in using his ideas for warfare. After the United States entered World War I, he developed several military rockets, but none were implemented at the time. During World War II, an anti-tank weapon similar to ones Goddard had designed were utilized — the bazooka. During World War II, the Navy employed Goddard to build liquid-fueled rockets for jet-assisted aircraft takeoff.
Liquid-fueled rockets
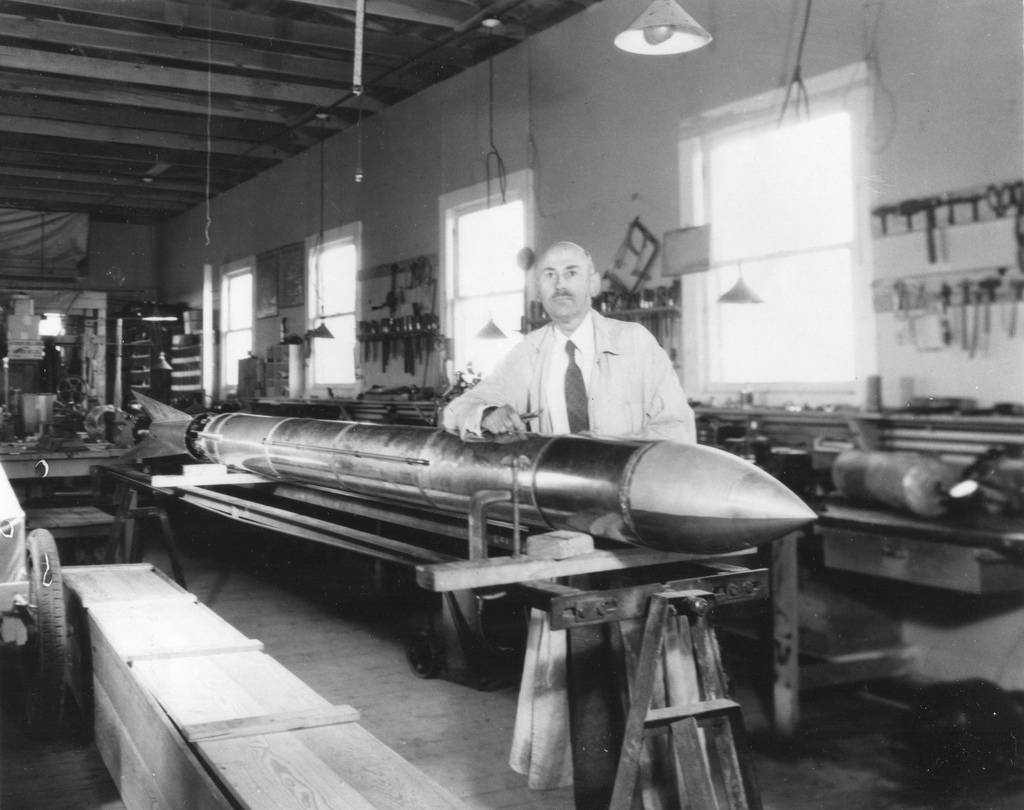
Powder rockets were still problematic. Goddard returned to an idea he first developed in 1914 for a liquid-fueled rocket. Hermann Oberth in Germany and Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in Russia had both reached the same conclusion. Working independently — with no apparent knowledge of one another's research — they made similar developments in the field of rocket science. All three are considered to be the fathers of modern rocketry.
Goddard's rocket relied on a combination of gasoline and liquid oxygen. Two lines ran into the combustion chamber. To overcome the high temperatures required for the combustion of pure oxygen, Goddard designed the extremely cold liquid oxygen to cool the combustion chamber as it traveled from the fuel tank, a method still used today.
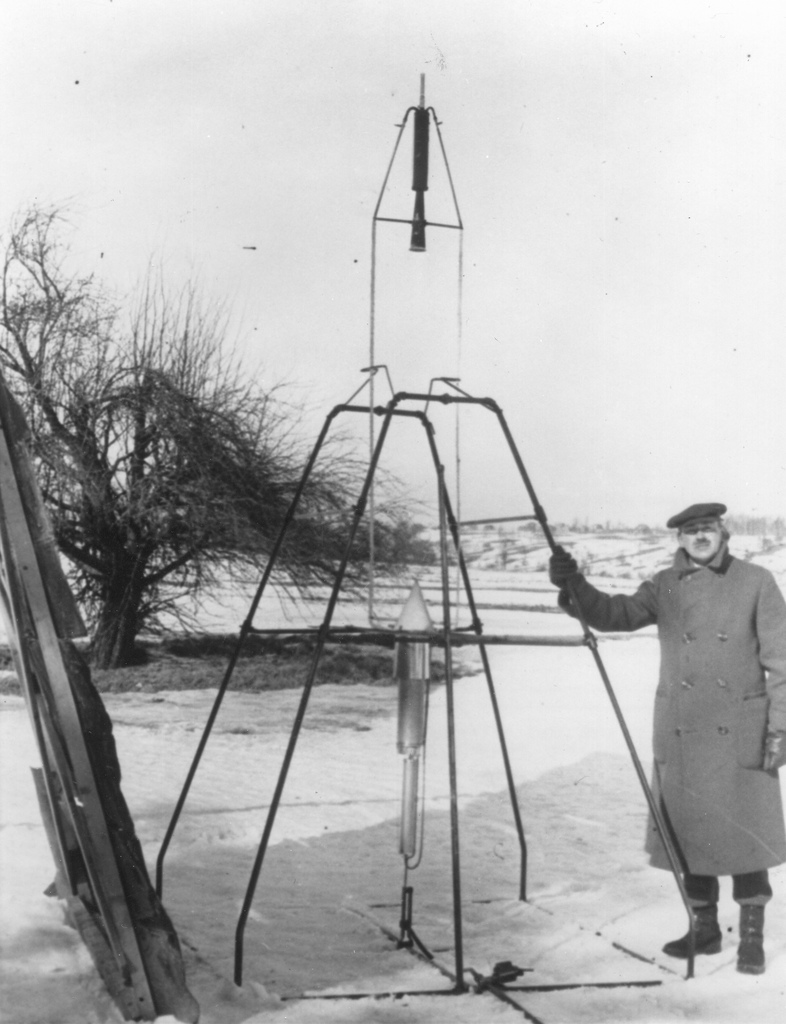
On March 16, 1926, Goddard fired his first liquid-fueled rocket. It burned for about 20 seconds before taking off, melting part of the nozzle. In 2.5 seconds, it traveled to a height of 41 feet, leveled off, and hit the ground, averaging about 60 miles per hour.
Over the next several years, Goddard continued to work on methods of stabilizing his rockets. He used gyroscopes to control motion and vanes thrust into the exhaust jet to steer them.
In 1929, one of Goddard's launches made headlines, attracting the attention of aviation hero Charles Lindbergh. Lindbergh began to provide financial backing for Goddard's research. Later contributions came from the Guggenheim family.
Goddard moved to Roswell, New Mexico, in the 1930s, where he continued to work on his rockets over the course of his lifetime. The open desolation provided the perfect place to work on his rockets in safety, and he launched 31 rockets over 15 years. [Photo Gallery: Best Rocket Launch Photos of 2012]
But Goddard never lived to see his dream of a rocket traveling into space. He died of throat cancer at his home in Baltimore on Aug. 10, 1945, twelve years before the launch of the Russian satellite, Sputnik.
Goddard was credited with 214 patents. Of these, 131 were filed by his wife after his death. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland was named for the scientist, as was the Goddard crater on the moon.
— Nola Taylor Redd, SPACE.com Contributor

Nola Taylor Tillman is a contributing writer for Space.com. She loves all things space and astronomy-related, and always wants to learn more. She has a Bachelor's degree in English and Astrophysics from Agnes Scott College and served as an intern at Sky & Telescope magazine. She loves to speak to groups on astronomy-related subjects. She lives with her husband in Atlanta, Georgia. Follow her on Bluesky at @astrowriter.social.bluesky